Tout ce que vous devez savoir sur l'acier inoxydable ferritique
- Par: dong
L'acier inoxydable ferritique, deuxième type d'acier inoxydable le plus courant, est devenu un matériau fréquemment utilisé dans de nombreux secteurs industriels grâce à ses caractéristiques et ses avantages. Ce blog vous propose une présentation détaillée de l'acier inoxydable ferritique, abordant ses propriétés, ses applications et ses atouts, afin de vous accompagner dans la conception de vos produits métalliques sur mesure.
Qu'est-ce que l'acier inoxydable ferritique ?
Définition
L'acier inoxydable ferritique est un type d'acier inoxydable à base de fer, caractérisé par une teneur en chrome (généralement 10,5%-30%) et une faible teneur en nickel, voire aucune.
Il conserve une structure cristalline cubique centrée (BCC) de la température ambiante jusqu'aux hautes températures.
Qu'est-ce que l'acide ferrique ?
La ferrite est une structure cristalline formée par l'agencement des atomes de fer selon un motif cubique centré. Cette structure métallographique confère à tous les aciers ferritiques leurs propriétés magnétiques, ainsi que leur formabilité et leur ténacité caractéristiques. 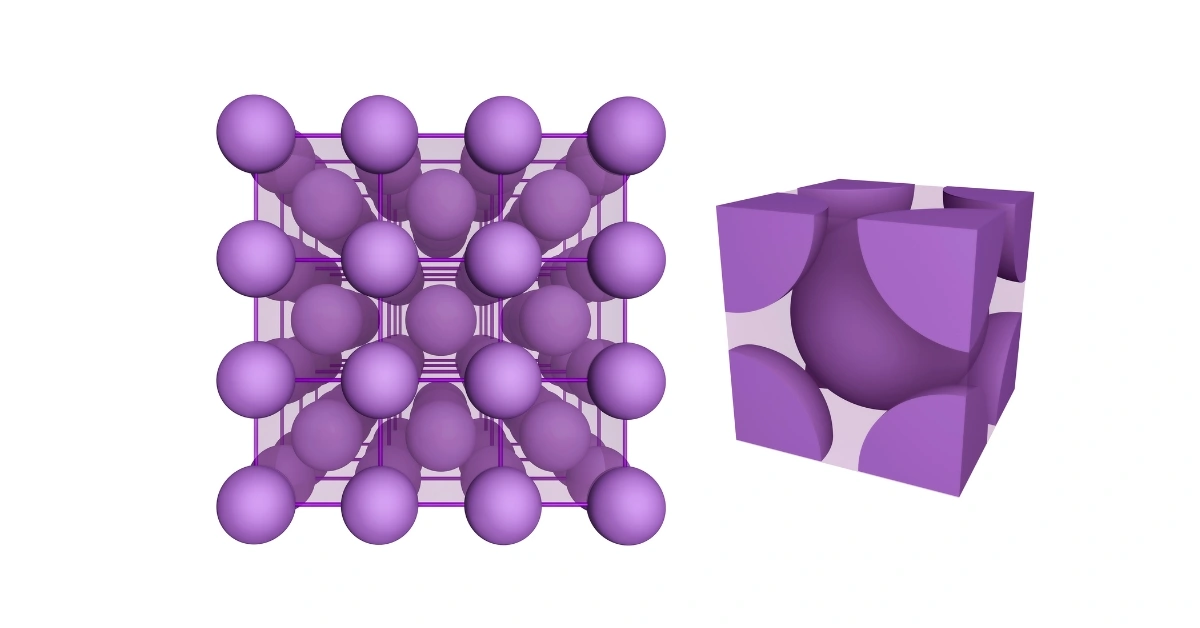
Composants chimiques
Élément | Contenu |
Fer (Fe) | Solde |
Chrome (Cr) | 10.5%-30% |
Nickel (Ni) | ≤0,5% |
Carbone (C) | ≤0,08% |
Manganèse (Mn) | ≤1,0% |
Sélénium (Si) | ≤1,0% |
Molybdène (Mo) | 0,5–2,0% |
Niobium (Nb)/Titane (Ti) | traces |
Principales propriétés de l'acier inoxydable ferritique
Propriétés physiques
- Magnétique
- Bonne conductivité thermique
- faible dilatation thermique
Propriétés chimiques
- Bonne résistance à la corrosion : notamment dans des environnements atmosphériques doux, en eau douce et dans des environnements contenant des milieux chimiques légers.
- Bonne résistance à l'oxydation : même dans un environnement à haute température de 600 à 800 °C.
Propriétés mécaniques
- Résistance à la traction et limite d'élasticité modérées.
- Résistance : Elle présente une certaine résistance à température ambiante, mais plus la température baisse, plus sa résistance diminue.
