HDC Aluminum Machining Service
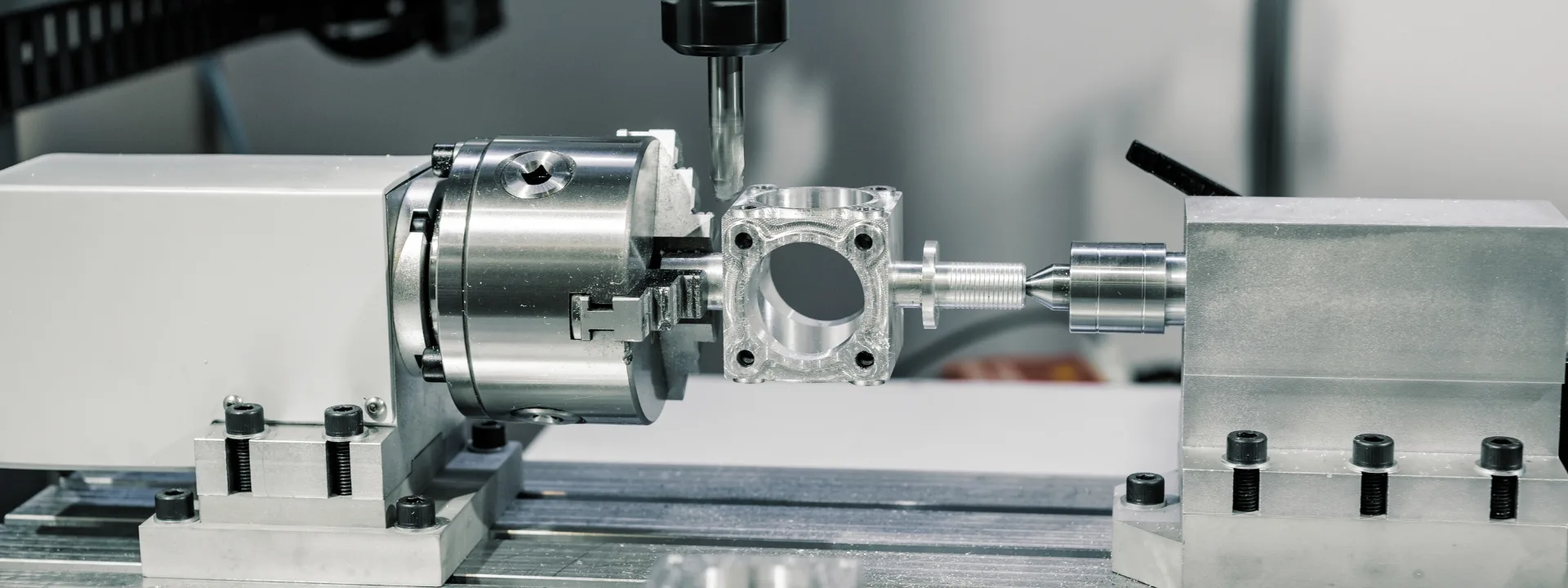

HDC for Aluminum Machining
Service
Why Choose HDC Aluminum
Machining
Exceptional CNC Processing Accuracy
HDC delivers exceptional CNC processing accuracy for intricate aluminum components, showcasing a commitment to precision in their machining services.
Proficiency in Multiple Techniques
HDC demonstrates proficiency in CNC, sheet metal manipulation, and casting, offering a comprehensive range of techniques for aluminum machining.
Vast Customization Options
The skilled professional team at HDC provides vast customization options, ensuring tailored solutions that align precisely with the distinctive demands of each project.
Proven Commitment to Timely Deliveries
With over 13 years of proven commitment to efficient and timely deliveries, HDC establishes itself as a reliable partner for precision aluminum machining services.
Tailor Your Aluminium Machined
Components With HDC

Exquisitely Crafted Aluminum Shafts
HDC specializes in the meticulous creation of unique aluminum shafts, distinguished by exacting dimensions and sophisticated surface finishes. Customization options span the spectrum, encompassing length, diameter, and distinctive features tailored with precision for specific applications.

Bespoke Aluminum Supports
HDC engineers personalized aluminum brackets catering to a diverse array of applications, whether it be for structural fortification or mounting requisites. Clients enjoy the autonomy to specify dimensions, hole configurations, and other particulars meticulously aligned with project specifications.

Tailored Aluminum Encasements
The robustness of internal machinery rests upon the pivotal role of housing components. HDC extends offerings of personalized aluminum housings, providing a plethora of choices in terms of size, shape, and mounting attributes. Various surface treatments and coatings can be strategically applied to enhance durability.
Aluminum Machined Components

Precision-Crafted Aluminum Flanges
Flanges play an indispensable role in seamlessly connecting pipes and components. HDC’s tailor-made aluminum flanges are intricately designed, incorporating specific bore sizes, hole patterns, and thickness parameters. The application of rigorous precision machining guarantees tight tolerances for the seamless integration of components.

