When mentioning the laser engraving, you may say it is a kind of marking technique. If you wonder how laser engraving works, what materials can be laser engraved, and its applications and benefits, this article may provide you with more processing design ideas.
What is laser engraving?
As a subtractive surface treatment method, laser engraving forms patterns or text by making use of a laser beam to remove or alter the material’s surface.
Advantages of engraving
High precision
Take the most used fiber laser engraving machine for example, it can engrave a thin line of 0.01mm(about 1/5 of human hair) at ±0.003mm accuracy. This far exceeds the precision achievable by hand.
Long durability
The marks made by laser engraving are permanent and highly durable.
Quick operation
The engraving laser can move precisely at a high speed of 500–1,000 mm/s, allowing it to cover and engrave an area of 100 cm² in a minute, which is about 1/6 of an A4 paper.
Highly automated
Program settings and computer control enable laser engraving to achieve highly automated processes and eliminate errors.
Environmental friendly
Laser engraving can reduce errors or waste caused by manual engraving, thereby being more environmentally friendly.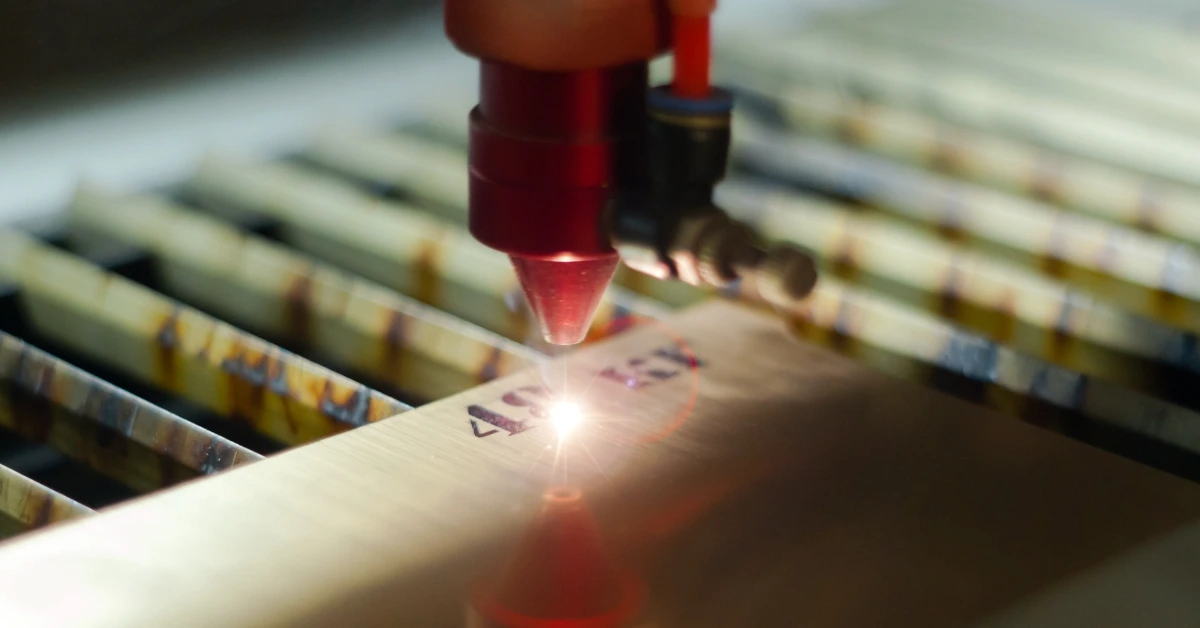
Types of laser engraving machines
According to the differences in laser wavelength and laser sources, laser engraving can be divided into the following three categories.
Fiber Laser
Fiber laser has high precision and speed, it is suitable for metals, plastics(like ABS), and coating materials(like paint coating and zinc plating). The operating cost of fiber laser machines is low, and the processing efficiency is high.
CO₂ Laser
As the most commonly used laser engraving equipment, the CO₂ laser is preferable for non-metals, like wood, glass, acrylic, and leather. Its cost is lower, and it has significant advantages in deep cutting and large-format processing.
UV Laser
UV lasers can perform high-precision engraving on fragile materials such as glass, mirrors, and porcelain without cracks, although their cost is relatively high.
How does laser engraving work?
Precisely controlled by the computer settings and programs, laser engraving utilizes a highly focused laser beam to release large amounts of thermal energy, and then the selected material surface heats up immediately. This heat burns or vaporizes a little material away. The computer precisely controls the laser beam to create unique, permanent engraved marks, which may appear as convex, concave, or darkened areas with patterns.
Process of laser engraving
So, how does laser engraving actually work step-by-step?
- Design the patterns or logos on a computer using the correct digital file format, like .jpg, .svg, or .pdf.
- Select the right materials for the project, such as stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium. Put the clean material on the machine bed firmly.
- Adjust the laser engraver’s settings, including power, speed, path, and focus, to ensure the best performance of materials and machines.
- After completing all the steps above, start the engraving process. Pay attention to the indoor ventilation during this step to prevent potential smoke from causing unnecessary danger.
- Cool the material and clean any residue on the surface to reveal a permanent and precise maker.
What materials can be laser-engraved?
Laser engraving, as a surface treatment method often used by custom product manufacturers or original brand owners, is suitable for a variety of materials.
Metal
For most metals, like aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, and carbon steel, laser engraving is one of the most efficient, precise, and durable marking methods.
However, due to differences in absorption rates, thermal conductivity, and melting points, not all metals are ideal for laser engraving. Polished metals like stainless steel and aluminum are challenging to engrave because their smooth surfaces reflect the laser light.
