Mastering Precision and Efficiency: Mold Die Casting Explained
In the dynamic landscape of manufacturing, one process stands out as a transformative force – Mold Die Casting. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the advantages, types, materials, applications, drawbacks, cost determinants, and the considerations for custom parts. Delving into the complexities of mold die casting equips businesses with valuable insights, enabling informed decisions and unlocking the full potential of this revolutionary manufacturing technique.
Understand Mold Die Casting
Mold die casting is a metal casting process characterized by the injection of molten metal into a mold cavity at high pressure. This technique yields intricately shaped and designed components, establishing it as a preferred choice across diverse industries. Its pivotal role in the manufacturing realm is underscored by the capability to produce complex, high-quality parts with precise tolerances. The efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and versatility inherent in mold die casting further solidify its standing as an indispensable method in the contemporary industrial landscape.
Advantages of Mold Die Casting
Mold die casting boasts a myriad of advantages, making it a sought-after method in the manufacturing world. Here’s a closer look at the key benefits:
- Superior Finish:Renders components with excellent surface finish, reducing the need for extensive post-processing.
- Precision and Consistency:Ensures dimensional accuracy and tight tolerances consistently.
- Efficiency: Enables high-volume production swiftly, enhancing overall manufacturing efficiency.
- Versatility:Accommodates various metals, offering flexibility for diverse project requirements.
- Cost-Effective:Efficient processes and large-scale production contribute to cost-effectiveness.
- Intricate Designs:Allows for the creation of detailed and complex shapes, expanding application possibilities.
- Reduced Assembly:Precision often eliminates the need for additional assembly processes, reducing labor costs.
- Long Tool Life: Durable molds contribute to prolonged tool life and cost efficiency.
- Low Scrap Rates: Controlled processes minimize material wastage, leading to low scrap rates.
- Consistent Quality: Integrated quality control ensures a high and consistent level of component quality.

Types of Mold Die Casting
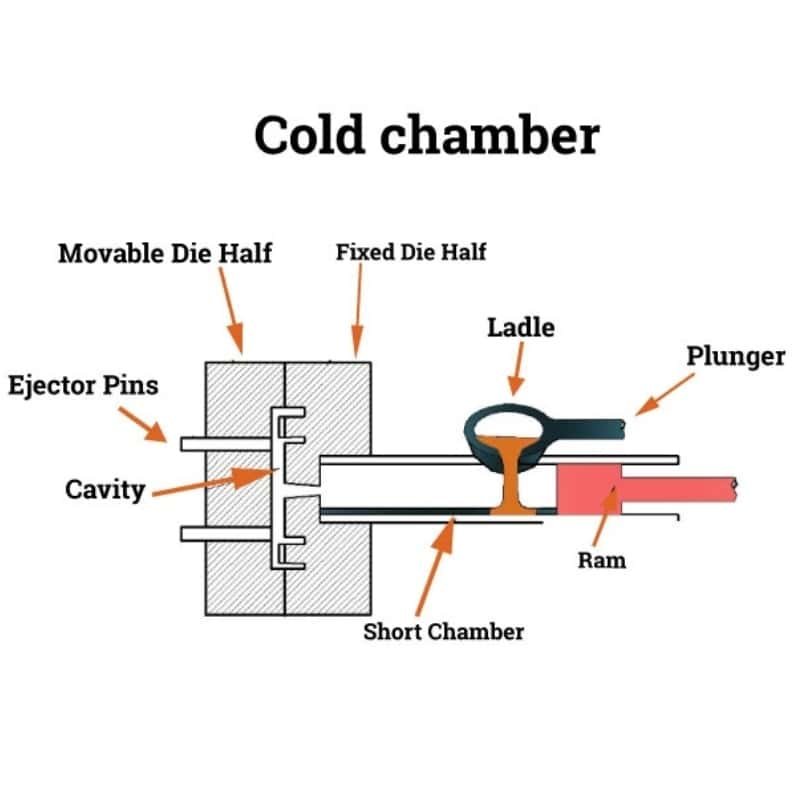
Cold Chamber Die Casting
In the process of Cold Chamber Die Casting, the metal undergoes melting within an external furnace, after which a ladle is employed for the transfer of the molten metal to the cold chamber machine. Suitable for alloys with higher melting points, offering precision and efficiency in the production of various components.
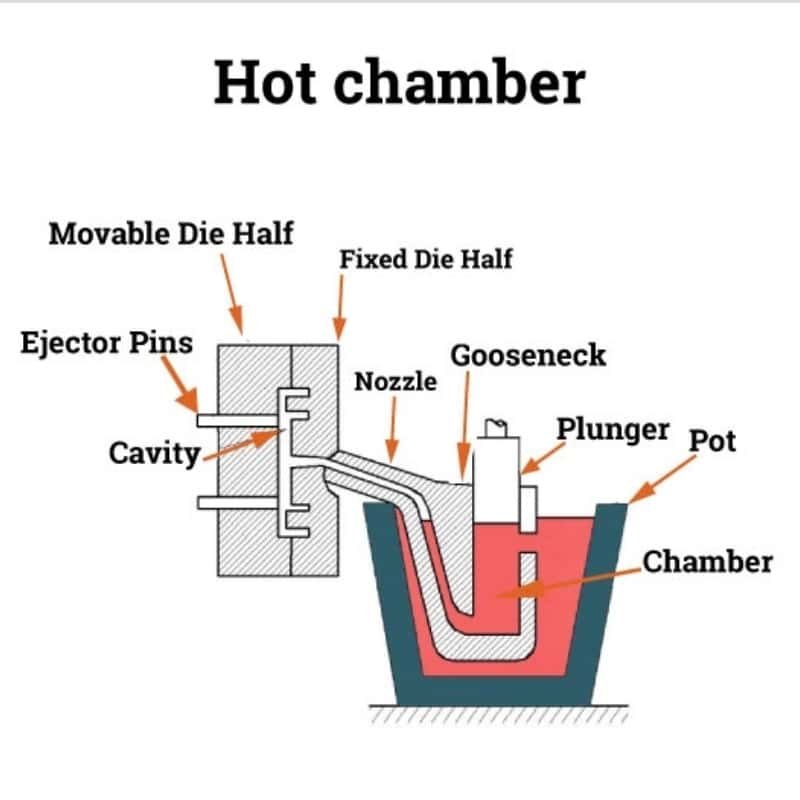
Hot Chamber Die Casting
Hot chamber die casting is characterized by melting metal within the casting machine itself. It is efficient for metals with lower melting points, like zinc. This method is favored for its speed and is suitable for producing small to medium-sized parts with intricate details.
Gravity Die Casting
Gravity die casting utilizes the force of gravity to fill the mold with molten metal. This method is renowned for its cost-effectiveness and suitability for large-scale production.

