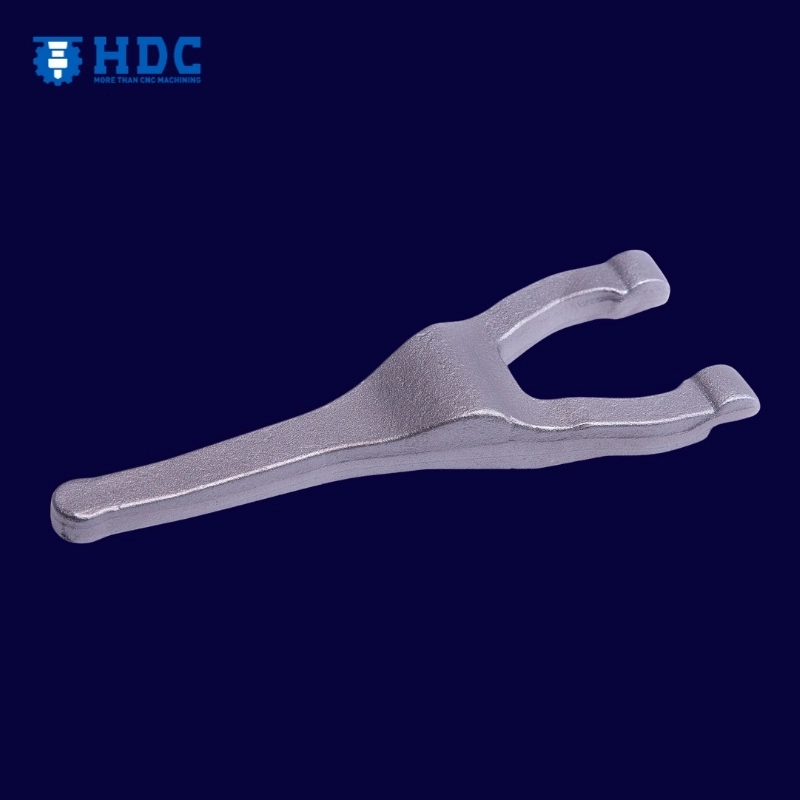
Литье в песчаные формы — это производственный процесс, основанный на литье, который используется для изготовления различных видов простых и сложных компонентов. Он существует уже около с древних времен, и он используется до сих пор, поскольку является недорогим вариантом и очень быстрым в настройке.
Литье в песчаные формы против других видов литья
Такие методы, как литье под давлением, используют металлические формы и высокое давление для получения качественной отделки, но это дорогой процесс. Литье по выплавляемым моделям может обеспечить более детальную отделку, но и стоит гораздо дороже.
С другой стороны, литье в песчаные формы является наилучшим вариантом, поскольку его можно использовать для сложных форм и оно предполагает менее дорогостоящую оснастку.
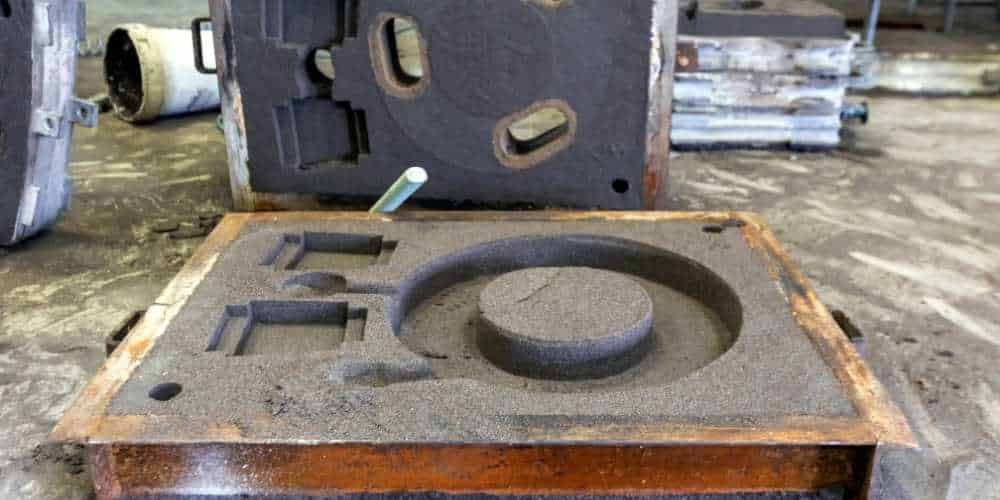

Как работает литье в песчаные формы: основной процесс
Перед началом процесса литья смешиваются несколько материалов, таких как песок, расплавленный металл и другие литейные инструменты. Песок служит основным формовочным материалом, и важно выбрать правильный тип песка, чтобы получить качественные литые детали.