In these cases, fiber laser engraving is necessary, or surface treatments such as sandblasting, brushing, or applying a specialized coating are performed before engraving to reduce reflectivity and improve the success rate and quality of laser engraving.
Wood
Wood has a moderate density, making it a perfect match for laser engraving. The laser creates a clear contrast pattern on its surface through the carbonization (burning) reaction.
Since different types of wood react differently to the laser, the burn marks and contrast will vary, so selecting wood with moderate hardness, like birch, walnut, and bamboo, will yield better carving results.
Plastic
Most plastic is appropriate for laser engraving due to its sensitive reaction to the heat energy. The laser vaporizes or makes a chemical change on the surface quickly to achieve precise engraving.
Because different plastic components (such as acrylic, ABS, polycarbonate) react completely differently to lasers, parameter testing must be conducted to determine the optimal power and speed.
Glass
Glass is ideal for laser engraving because of its brittle and hard texture. As a poor conductor of heat, the glass is subjected to micro-cracking generated by the thermal energy of the laser, and then forms a matte frosted mark through diffuse reflection.
However, improper control of the laser beam may lead to glass cracking, so cautious parameter adjustments before engraving are necessary.
It is worth mentioning that different materials will have better effects when processed with specific types of laser engravers.
Most importantly, before selecting the material for processing, you should check the Material’s Safety Data Sheet to prevent it from releasing toxic gases due to high heat, which may pose a safety risk.
Applications of laser engraving
If you want to know whether laser engraving can be applied to your project, the following content may help you make a proper judgment.
Industry and Manufacturing
Many original brand manufacturers use laser engraving to print their own brand logo, or mark a unique serial number or QR code for quality control, ensuring product traceability.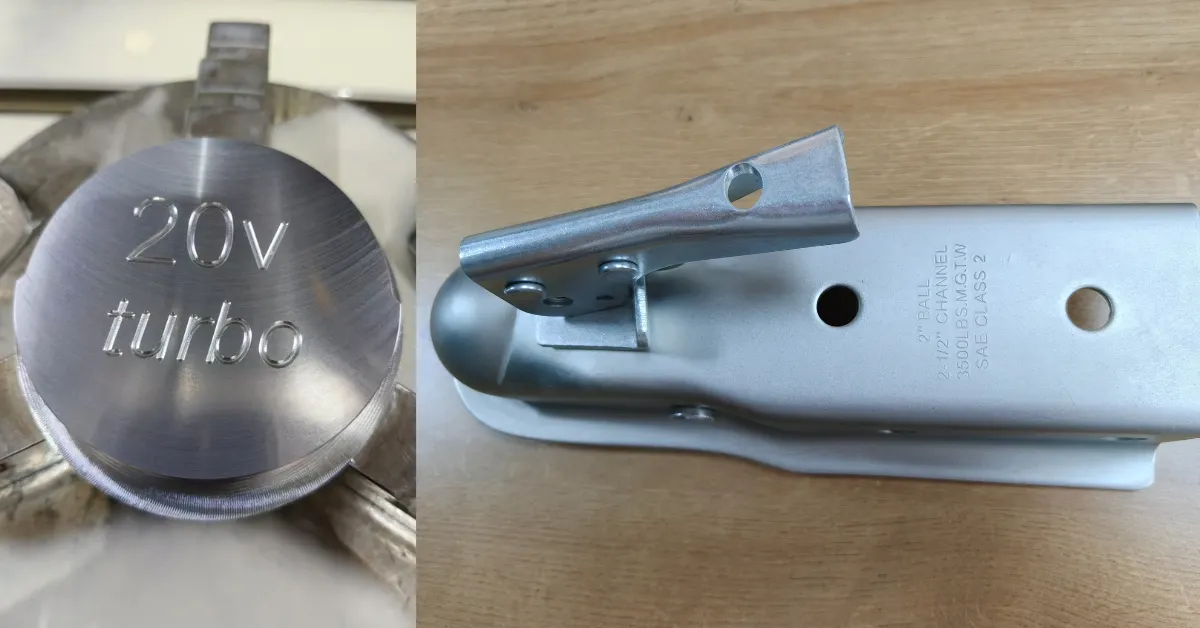
Electronic and Medical Industries
Laser engraving codes can be applied to electronic components such as chips and resistors, as well as to model numbers and batch information on surgical instruments and orthopedic implants.
Packaging and Printing
Laser engraving of production dates and expiration dates that will never fade can be done on drug and food packaging.
Art Creations
Laser engraving can perfectly transform complex digital designs into tangible works, allowing for the creation of detailed landscapes or portraits on wood or acrylic panels.
Laser Engraving Vs Other Marking Methods
Laser engraving vs Laser etching
The depth of effect of laser engraving on materials can reach 25-150 microns, while laser etching typically only changes the microstructure of the material’s surface (with a depth of effect of about 25 microns), therefore, compared to laser etching, laser engraving markings are clearer and more durable.
Laser engraving vs Stamping
Laser engraving is a non-contact, digital process that does not require molds, whereas stamping is a contact-based mechanical process that uses custom molds to create raised or recessed patterns on sheet materials as markings. Therefore, compared to stamping, laser engraving offers greater flexibility and a higher level of automation.
Conclusion
So far, you have a general understanding of the basic information about laser engraving. If you have an idea for a laser engraving project, or are looking for a supplier that can provide one-stop custom metal processing services, HDC Manufacturing will provide you with timely, professional and reliable assistance.