- Aptitude à la mise en forme : Sa plasticité est généralement faible, surtout à basse température.
nuances courantes d'acier inoxydable ferritique
Acier inoxydable 430
L'acier inoxydable 430 contient 16 à 181 % de chrome et est l'acier inoxydable ferritique le plus courant et le plus polyvalent.
Il présente une bonne résistance à la corrosion dans les environnements secs et tempérés.
Sa soudabilité est relativement faible, ce qui la rend adaptée aux méthodes de fabrication de tôles telles que la découpe et le pliage pour le formage intégré.
Les applications courantes du 430 comprennent les boîtiers de fours à micro-ondes, les panneaux muraux d'ascenseur et les éviers de cuisine.
Acier inoxydable 434
L'acier inoxydable 434 ajoute environ 1% de molybdène à la base de 430. L'ajout de molybdène améliore la résistance à la corrosion par piqûres et à la corrosion caverneuse de l'acier inoxydable, tout en augmentant légèrement son coût.
Les composants courants de la pièce 434 comprennent les poignées de portières de voiture, les bras d'essuie-glace et les doublures de lave-vaisselle.
Acier inoxydable 409
L'acier inoxydable 409 a une teneur en chrome d'environ 11% et contient du titane, un élément stable.
L'ajout de titane améliore sa résistance à la corrosion intergranulaire, lui conférant d'excellentes performances de soudage.
Du fait de sa faible teneur en chrome, son coût est réduit, mais sa résistance à la corrosion est considérablement affaiblie.
Les applications courantes du 409 sont les tuyaux d'échappement automobiles, les silencieux automobiles et les tuyaux d'échappement des équipements agricoles.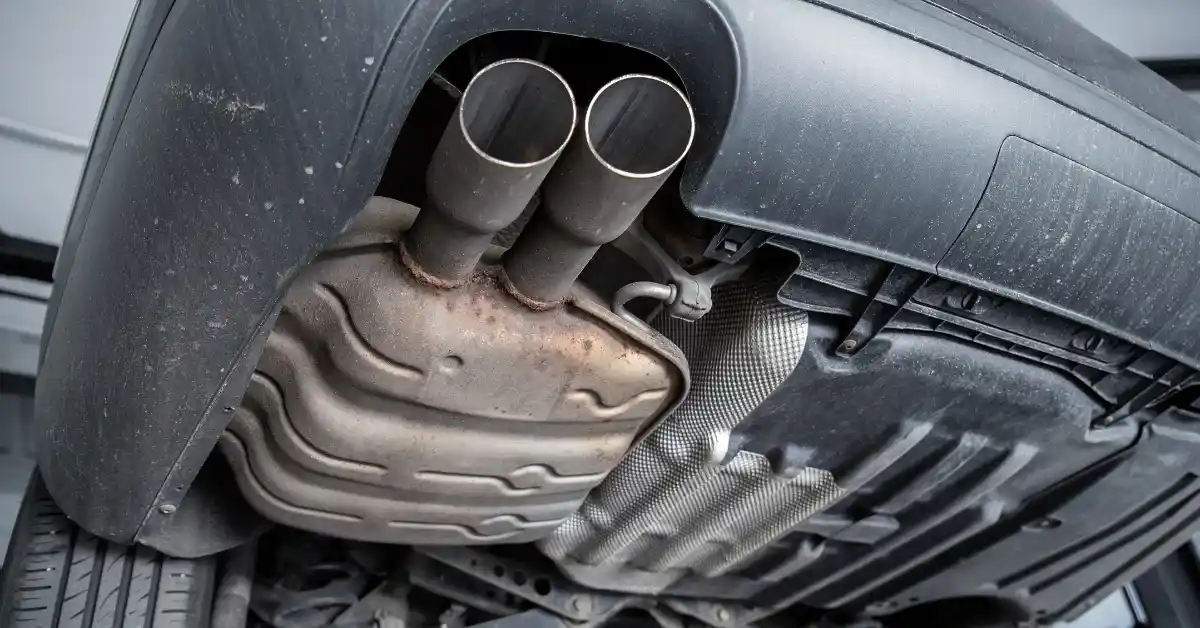
Acier inoxydable 439
La teneur en chrome de l'acier inoxydable 439 est d'environ 17-19%, et le titane est utilisé comme élément stabilisateur pour améliorer la résistance à la corrosion intergranulaire, de sorte que les performances de soudage sont excellentes.
Les pièces nécessitant des performances de soudage élevées et une bonne résistance à la corrosion peuvent être fabriquées en 439, telles que les revêtements de chauffe-eau, les conduites de gaz, etc.
Acier inoxydable 444
L'acier inoxydable 444 est un acier inoxydable ferritique à haute teneur en molybdène contenant 18 à 20% de chrome, environ 2% de molybdène et du niobium comme élément stabilisant, empêchant efficacement la corrosion intergranulaire.