Создание узора:
Шаблон — это модель детали. Он изготавливается из дерева, пластика или металла. Эта модель прессуется в формовочный песок для придания формы.
Модели должны быть разработаны с учетом усадки и обработки. Некоторые из них разделены на две части для легкого снятия формы.
Изготовление сердечника:
Стержни используются для изготовления полых секций. Они помещаются в форму перед заливкой расплавленного металла. Обычно они изготавливаются из специального песка, смешанного со связующими веществами, которые помогают стержню сохранять форму при сильном нагреве. После завершения литья стержень разламывается и удаляется.
Подготовка формы:
Внутри нижней и верхней половин формы песок прессуется вокруг модели. Они называются «крышка» (верхняя часть) и «подложка» (нижняя часть). После того, как песок затвердеет, модель удаляется. Это оставляет полость, имеющую форму детали.
Некоторые формы используют специальные покрытия для лучшей отделки поверхности. Другие добавляют металлические или песчаные вставки для придания формы мелким деталям. Песок должен быть плотно утрамбован для повышения прочности формы.
Литники и стояки:
Расплавленный металл поступает через литники. Это туннели, прорезанные в форме. Металл течет из литника в основную полость. Над деталью добавляются стояки. Они удерживают дополнительный металл для подачи детали по мере ее охлаждения и усадки. Некачественное литниковое управление может привести к различным видам дефектов.
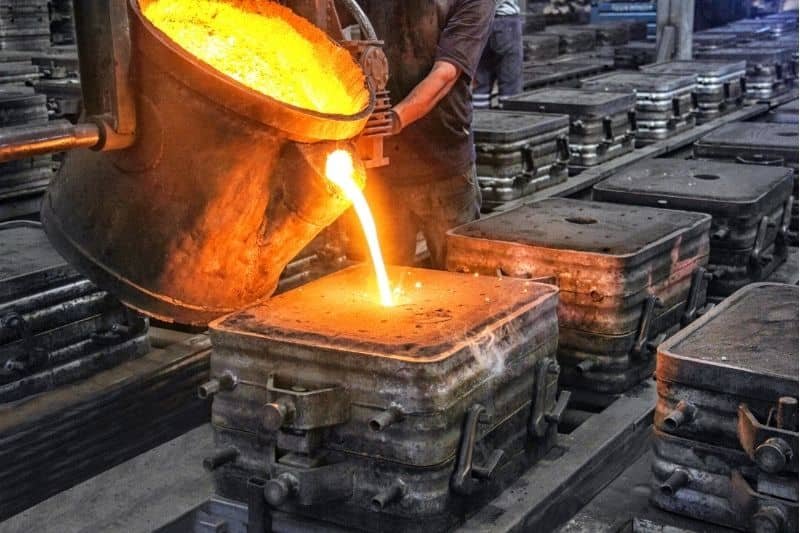
Плавка и заливка:
Металл нагревается в печи. Он плавится и заливается в форму. Металл должен быть чистым и достаточно горячим, чтобы заполнить каждый уголок.
Заливка должна быть равномерной. Если слишком быстро, могут возникнуть брызги, а если слишком медленно, металл затвердеет слишком быстро. Литейщики обучают рабочих или используют машины, чтобы сделать этот шаг правильно.
Охлаждение и вытряхивание:
Металл остывает внутри формы. После того, как он затвердевает, песок выламывается. Это называется выбивкой. Оставшийся металл с литников и стояков отрезается.
Деталь очищается с помощью шлифовальных машин или струйной обработки. Инспекторы обычно проверяют деталь на наличие дефектов. При необходимости она проходит механическую обработку для соответствия окончательным спецификациям.
