Understanding Motorcycle Radiator
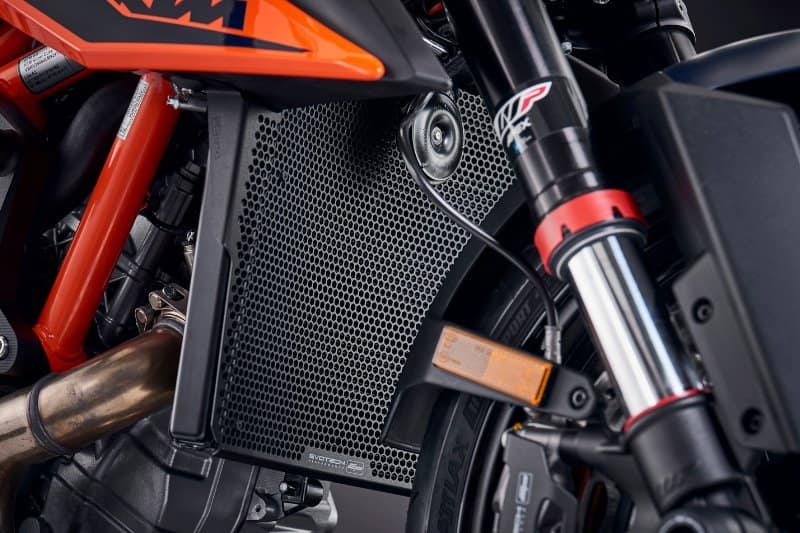
A motorcycle radiator is a crucial part of the engine cooling system. It is designed to dissipate excess heat generated during the combustion process and maintain the engine’s operating temperature within an optimal range. By preventing overheating, a motorcycle radiator ensures that the engine operates efficiently and avoids potential damage due to excessive heat.

The Components of a Motorcycle Radiator
A typical motorcycle radiator consists of several key components:
- Core: The core is the central part of the radiator where heat exchange occurs. It is made up of small tubes and fins that help dissipate heat.
- Tubes: Tubes in the core carry coolant from the engine to the radiator.
- Fins: Fins are thin metal plates or blades that are attached to the tubes. They increase the surface area for heat dissipation.
- Coolant Inlet and Outlet: Connects to the motorcycle liquid cooling system’s coolant circulation pipes, transporting coolant into the radiator’s pipes.
- Frame: Supports and protects the relatively fragile radiator core, equipped with mounting holes for installation onto the motorcycle.
Impacts of Radiator on Motorcycle Performance
The performance of a motorcycle radiator directly affects the overall performance of the bike. When a radiator is functioning optimally, the engine operates at the ideal temperature, ensuring maximum power output and efficiency. An overheating engine can lead to reduced performance, potential engine damage, and even engine failure.
How Does a Motorcycle Radiator Cool the Engine?
A motorcycle radiator cools the engine through a process of heat exchange. Coolant circulates through the engine, absorbing heat, and then flows into the radiator. As the air passes over the radiator’s fins, it removes heat from the coolant, reducing its temperature. The cooled coolant is then recirculated into the engine to continue the cooling process.