La présence de molybdène lui confère une résistance extrêmement élevée à la corrosion sous contrainte par les chlorures et à la corrosion par piqûres.
Les produits courants de la catégorie 444 comprennent des réservoirs de stockage d'eau chaude et des matériaux de toiture pour les bâtiments côtiers.
Acier inoxydable 446
L'acier inoxydable 446 est un acier inoxydable ferritique à haute teneur en chrome avec une teneur en chrome de 23-27%, ce qui lui confère une résistance à l'oxydation à haute température extrêmement élevée et une température de résistance à la chaleur maximale allant jusqu'à 1100℃.
Cependant, son coût est relativement élevé parmi les aciers inoxydables ferritiques, et son usinabilité est généralement moyenne.
Les produits courants en acier inoxydable 446 comprennent les tubes de recuit pour fours industriels et les équipements de traitement thermique.
Normes internationales et équivalences de grade
AISI | EN (Numéro de matériau) | ISO | JIS | Go |
430 | 1.4016 | X6Cr17 | SUS430 | 10Cr17 |
434 | 1.4113 | X6CrMo17-1 | SUS434 | 10Cr17Mo |
409 | 1.4512 | X6CrTi12 | SUS409 | 06Cr11Ti |
439 | 1.4510 | X2CrTiNb18 | SUS439 | 022Cr18Ti |
444 | 1.4521 | X2CrMoTi18-2 | SUS444 | 019Cr18Mo2Ti |
446 | 1.4762 | X10CrMoSi25-4 | SUS446 | 16Cr25N |
Avantages et inconvénients de l'acier inoxydable ferritique
Avantages
- La teneur en chrome de l'acier inoxydable ferritique lui confère une excellente résistance à la corrosion. Si votre produit sur mesure doit résister à des environnements modérément corrosifs, l'acier inoxydable ferritique répondra à vos besoins d'utilisation à long terme.
- L'acier inoxydable ferritique présente une bonne résistance à l'oxydation à haute température et un faible coefficient de dilatation thermique, ce qui garantit que les produits en acier inoxydable ferritique conservent de bonnes performances même dans des environnements d'utilisation à haute température.
- La plasticité et la ténacité de l'acier inoxydable ferritique le rendent excellent pour la transformation à température ambiante, et si vous choisissez l'acier inoxydable ferritique comme matériau de production, l'ensemble du processus de production sera très efficace.
- L'acier inoxydable ferritique contient très peu, voire pas du tout, de nickel, ce qui réduit les coûts de production. Si votre produit privilégie la rentabilité, l'acier inoxydable ferritique est un excellent choix.
Désavantages
Comparé à d'autres types d'acier inoxydable, l'acier inoxydable ferritique présente certains inconvénients dans des applications spécifiques.
- Comparé à l'acier inoxydable austénitique, l'acier inoxydable ferritique présente une résistance à la corrosion relativement plus faible, notamment dans les environnements humides, chimiques et chlorés.
- L'acier inoxydable ferritique présente une mauvaise soudabilité et, après soudage, il devient cassant, développe des fissures à chaud et subit une corrosion intergranulaire, ce qui entraîne généralement une mauvaise qualité de soudure.
- L'acier inoxydable ferritique n'est pas aussi résistant que l'acier inoxydable austénitique et l'acier inoxydable PH, il ne présente donc pas beaucoup d'avantages dans les applications exigeant une résistance élevée.
- Dans les environnements à basse température, l'acier inoxydable ferritique présente une faible plasticité et une faible ténacité, ce qui le rend inadapté aux applications à basse température ou aux scénarios nécessitant une résistance à la traction élevée des composants.
Procédés de traitement de l'acier inoxydable ferritique
Usinage CNC
L'usinage CNC est la méthode de traitement la plus courante pour l'acier inoxydable ferritique, produisant des produits de haute précision, aux surfaces lisses et aux excellentes performances, ce qui la rend parfaitement adaptée aux projets sur mesure de petite et moyenne série.
Il est toutefois important de noter que des augmentations localisées de température pendant la coupe peuvent provoquer un durcissement de la surface et accélérer l'usure de l'outil.
Il est recommandé d'utiliser des outils en acier rapide ou en carbure, associés à des vitesses de coupe et à un fluide de coupe moyens à faibles, pour obtenir de meilleurs résultats d'usinage.
Forgeage à chaud
L'acier inoxydable ferritique peut être traité à chaud, mais il est nécessaire de contrôler avec précision la température de la pièce entre 950 et 1250 °C pendant le traitement.
Une température trop basse entraînera un écrouissage, tandis qu'une température trop élevée entraînera un grain grossier, une diminution des propriétés mécaniques et une moindre résistance à la corrosion.