Переработка песка:
Использованный песок можно очищать и повторно использовать, чтобы сэкономить деньги и сократить отходы. Песок проходит через машины, которые встряхивают, просеивают и нагревают его. Это удаляет пыль, связующие вещества и металлические частицы. Известно, что большинство литейных заводов перерабатывают более 90% своего песка.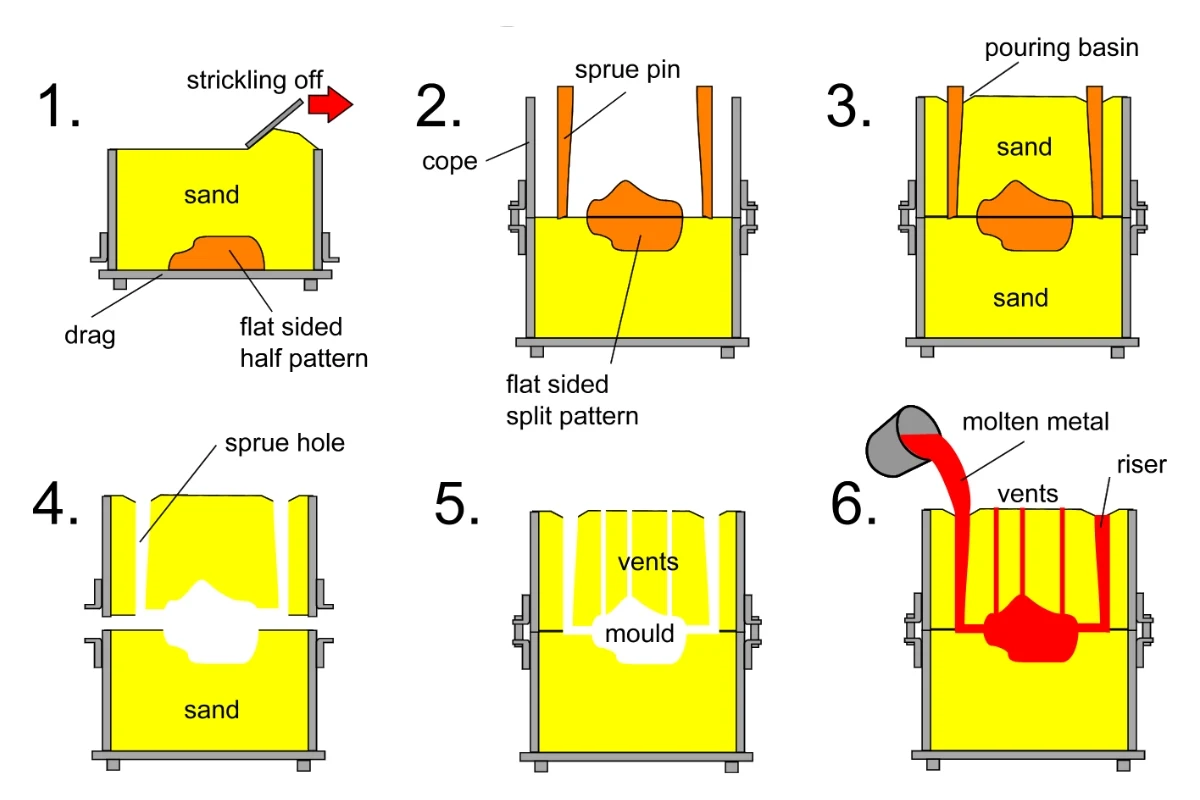
Типы песка, используемые для литья в песчаные формы
При литье в песчаные формы используются различные виды песка, каждый из которых обладает уникальными свойствами.
Смоляный песок:
Этот тип песка использует синтетические связующие для сохранения формы. Это помогает сделать формы прочнее и обеспечивает лучшую отделку деталей. Он используется там, где качество деталей имеет большее значение, поскольку он довольно дорогой и его сложнее использовать повторно.
Сухой песок:
Сухой песок похож на зеленый песок, за исключением того, что его запекают в печи, чтобы сделать его тверже и удалить влагу. Он идеально подходит для больших деталей, требующих точных деталей, но также требует больше времени на подготовку и охлаждение.
Силикат натрия или жидкое стекло:
В качестве связующего используется силикат натрия, а затвердевание происходит с помощью углекислого газа. Формы и стержни, изготовленные таким образом, очень прочные и выдерживают высокие температуры. После литья они легко разрушаются, что ускоряет выбивку и очистку.
Зеленый песок:
Зеленый песок изготавливается из кварцевого песка, воды, глины и других видов добавок. Это наиболее распространенный тип песка, используемый на заводах. Он называется зеленым, потому что он мокрый. Он также очень дешевый и его легко использовать повторно.

