Exploring the Versatility of Living Hinges in Modern Design
Discover the innovative world of living hinges, their applications, advantages, and types. Learn how these flexible, cost-effective components are revolutionizing industries like packaging, aerospace, and medical devices with their durability and sustainable design.
What are Living Hinges
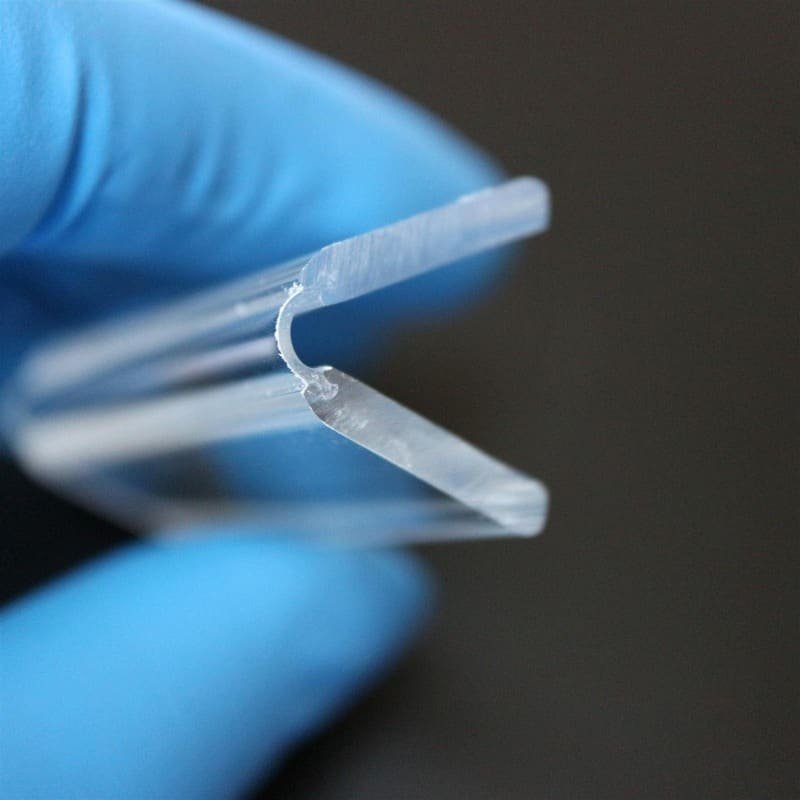
Living hinges are flexible, thin sections integrated into objects, like containers or lids, enabling repeated bending without breaking. Typically made from the same material as the object itself, these hinges are seamlessly designed for flexibility, resembling biological joints. Often employed in plastic products through processes like injection molding, living hinges are cost-effective solutions for applications requiring frequent opening and closing, such as flip-top lids and clamshell packaging. Their engineered design allows for dynamic movement without the need for additional components, making them efficient for creating moving parts in various products.

Advantages of Living Hinges
Flexibility and Durability
One of the primary advantages of living hinges is their exceptional flexibility, allowing for repeated bending without compromising structural integrity. This flexibility contributes to the overall durability of products.
Cost-Effectiveness
The incorporation of living hinges in product design often leads to cost savings. The simplicity of these hinges eliminates the need for additional components, reducing manufacturing expenses.
Sustainable Design
As sustainability gains prominence, living hinges stand out as eco-friendly solutions. Their integration into product design promotes a reduction in material usage, contributing to a more sustainable manufacturing process.
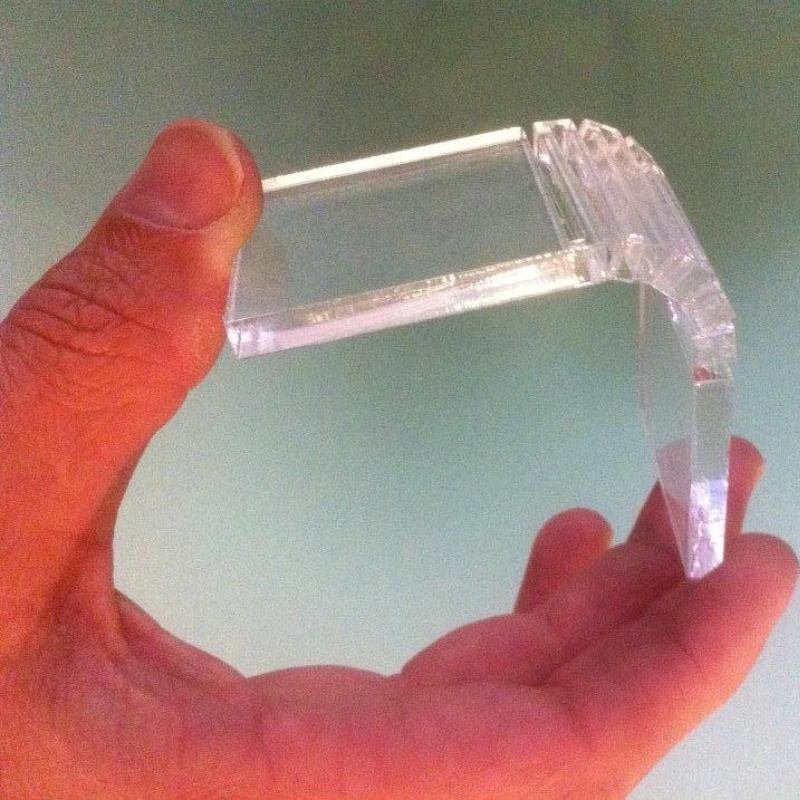