Par conséquent, il est moins utilisé pour le traitement thermique et est principalement utilisé pour un petit nombre de pièces de grande épaisseur ou de formes spéciales.
Moulage d'investissement
Bien que l'acier inoxydable ferritique puisse être utilisé pour le moulage à la cire perdue, sa faible fluidité et sa sensibilité à la fissuration à froid et à la fissuration intergranulaire lors d'un refroidissement rapide limitent son application.
Par conséquent, il est généralement utilisé uniquement pour le moulage en petites séries de pièces de formes complexes et de haute précision.
Un contrôle strict de la température de fusion, de la vitesse de coulée et de la méthode de refroidissement est nécessaire lors du processus de coulée afin d'éviter les fissures.
De plus, un recuit après coulée est nécessaire pour éliminer les contraintes et garantir les propriétés mécaniques et la résistance à la corrosion.
Découpe et pliage
Les procédés de travail à froid, tels que le pliage et l'estampage, sont les méthodes de transformation industrielle les plus courantes pour l'acier inoxydable ferritique, principalement pour les deux raisons suivantes :
- Faible coût et bonne résistance à la corrosion, offrant des avantages économiques pour les applications à grande échelle.
- Le travail à froid utilise des feuilles minces, ce qui permet d'éviter efficacement les inconvénients liés à la plasticité limitée et à l'écrouissage de l'acier inoxydable ferritique.
Soudage
La soudabilité de l'acier inoxydable ferritique est généralement moyenne. Si l'apport de chaleur de soudage et la température entre passes ne sont pas rigoureusement contrôlés pendant le processus de production, des fissures à chaud peuvent apparaître au niveau de la soudure, affectant ainsi les performances du produit.
Cependant, la sélection de nuances ayant une bonne soudabilité, telles que 439 et 444, peut efficacement prévenir la corrosion intergranulaire après soudage.
Traitement de surface
- Traitement fonctionnel : décapage, passivation, électropolissage…
- Traitements décoratifs : polissage, sablage, revêtement…
Application de l'acier inoxydable ferritique
- Automobile : tuyaux d’échappement, collecteurs d’échappement, silencieux, poignées de porte, pièces d’essuie-glace…
- Appareils électroménagers et articles de cuisine : cuves de chauffe-eau, tambours de lave-linge, coques de four à micro-ondes, éviers, plaques à induction et casseroles…

- Architecture et décoration : panneaux de portes d’ascenseur, charnières de portes et de fenêtres, structure des bâtiments côtiers…
- Industrie et énergie : ballon de chaudière, pipeline de transport de produits chimiques, tube d’échangeur de chaleur…
- Biens de consommation durables : cadres de motos, fixations (boulons, écrous)…
Résumé
Ce blog vous a permis de mieux comprendre les caractéristiques, les avantages et les applications de l'acier inoxydable ferritique. Si vous souhaitez faire réaliser des produits en acier inoxydable ferritique sur mesure, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter pour obtenir un devis. Nous proposons des services complets, incluant l'usinage, la fonderie de précision, la fabrication de tôles et le traitement de surface.
FAQ
L'acier inoxydable ferritique est-il magnétique ?
Oui, et le magnétisme ne disparaîtra pas complètement ; il peut s'affaiblir en raison de températures élevées ou d'un traitement à froid intense.
Quelle est la différence entre l'acier inoxydable ferritique et l'acier inoxydable austénitique ?
L'acier inoxydable ferritique est magnétique, tandis que l'acier inoxydable austénitique ne l'est pas ; la résistance à la corrosion de l'acier inoxydable ferritique est inférieure à celle de l'acier inoxydable austénitique ; l'acier inoxydable ferritique est généralement moins cher que l'acier inoxydable austénitique.
L'acier inoxydable ferritique est-il apte au contact alimentaire ?
Les aciers inoxydables 430, 443 et 439 sont de qualité alimentaire, mais en raison de la résistance modérée à la corrosion de l'acier inoxydable ferritique, leur sécurité alimentaire est limitée.
Quel est le prix de l'acier inoxydable ferritique ?
Comme l'acier inoxydable ferritique ne contient pas de nickel, un métal précieux, son prix est relativement bas et stable, nettement inférieur à celui de l'acier inoxydable austénitique.
Quelles méthodes de traitement proposez-vous pour les pièces sur mesure en acier inoxydable ferritique ?
Nous proposons des services d'usinage CNC, de forgeage à chaud, de fonderie à cire perdue, d'emboutissage, de découpe, de pliage et de finition de surface.
Acceptez-vous les fichiers CAO ou les échantillons fournis par les clients ?
Oui. Nous fabriquons exclusivement sur la base des dessins, fichiers CAO ou échantillons physiques du client.
Découvrez-en davantage avec nos articles de blog.
Messages récents
Découvrez-en plus sur nos produits
Produits personnalisés
Devis gratuit et immédiat !