Типы дефектов и их профилактика
Дефекты литья могут привести к различным проблемам. Знание этих проблем облегчает их устранение.
Распространенные дефекты:
- Газовая пористость: Это крошечные отверстия в литом изделии, которые вызваны захваченными газами или паром в форме. Эти отверстия могут быть открытыми отверстиями, отверстиями для штифтов или газовыми раковинами.
- Усадка: Это серьезный дефект, который влияет на качество литья. Он вызван зазорами или трещинами, где металл отрывается при охлаждении. Обычно это происходит, когда нет достаточного количества дополнительного металла.
- Прожилки: Это тонкие, выпуклые линии на поверхности детали. Это происходит, когда песок расширяется или трескается в процессе заливки.
- Проникновение металла: Это происходит, когда расплавленный металл попадает в песок, из-за чего поверхность детали становится очень трудно очистить.
Чтобы предотвратить такие проблемы, можно использовать охладители для быстрого охлаждения толстых участков и предотвращения усадки. Вентиляционные отверстия, представляющие собой небольшие отверстия в форме, можно сделать для того, чтобы газы выходили во время заливки и снижали вероятность газовой пористости.
Также можно создать более совершенные литниковые системы, позволяющие контролировать подачу металла в форму.
Передовые и современные методы
Современные инструменты и методы помогают сделать процесс литья в песчаные формы намного быстрее и точнее.
Новое программное обеспечение теперь помогает заводам тестировать конструкции перед литьем металла. Оно показывает им, как металл будет течь и охлаждаться. Некоторые также отслеживают тепло в процессе заливки с помощью датчиков в режиме реального времени. Благодаря этому экономится время, а детали получаются более точными.
Цифровые чертежи песчаных форм можно использовать для изготовления самой формы с помощью 3D-принтеров. Это помогает пропустить процесс создания шаблона. Это хорошо для тестирования новых деталей и хорошо работает со сложными формами. Также есть литье методом абляции, который использует специальные формы, которые быстро остывают и быстро отрываются. Это также помогает сделать изделия намного прочнее.
Плюсы и минусы литья в песчаные формы
Как и в любом производственном процессе, здесь есть свои положительные стороны, но также есть и недостатки.
Преимущества:
- Процесс очень гибкий. Формы можно изготавливать вручную или с помощью тяжелой техники.
- Если что-то пойдет не так, вы сможете легко исправить ситуацию, поскольку шаблон или форму легко отрегулировать.
- Он хорошо подходит для больших форм и других форм, которые сложно отлить другими методами.
- Это можно сделать в простых условиях с ограниченным пространством или оборудованием.
- Это простой для освоения процесс, который может эффективно применяться как на малых, так и на крупных предприятиях.
Проблемы:
- При крупномасштабном производстве деревянные или пластиковые шаблоны со временем могут изнашиваться.
- Из-за размера песчинок трудно воспроизвести тонкие текстуры или острые края.
- Детали часто требуют дополнительной обрезки, шлифовки или механической обработки для соответствия конечным требованиям.
- Если сердечник установлен неправильно, это может привести к выходу деталей из строя.
Приложения и рыночный ландшафт
Литье в песчаные формы подходит для многих отраслей промышленности, поскольку оно работает с различными металлами. Эти металлы предлагают свои собственные преимущества и цели.
Распространенные сплавы:
- Железо и сталь: Эти металлы очень прочные и долговечные. Они также выдерживают очень высокие температуры, что делает их идеальными для деталей, которые служат долго.
- Алюминий: Он намного легче по весу и его легче формовать или обрабатывать. Он не такой прочный, как сталь, но все еще может выдерживать умеренное давление.
- Бронза и латунь: Эти сплавы сделаны из меди. Они также очень прочные и не ржавеют. Они оба хороши в соленых или влажных условиях, когда детали движутся друг против друга.
- Другие металлы: Некоторые другие металлы, такие как цинк, легко отливаются и хорошо подходят для мелких деталей. Магний также легкий и хорошо подходит, когда вес должен быть небольшим. Эти металлы выбирают для специальных работ из-за их уникальных особенностей.