Difference Between Traditional Hinges and Living Hinges
Traditional hinges and living hinges differ in material, design, flexibility, manufacturing processes, applications, and limitations. Traditional hinges are separate mechanical components typically made of metal or plastic, rigid, and designed for durability and stability in applications like doors and windows. In contrast, living hinges are integral to a single, flexible material, highly flexible, often made of polymers, and suitable for cost-effective, simple, and flexible joints in applications such as packaging and small enclosures. The manufacturing of traditional hinges involves separate components and additional assembly steps while living hinges are often molded or formed as part of a single-piece manufacturing process, reducing complexity. However, traditional hinges may be bulkier, and living hinges may be less durable in heavy-duty or high-stress scenarios.
Types of Living Hinges
Living hinges come in various types tailored for specific applications and materials:
- Straight Living Hinges: Linear hinges for basic, repetitive bending motions.
- Curved Living Hinges: Designed with bends or curves for flexibility along more complex paths.
- Interlocking Living Hinges: Feature interlocking elements for enhanced stability and controlled movement.
- Dual Living Hinges: Consists of two parallel sections, providing increased strength and durability.
- Multi-Axis Living Hinges: Allow flexibility in multiple directions, accommodating movements along different axes.
- Bi-Stable Living Hinges: Have two stable positions, useful for applications requiring specific flexed or extended states.
Choosing the right hinge depends on the application, material, and the required range of motion and durability.
Materials for Living Hinges
Living hinges, designed for repetitive bending without breaking, commonly use materials like Polyethylene (PE) for cost-effectiveness, Polypropylene (PP) for excellent fatigue resistance, and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) for versatility. Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) combine rubber-like elasticity with thermoplastic advantages, while Nylon (PA) and Acetal (POM) offer strength with flexibility. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) provides a balance of rigidity and flexibility, and Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) is ideal for over-molding. The material choice depends on factors like application requirements, cost, and expected lifespan, ensuring optimal performance based on specific mechanical and thermal properties.
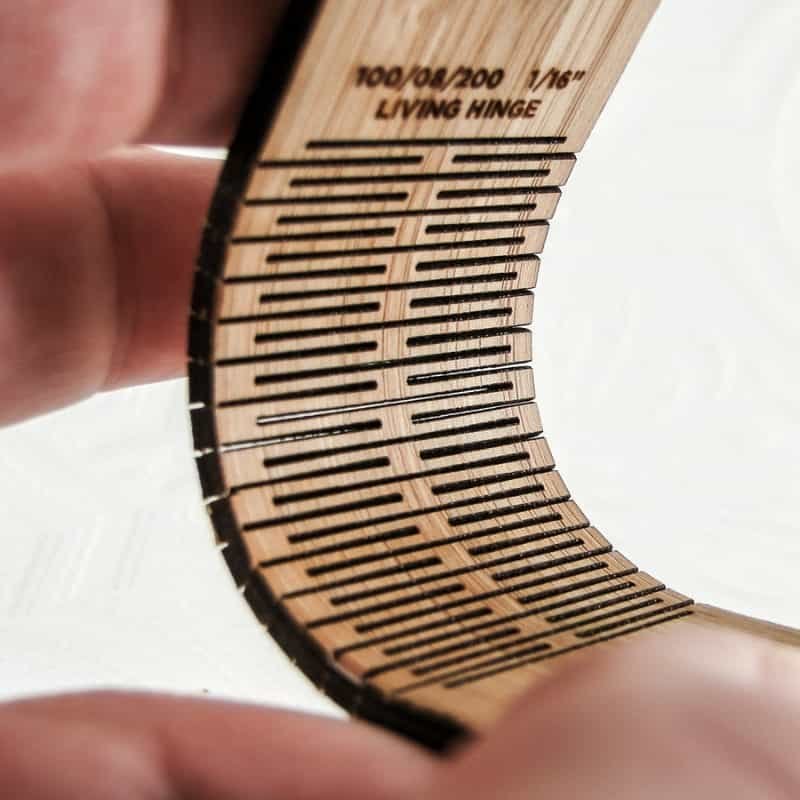

