Are you looking for a casting technique that helps you manufacture complex metal parts with minimal to zero waste? Well! Lost foam casting is one of the modern techniques helping you achieve precise results in fewer steps.
If you want to learn more about these casting methods, then keep reading this blog. As we’ll discuss in detail its working procedure, pros & cons, and also its applications in various industries.
What is lost foam casting?
“Lost foam casting is a type of evaporative metal casting in which a polystyrene foam is used as a mold to shape the molten metal parts, which later on vaporize when the job is done.
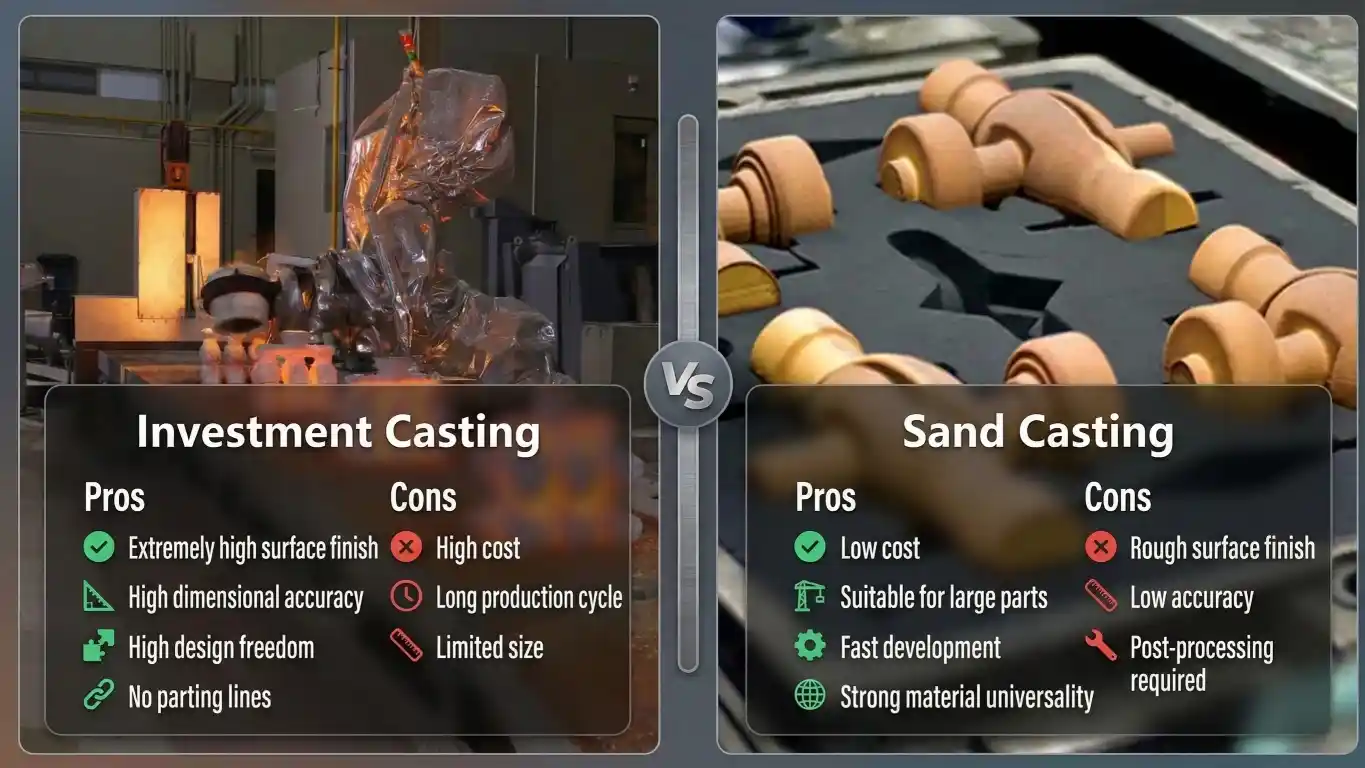
You know, in earlier practices, people relied on the investment casting process to make the metal parts. However, this process uses the wax pattern, which needs to be melted before pouring the metal. Well! This extra step requires both time and energy, which increases the overall production costs.