Specialized Aluminum Junctions
Junctions assume a crucial role in harmonizing disparate segments within a system. HDC’s uniquely crafted aluminum connectors are meticulously fashioned to meet exacting connection prerequisites. A diverse array of options is available, including thread types, angles, and surface textures.

Tailor-Made Aluminum Slabs
Aluminum slabs find applications across a myriad of industries. HDC facilitates customization concerning dimensions, thickness variations, and surface treatments, all precisely attuned to meet the distinctive needs of a given project. Stringent quality control protocols ensure uniformity and unwavering reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) – Aluminum Machining Service
In the realm of industrial operations, the pivotal function of aluminum machining services transcends various sectors, ensuring meticulousness and dependability in the fabrication of intricate constituents and elements. Within the confines of this discourse, we shall delve into the inquiries frequently posed concerning aluminum machining services, elucidating the significance, advantages, and factors to contemplate when embracing such instrumental services.
What Are the Processing Methods for Aluminum Components?
Aluminum constituents may undergo diverse procedural methodologies to attain specific contours, dimensions, and attributes. The selection of procedural modality hinges upon the envisaged final product and the requisite characteristics. Presented below are several prevalent procedural modalities for aluminum constituents:
- Extrusion: A heated aluminum billet is compelled through a configured die to engender an uninterrupted profile. Employed for fabricating intricate cross-sectional configurations such as rods, bars, tubes, and assorted profiles.
- Casting: Molten aluminum is poured into a mold and permitted to congeal, assuming the configuration of the mold. Employed for fabricating intricate and expansive constituents, such as engine components and structural elements.
- Machining: Material is excised from a monolithic aluminum block utilizing cutting implements to achieve the desired structure. Commonly employed for precision constituents necessitating stringent tolerances, such as aerospace components.
- Forming: Aluminum sheets or plates are contorted, elongated, or imprinted to attain specific configurations. Utilized for fabricating lightweight, high-tensile constituents like automotive body panels.
- Welding: Cohesion of aluminum fragments is realized through liquefaction and amalgamation. Employed across various industries, inclusive of automotive, construction, and aerospace, to forge robust and enduring connections.

These procedural modalities may be employed autonomously or in tandem, contingent on the stipulations of the specific aluminum constituent and its intended application.
Which Types of Aluminum Alloys Are Commonly Used in Metal Machining?
In the domain of metallurgy, aluminum alloys emerge as protagonists, acclaimed for their distinctive amalgamation of diminished density, remarkable strength-to-weight proportion, and immunity to corrosion. Remarkable alloy sequences encompass:
- 6000 Series Alloys: Esteemed for their adaptability, these alloys showcase prowess in machinability and weldability, serving a spectrum of applications.
- 5000 Series Alloys: Applauded for their pliability and resistance to corrosion, they secure their niche in the realm of sheet metal crafting and intricate machining.
- 7000 Series Alloys: Recognized for elevated potency, particularly in aerospace applications, albeit not devoid of machining complexities surmountable with the correct implements.
- 2000 Series Alloys: Renowned for robustness and ease of machination, these alloys attain eminence in aerospace domains.
- 3000 Series Alloys: While lacking peak robustness, they proffer effortless machination and welding capabilities, frequently employed in sheet metal craftsmanship.