Industries Utilizing Living Hinges
Packaging
In the packaging industry, living hinges are widely used for creating hinged lids and closures. This application ensures easy access to the contents while maintaining a secure seal.
Aerospace
Living hinges find crucial applications in aerospace engineering, where weight and flexibility are paramount. Their lightweight nature and ability to withstand repeated stress make them ideal for various components.
Medical Devices
The medical field benefits from living hinges in the design of devices requiring controlled movement, such as pill dispensers and surgical instruments.
Challenges and Solutions
Wear and Tear
While living hinges excel in flexibility, wear and tear can be a concern over time. Ongoing research focuses on developing materials with enhanced durability to address this challenge.
Material Innovation
Innovation in materials is key to overcoming challenges. Researchers are exploring new polymers and composites to enhance the performance and lifespan of living hinges.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for products with living hinges. Simple cleaning and lubrication can extend the lifespan of these hinges, ensuring optimal performance.

Future Trends
Technological Advancements
Advancements in material science and manufacturing technologies are expected to lead to even more resilient and versatile living hinges.
Integration in New Industries
As designers and engineers continue to explore possibilities, living hinges are likely to find applications in new and unexpected industries, further expanding their reach.
Environmental Impacts
The environmental impact of living hinges is a growing consideration. Future trends may involve a shift towards even more sustainable materials and manufacturing processes.
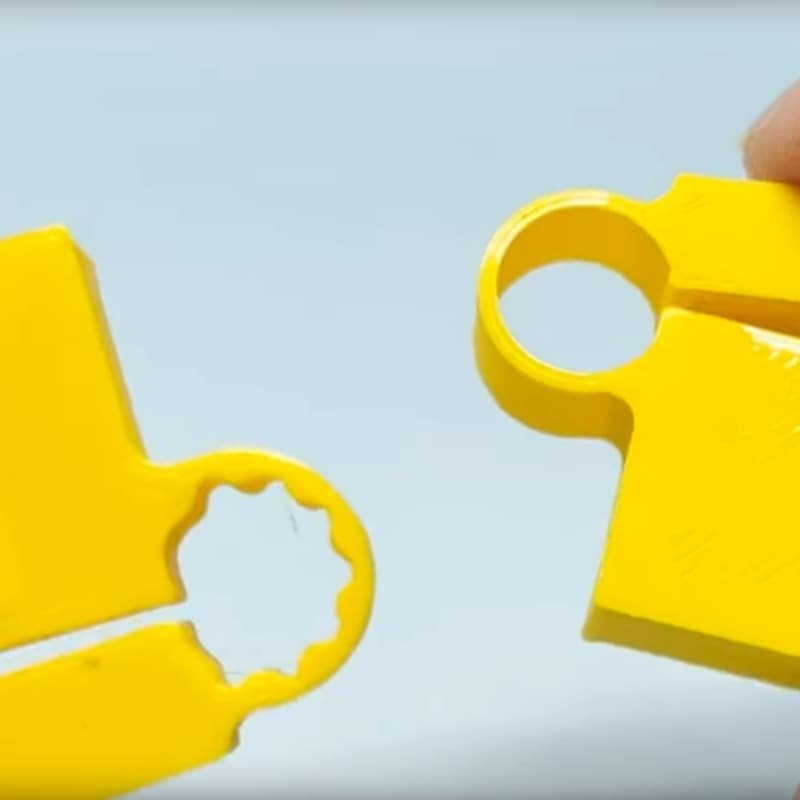

Custom Living Hinges
Customizing living hinges from manufacturers involves a systematic process:
- Clearly define project requirements, considering material, dimensions, and flexibility.
- Research manufacturers specializing in custom plastic or rubber components.
- Submit detailed design specifications, including CAD files if available.
- Request quotations from selected manufacturers, considering quantity and lead time.
- Review samples to verify quality before committing to mass production.
- Negotiate terms such as pricing, payment, and production lead times.
- Place the order with clear documentation of specifications and quantities.
- Maintain communication during production for updates and quality assurance.
- Upon delivery, thoroughly inspect and provide feedback for future improvements.
By following these steps, you can work with manufacturers to customize living hinges that meet your specific requirements. Clear communication and attention to detail are key to a successful collaboration.

Conclusion
Living hinges, with their flexibility, durability, and versatility, have become indispensable in various industries and everyday products. As technology advances and sustainability takes center stage, the future looks bright for living hinges, with continued innovations and widespread applications.