Thus, to overcome the limitations of the traditional casting method in 1958, H.F. Shroyer ( American inventor and engineer) presented that you can use the foam pattern instead of wax.
This is because the boiling point of foam materials ( like polystrene) is usually very low, around 100–200°C. As a result, when you pour the hot molten metal ( above 600–1500°C) on the foam filled in the mold, it easily evaporates.
So, in 1960 and 1970, manufacturing began to implement this technique, especially in the automotive industry. And after 1980s, it became extremely popular and considered a good alternative to investment or sand casting methods owing to its low production costs.
Types of Materials and Metals Used
| Melting Point (°C) | Density (g/cm³) | Key Properties | Common Applications | |
| Aluminum & Alloys | 660 – 750 | 2.7 | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, high thermal conductivity | Engine parts, gear housings, brackets |
| Cast Iron | 1,150 – 1,200 | 7.0 – 7.8 | Excellent wear resistance, good fluidity, and strong compressive strength | Engine blocks, pipes & machinery bases |
| Copper & Brass | 1,083 (Cu), 900 – 940 (Brass) | 8.4 – 8.9 | Excellent electrical & thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance | Electrical components, plumbing fittings, decorative parts |
| Magnesium & Alloys | 650 – 670 | 1.7 – 1.9 | Extremely lightweight, good strength-to-weight ratio, easy to machine | Aerospace parts, auto wheels, electronics housings |
| Nickel Alloys | 1,350 – 1,450 | 8.5 – 8.9 | Exceptional corrosion and heat resistance, maintains strength at high temperatures | Turbine blades, valves, aerospace components |
| Stainless Steel | 1,370 – 1,530 | 7.7 – 8.0 | Corrosion-resistant, durable, strong, and aesthetically smooth finish | Pumps, medical tools, food processing & marine equipment |
How does the lost foam casting process work?
Hopefully, now you have a better idea about what the LFC process is. However, for a deep understanding, here I’m going to discuss its step-by-step process that how using a foam pattern you finally reach your desired metal shape.
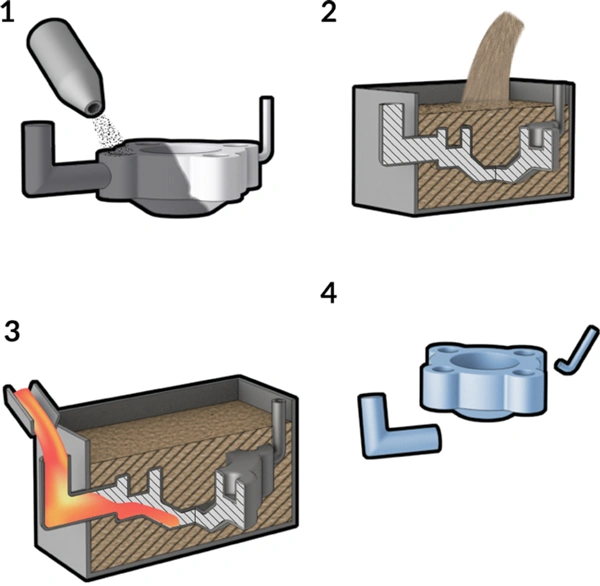
Well! The LFC process is accomplished mainly in 5 steps, let’s have a look at each one by one!
Step 1: Designing the Pattern
First of all, you’ll prepare your foam pattern ( usually made of expanded polystyrene ) to help you make your desired shape. Alright! You can make this pattern in different ways depending on the type of product. For instance, for small-scale production, factories mostly hand-cut or machine the pattern from solid-black foam.
On the other hand, in large-scale production, factories mostly inject the polystyrene beads into the pre-heated aluminum mold, usually at low pressure. Later on, the application of steam helped the beads expand and fuse together.
The amazing thing is that the final foam pattern is about 97.5% air and 2.5% polystyrene, thus making it lightweight and easy to handle.

Step 2: Applying Insulation Painting
Once the foam pattern is ready, you’ll coat it with the insulation or refractory paint. That’s very crucial because the foam pattern is very fragile; thus, this coating would add a thin shell, helping to control how the foam would evaporize when hot molten metal is poured.
| Types of coatings | Main Ingredients | Suitable metals | Benefits |
| Zircon-based coating | Zircon (ZrSiO₄) powder + water/alcohol binder | Steel, Cast Iron | Excellent heat resistance and smooth surface finish. |
| Alumina-based coating | Aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) | Ferrous Alloys | Provides superior thermal stability & prevents metal penetration into sand |
| Silica-based coating | Silica (SiO₂) | Aluminum, Non-ferrous Alloys | Economical option; offers good insulation |
| Magnesium silicate or graphite-based coating | Talc, graphite, or other minerals | Aluminum, Magnesium, Light Alloys | Improves gas permeability |
Step 3: Placing the Pattern into the Sand Flask
After this, the coated pattern is placed inside the sand flask ( filled with dried sand). This would also support the foam, so that it may maintain its shape.