Which Elements Are Commonly Added in Aluminum Alloys?
In metallurgy, aluminum amalgams epitomize meticulously crafted compositions where the paramount constituent, aluminum, orchestrates a melange of additives to augment distinct attributes. These alloys function as pliable substances, with elements such as Cuprum (Cu) synergistically enhancing robustness and thwarting corrosion. Silicon (Si) assumes a pivotal role in honing casting fluidity and fortifying wear resistance.
Magnesium (Mg), an omnipresent alloying element, heightens both potency and hardness, while Manganum (Mn) augments both tenacity and workability. The synergistic pairing of Zinc (Zn) and Magnesium fortifies resilience and combats corrosion. Ferrum (Fe), albeit in modest quantities, contributes to structurally reinforcing the alloy.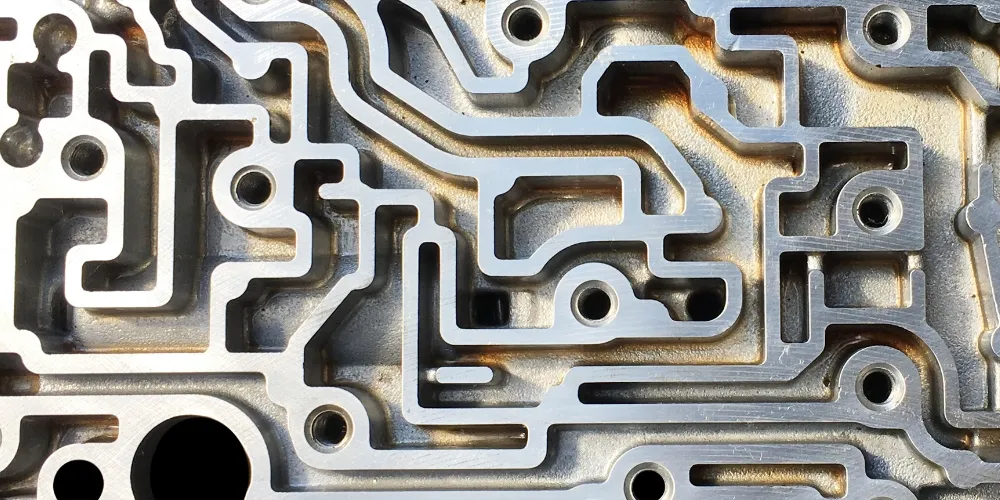
Transitioning to the aerospace domain, Titanium (Ti) emerges as a virtuoso in refining grain structure and amplifying overall potency. Simultaneously, Nickel (Ni) takes the spotlight, intensifying both robustness and resistance to corrosion, particularly in the exacting marine applications.
Lithium (Li) exerts its influence on high-performance alloys, endowing them with a nuanced equilibrium of lightweight characteristics and formidable potency. Wrapping up this elemental ensemble, Chromium (Cr) materializes as an unwavering guardian against corrosion, particularly when interwoven into the tapestry of alloyed companions.
What Are the Advantages of Aluminum Alloy in Metal Processing?
In the realm of metallurgy, aluminum alloys present a myriad of merits within the crucible of metal manipulation. A compendium of these merits encompasses:
- Lightweight: Acknowledged for its diminutive density, proving pivotal in abating mass within the realms of transportation and aerospace spheres.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Despite its ethereal mass, it manifests a formidable strength, indispensable for optimal weight distribution and utilization.
- Corrosion Resistance: Innately engenders a protective oxide stratum, rendering it impervious to corrosive forces and suitable for deployment in diverse environmental milieus.
- Excellent Formability: Profoundly malleable, it acquiesces effortlessly to intricate configurations, facilitating seamless integration into multifaceted metal shaping procedures.
- Good Conductivity: Professing commendable prowess in both electrical and thermal conductivity, it proves advantageous in the production of electronic components, where efficient heat dissipation is paramount.
- Recyclability: Demonstrating a proclivity for facile recycling with diminished energy requisites, it emerges as an environmentally conscientious choice.
- Cost-Effective: Abounding in abundance and facile extraction, it frequently emerges as an economically judicious option, accentuating savings, particularly in the purview of transportation.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Amenable to diverse treatments culminating in aesthetically pleasing surface finishes, it assumes a pivotal role in design applications, contributing to visual appeal.