Factors Affecting the Cooling Efficiency of a Motorcycle Radiator
Several factors can influence the cooling efficiency of a motorcycle radiator:
- Coolant Type: The choice of coolant and its mixture with water can impact the radiator’s ability to dissipate heat effectively.
- Radiator Size: A larger radiator typically has more surface area for heat dissipation and can cool the engine more efficiently.
- Airflow: Proper airflow is essential. Any obstructions or damage to the radiator’s fins can hinder heat exchange.
- Radiator Position: The radiator’s location on the motorcycle can affect its exposure to airflow, affecting cooling efficiency.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance, including cleaning and flushing the radiator, is crucial for optimal performance.
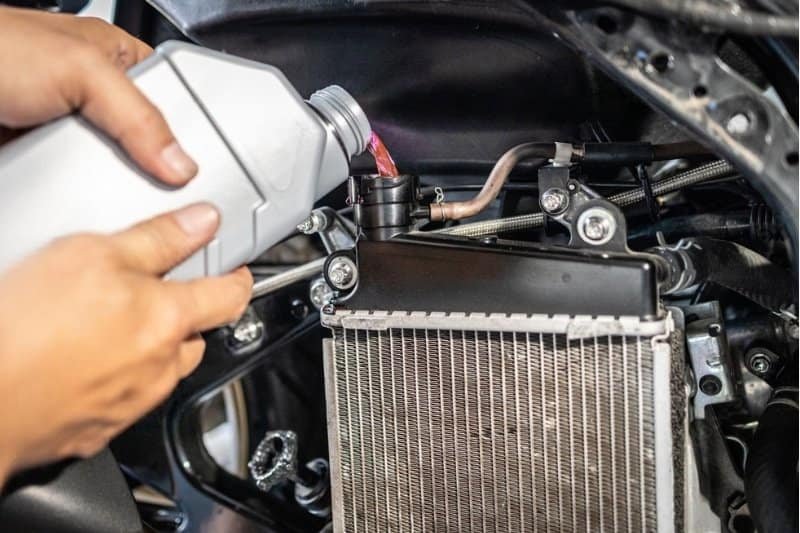
Do I Add Coolant to the Radiator or Reservoir?
Adding coolant to the reservoir rather than the radiator is generally recommended because it allows for the expansion and contraction of the coolant as the engine heats up and cools down. Opening the radiator cap directly can be dangerous when the engine is hot, as it may release hot coolant and steam, potentially causing burns or injury. Always exercise caution and follow your vehicle’s specific guidelines for coolant maintenance, which can be found in the owner’s manual.

Materials That Motorcycle Radiators Are Typically Made Of
Motorcycle radiators are typically made from materials such as aluminum or copper. These materials are chosen for their excellent heat conductivity and durability, making them ideal for heat exchange in radiators.

How Is a Motorcycle Radiator Manufactured?
Motorcycle radiators are precision-engineered components. They are manufactured using various techniques, including CNC machining for precise tube and fin alignment, ensuring efficient heat transfer. The manufacturing process involves assembling the core and pressure testing the radiator to ensure it functions correctly.
Different Types of Motorcycle Radiators
There are different types of motorcycle radiators, including water-cooled and oil-cooled radiators.
- Water-Cooled Radiators: Water-cooled radiators are the most common type in motorcycles. They use a mix of water and coolant to absorb engine heat and transport it to the radiator. Airflow through the radiator cools this mixture efficiently, effectively regulating the engine temperature.
- Oil-Cooled Radiators: Oil-cooled radiators, less common today, rely on engine oil to dissipate heat. Engine oil circulates through the radiator’s passages, absorbing heat from the engine, and the radiator cools the oil with airflow.
Inspect and Maintain Motorcycle Radiator
Regular inspection and maintenance of your motorcycle radiator are essential. It is recommended to check the radiator for damage, leaks, and debris buildup regularly. Additionally, flushing and replacing coolant as per the manufacturer’s recommendations is crucial for long-term radiator performance.
Typical Lifespan of a Motorcycle Radiator
The lifespan of a motorcycle radiator can vary depending on factors such as usage, maintenance, and environmental conditions. However, a well-maintained radiator can last the lifetime of the motorcycle. It’s essential to monitor its condition and address any issues promptly to extend its lifespan.

Customization Options Possible for a Motorcycle Radiator
In HDC Manufacturing, we offer several customization options for motorcycle radiators, including radiator size, material, and design to suit specific performance requirements. Whether you need a larger radiator for improved cooling capacity or a custom design to match your bike’s aesthetics, our team can work with you to create a radiator that meets your unique needs.
Conclusion
A motorcycle radiator is a vital component that plays a pivotal role in maintaining the engine’s optimal temperature, ensuring peak performance, and preventing overheating. Regular maintenance and understanding the factors that affect cooling efficiency are essential for every motorcycle enthusiast. When it comes to motorcycle radiators, quality and efficiency are key to a smooth and trouble-free ride.