Step 4: Pouring the Molten Metal
Now, you’ll pour the hot molten metal directly on the foam pattern. Here, the heat of the metal vaporizes the foam and eventually the metal takes its shape.
Step 5: Collecting the Castings
Finally, you’ll allow the mold to cool and then collect the final metal casting product. It is then cleaned, trimmed, and inspected for accuracy, leaving a smooth, detailed metal part with minimal machining required.
Pros and cons of the lost foam casting process
Let’s move ahead and have a look at why the lost foam casting method is preferred over the others. Also, we’ll tell you some of its drawbacks for a wise decision.
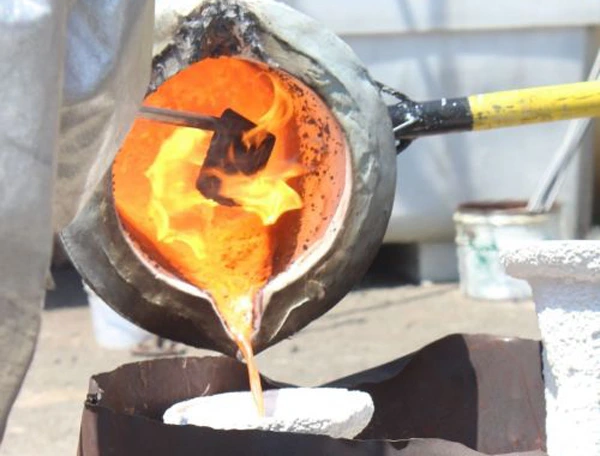

Pros
- Dimensional Accuracy
- Reduced Steps in Machining
- Integration of Assemblies
- Low environmental impact
- Widest Variety of Densities to match the size or complexity of metal type.
Cons
- High Pattern Cost
- Slow Production Rate
- Pattern Fragility
- Limited Metal Types
Lost-Foam Casting vs. Sand Casting: What’s the difference
| Lost-Foam Casting | Sand Casting | |
| Pattern Material |
|
|
| Mold Type |
|
|
| Pattern Reusability |
|
|
| Surface Finish |
|
|
| Dimensional Accuracy |
|
|
| Production Cost |
|
|
| Complex Shapes |
|
|
| Environmental Impact |
|
|
What are the Applications of the lost foam casting process?
Well, the LFC process explores its charm in a number of industries owing to its ability to produce complex shapes with quite accuracy.
- Automotive Industry: You can deploy this process to produce the Engine blocks, cylinder heads, gear housings, and suspension components.
- Aerospace Industry: Furthermore, the LFC process finds its applications in Lightweight structural components, brackets, and housings. As mentioned earlier, this process is more compatible with the aluminum alloys which are very lightweight and corrosion resstent used in the aerospace machinery parts.

- Energy Sector: Moreover, you can use this process to produce intricate shapes like Turbine casings, impellers, and pump components.
- Consumer Goods & Electronics: Also, the LFC process is best for making housings, frames, and decorative components. This is because such goods are usually made up of aluminum or magnesium alloys, which are the most suitable metals for the LFC process, thus producing lightweight yet durable goods that you can easily carry from one place to another.
FAQs
1. What is the LFC process?
LFC is actually a metal casting process that uses the foam pattern ( expandable polystyrene) to get the desired metal parts’ shapes.
2. What is the difference between lost foam casting and investment casting
The lost foam casting process basically uses the foam pattern, while the investment casting uses a wax pattern. Moreover, the investment casting has more steps, like removing of wax, compared to LFC, where the foam itself gets vaporized by pouring hot molten metal.
3. Are lost foam casting products heat-resistant?
Well, it depends on the kind of material you are used to using to create your molds. So, yes, if you use the heat-resistant materials like aluminum or steel alloys, then your final product will definitely retain its properties.
Final Verdict
In short, the lost foam coating process is a modern casting technique that gives you precise results within a short time. Also, if you are an eco-conscious person, which everyone has to be, then this LFC process is the best compared to other techniques. As it uses unbounded sand or few binders, so there is no fear of chemical emissions.
So, if you want highly reliable custom metal casting solutions for your industry, then we at HDC Manufacturing are here to help you. We have almost 15+ years of experience in providing casting services and are also ISO 9001 certified. So, get in touch with us today!