Масштаб отрасли
Рынок литья в песчаные формы очень велик. Отчеты показывают что в 2023 году объем рынка составил $345,5 млрд. долл. США, и ожидается, что к 2031 году он вырастет до $584,5 млрд. долл. США, а годовой прирост составит около 7,8%.
Основные секторы
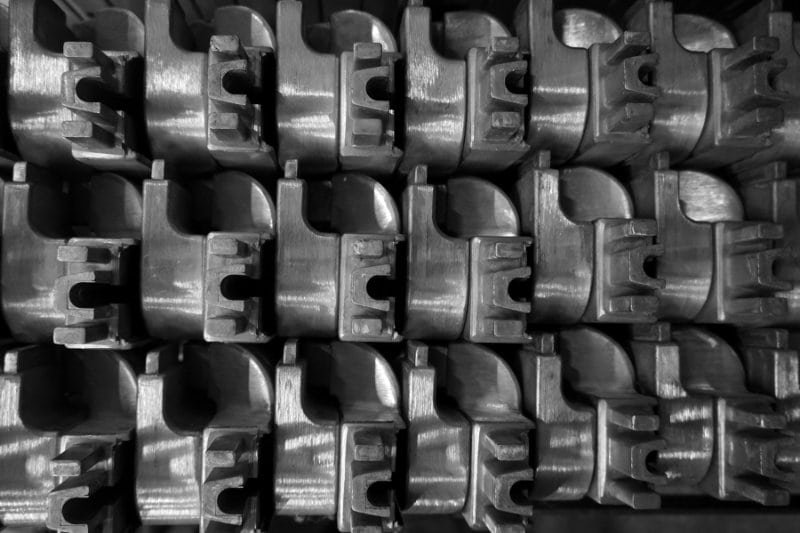

Литье в песчаные формы используется во многих крупных отраслях промышленности, где требуются прочные, индивидуальные детали, изготавливаемые по более низкой стоимости.
- Транспорт: Производители автомобилей используют литье в песчаные формы для изготовления крупных и прочных деталей, таких как блоки двигателей, картеры коробок передач и тормозные системы.
- Авиационная промышленность: Самолетам обычно нужны детали, которые одновременно прочны и легки. Литье в песчаные формы может помочь изготовить такие вещи, как кронштейны из алюминия и других сплавов. Эти детали также должны соответствовать строгим правилам безопасности и веса.
- Энергетика и коммунальные услуги: Электростанции и ветровые электростанции используют литые детали в турбинных системах, клапанах и генераторах. Эти детали обычно подвергаются воздействию высокой температуры или давления, что можно сделать с помощью подходящего типа металла.
- Строительство: Тяжелые машины и насосы, используемые в строительстве, нуждаются в прочных металлических деталях для хорошей работы. Литье в песчаные формы может использоваться здесь для изготовления таких вещей, как крюки, рамы и корпуса насосов.
Экологические и экономические соображения
Хотя литье в песчаные формы — это просто, оно все равно может оказывать влияние на окружающую среду. Вот почему многие заводы сейчас работают над сокращением отходов и улучшением процесса.
Литье в песчаные формы по-прежнему сжигает топливо для расплавления металлов, что в свою очередь выделяет тепло и дым в воздух. Если это не контролировать должным образом, это загрязняет воздух и вредит рабочим. Чтобы решить эту проблему, некоторые заводы теперь используют более чистое топливо, а также отслеживают выбросы, чтобы соблюдать правила безопасности. Также используются более совершенные системы воздушного потока для отслеживания вредных паров.
Это также помогает местному производству. Небольшие мастерские могут выполнять индивидуальные заказы без необходимости в дорогостоящих станках. Процесс меньше зависит от задержек в цепочке поставок. Кроме того, шаблоны и песок легко найти или использовать повторно. Поскольку формы уничтожаются после каждого использования, это освобождает место и сокращает расходы на хранение.
Вывод
Люди веками льют металл в песок, и не только потому, что он старый. Он все еще работает. Он груб по краям, конечно, но он выполняет работу без суеты. Большая деталь, маленький заказ, странная форма? Литье в песчаные формы не имеет значения.
Если вам нужны детали, которые выдержат испытание временем и не будут стоить целое состояние, свяжитесь с нами и мы это осуществим.
Узнайте больше из наших сообщений в блоге.
Недавние Посты
Узнайте больше о нашей продукции.
Последние продукты
Мгновенная цена!