What Are the Common Aluminum Components?
Aluminum, an adaptable metal, finds widespread utility across diverse industries owing to its feathery nature, immunity to corrosion, and superior thermal conductance. Noteworthy aluminum constituents encompass:
- Automotive Parts: The automotive sector increasingly incorporates aluminum in pivotal components like powerplant blocks, rims, and outer panels, aiming to curtail weight and augment fuel efficiency.
- Aerospace Components: The aerospace domain extensively employs aluminum for crafting aircraft parts, encompassing wings, fuselage segments, and framework components.
- Sporting Goods: Aluminum takes center stage in the production of sporting gear such as bicycle frameworks, baseball cudgels, and tennis raquets, owing to its lightweight and enduring attributes.
These represent merely a handful of instances, and the utilization of aluminum continues to burgeon with the advent of novel alloys and manufacturing methodologies.
What Challenges Arise When Using Aluminum Alloys in Metal Machining?
Machining aluminum alloys poses intricate challenges, demanding precision and attention. The alloy’s complexity requires exact tooling, and chip control during machining processes is crucial. Tool wear, built-up edge formation, and managing thermal conductivity present further hurdles.
Achieving the desired surface finish demands meticulous adjustments, and material adhesion during machining requires measures for efficiency. Maintaining tolerance and stability with aluminum alloys proves challenging. Machinists must deploy specialized techniques, tools, and a profound understanding for optimal outcomes.
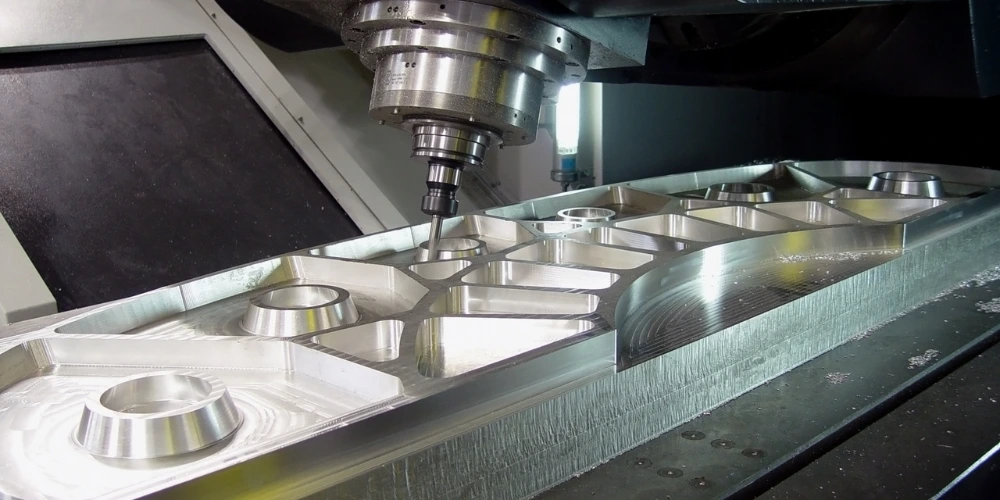
What Factors Should I Consider When Choosing a Machining Service?
Carefully selecting a machining service is vital for manufacturing success. Start by assessing their capabilities, specializing in CNC processes like milling or turning. Prioritize experience, reputation, and quality certifications such as ISO. Ensure they handle your project’s materials and meet specified tolerances, favoring those with modern technology.
Consider production capacity, adherence to timelines, and a transparent pricing structure. Communication is key, so choose a service providing regular project updates. Evaluate flexibility for design changes, location for optimal shipping, and commitment to sustainability and ethics. Weigh these factors to make an informed decision aligning with your project needs and quality standards.
How To Consider Cost Issues When Customizing Aluminum Components?
In the realm of customizing aluminum components, a delicate equilibrium must be struck between tailoring and fiscal prudence. Consider the following pivotal elements:
- Material Selection: Deliberate on aluminum grades tailored to specific properties, mindful of fiscal parameters.
- Design Complexity: Streamline designs to curtail manufacturing duration and expenses.
- Precision Tolerances: Prescribe tolerances judiciously to harmonize precision with cost-effectiveness.
- Production Volume: Augmented volumes often yield diminished per-unit costs, owing to economies of scale.
- Finishing Options: Ponder surface finish expenses and navigate trade-offs amid aesthetics, corrosion resilience, and expenditure.
- Tooling Costs: Comprehend and spread tooling expenses over projected production volumes.
- Assembly Processes: Conceive components with facile assembly in mind to truncate labor expenses.
- Transportation and Logistics: Diminish transportation expenses by procuring materials from proximate sources.
- Supplier Quotes: Garner diverse quotes, considering reputation, dependability, and competencies.
- Quality Control: Allocate resources to robust quality control protocols, averting costly reworks or recalls.
- Lead Times: Scrutinize lead times, maintaining a cost-chronology equilibrium in project timelines.

A cyclic scrutiny of these facets throughout the project lifecycle ensures a nuanced equilibrium amid customization, functionality, and fiscal prudence.
How To Custom Aluminum Parts From Manufactures?
When customizing aluminum parts from manufacturers, start by clearly defining your specifications and requirements. Research reputable manufacturers with a track record of quality and expertise in your industry. Request detailed quotes, providing comprehensive project details for accurate pricing.
Collaborate with the manufacturer to select the appropriate aluminum alloy, considering factors like strength, corrosion resistance, and cost. Seek design assistance if needed to optimize for manufacturability. Discuss tooling requirements and consider creating prototypes to identify and address design issues early.
Ensure the manufacturer has robust quality control processes, including testing and inspection. Clarify lead times for production and negotiate costs based on overall value, including quality and additional services. Maintain open communication throughout the process to address any issues promptly.
Consider shipping options and logistics, determining the most efficient method for transportation. Inquire about post-production support, including warranties and the manufacturer’s willingness to address any issues after delivery. By following these steps and fostering collaboration, you can successfully customize aluminum parts to meet your specific needs.
Conclusion
In the contemporary landscape of industrial craftsmanship, the significance of aluminum machining services emerges as a pivotal cornerstone in advanced production methodologies, proffering a myriad of advantages and bespoke solutions across diverse sectors. Whether navigating the realms of aerospace, automotive engineering, or electronic fabrication, the meticulous precision and tailoring options intrinsic to these services substantially augment the holistic efficacy and caliber of the final commodities.
[toc]