Materials for Mold Die Casting
Mold die casting employs a range of materials, each chosen based on specific project requirements. The versatility of this casting method allows for the use of various metals and alloys, catering to diverse industry needs. Here are some commonly utilized materials:
- Aluminum:
Lightweight with excellent heat dissipation. Widely used in automotive and aerospace.
- Zinc:
Precision casting with dimensional stability. Ideal for intricate designs and thin sections.
- Magnesium:
Low density, high strength-to-weight ratio. Applied where weight reduction is crucial.
- Copper:
Excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. Used in electrical and electronic
components.
- Brass:
Copper-zinc alloy balancing strength and machinability. Popular in decorative
applications.
- Lead and Tin Alloys:
Limited use due to environmental concerns. Suited for applications requiring low melting
points.
- Steel:
Durable and strong for high-stress applications. Common for die molds.

Applications of Mold Die Casting
Mold die casting finds diverse applications across industries. In the automotive sector, it shapes engine components and structural parts, ensuring both intricacy and efficiency. The electronics industry benefits from its ability to craft precise components, while the aerospace field values its contribution to lightweight yet robust parts. Mold die casting extends its reach to consumer goods, medical devices, lighting, industrial machinery, telecommunications, sporting goods, and renewable energy, providing a cost-effective solution for crafting intricate and high-quality components in each sector. Its versatility makes it a cornerstone in manufacturing, meeting the demands of various industries seeking efficient and precise production methods.

Drawbacks of Mold Die Casting
Despite its advantages, mold die casting has inherent drawbacks to consider. High initial tooling costs make it less feasible for small-scale production, and certain alloys may pose challenges. Porosity concerns, limitations in size and weight, and restricted surface finish options are notable issues. Environmental impact and cycle time are also drawbacks. Repairing damaged molds is challenging, and the energy-intensive nature of the process contributes to production costs. While mold die casting excels in many areas, careful consideration of these limitations is crucial for informed decision-making in manufacturing.
The Factors Influencing the Cost of Mold Die Casting
The cost of mold die casting is influenced by various factors that manufacturers must carefully consider. Understanding these determinants is essential for effective budgeting and decision-making in the manufacturing process. Key factors influencing the cost of mold die casting include:
- Tooling Complexity
- Material Choice
- Production Volume
- Part Complexity
- Post-Processing and Finishing
- Tolerances and Quality Standards
- Lead Time and Urgency
- Quality Assurance and Testing
Understanding these factors allows manufacturers to make informed decisions during the planning and execution of mold die casting projects, ensuring cost-effective and efficient production processes.

Considerations for Custom Mold Die Casting Parts
When opting for custom mold die casting parts, several key considerations are crucial.
- Evaluate the manufacturer’s expertise in achieving precise designs and tight tolerances, ensuring a match with industry requirements.
- Confirm the flexibility for material selection and customization, aligning with unique project needs.
- Assess the manufacturer’s quality control measures, production capacity, and cost-effectiveness.
- Clarify delivery timelines and prioritize clear communication and collaboration throughout the process.
- Consider environmental practices, ensuring alignment with sustainable business standards.
By carefully considering these factors, businesses can make informed decisions when opting for custom mold die casting parts from manufacturers, ensuring a successful and tailored solution that meets their specific requirements.

Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of mold die casting, it’s evident that this manufacturing method is a dynamic force in the industry. Its advantages, coupled with an understanding of its limitations, empower businesses to make informed decisions for their production needs.




