Permanent Mold Casting: Understanding Process, Types, and Benefits
- By: HDCMFG
Permanent mold casting plays a very crucial role in modern manufacturing units varying from the aerospace to simple decorative one. Whether you are a manufacturer or researcher actually looking to understand or apply this casting process, then trust me, this guide is just for you.
Here, we’ll discuss in detail about what this PMC metal casting process is and also share with you its detailed step-by-step process. Also, we’ll provide insight into its types and tell you what kind of benefits you’ll usually get by using this process. So, keep reading this blog!

What is the permanent mold casting process?
“Permanent mold casting (PMC) is actually a type of metal casting process in which you’ll use a reusable mold ( often made of steel/cast iron) to produce high-quality metal components.”
Well! Do remember that in the PMC process, the hot molten metal that you pour directly on the mold must have a low melting point. The reason is that you have to reuse the mold, compared to sand or investment casting, in which it gets broken. So, casting metals having high melting points, like iron or steel ( above 1,500°C,) would cause severe thermal stress, erosion, or even cracking in the mold.
That’s why below, I’m going to give you an overview of which types of casting metals are suitable for this process!
Best Casting metals for permanent mold casting
| Melting points | Key properties | Applications | |
| Zinc Alloys | ~420°C |
| Decorative hardware, small machine parts, toy components |
| Aluminum Alloys | ~660°C |
| Automotive parts, housings, engine components, machinery parts |
| Magnesium Alloys | ~650°C |
| Aerospace parts, electronics housings, automotive wheels |
| Copper Alloys (Brass, Bronze, Muntz Metal) | 950–1,000°C |
| Decorative fittings, bearings, bushings, marine hardware |
| Lead and Tin Alloys (less common) | 230–330°C |
| Art objects, figurines, prototype castings |
Types of mold materials
On the other hand, if talking about mold materials, then you can use cast iron, steel, graphite, and copper-based alloys. This is because all of these offer high strength, good heat resistance, and excellent durability. Thus, your mold could withstand the heating or cooling cycles no matter how many times you reuse it.
How does it work? A step-by-step guide
Well! Just like all other casting processes, in permanent mold casting, you also pour the entire hot molten metal into a reusable metal mold. Thus, it gets solidified under controlled cooling, and you get your desired shape. However, all this process actually involves a no. of steps which I’m going to discuss below!
1. Mold Preparation
Do remember! The permanent metal mold is usually formed in two halves called the cope (top) and the drag (bottom). So, you’ll machine these parts just like two puzzle pieces that fit perfectly to match the desired shape. Then do the three further steps:
Cleaning: You’ll remove all the contaminants; otherwise, any dust, moisture, or oil may chemically react with the molten metal. This leads to surface defects, gas formation, and poor adhesion of the mold coating.
Preheat: Then, preheat the mold to a moderate temperature (typically 150–400°C, depending on the alloy). Keep in mind that if you don’t do this, then hot molten metal ( often above 600–700°C) in contact with cold mold can cause thermal stresses in the mold.
Coating: Also, you have to add a thin graphite-based coating to your mold. Well! This coating actually reduces metal adhesion, controls cooling rate, and also prevents chemical reactions between the molten metal and mold surface.
2. Mold Assembly
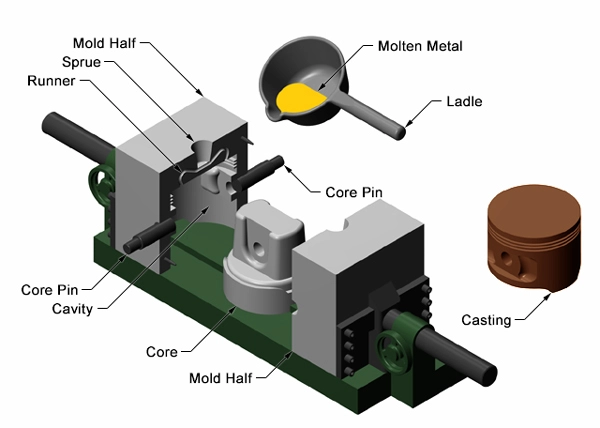
After coating, you have to carefully align these halves using guide pins or locks and then clamp them together to prevent molten metal from leaking out. Also, if the metal component that you’re designing has holes, then you need to place cores ( made of metal or sand) inside the mold cavity.
Moreover, to ensure bubble-free casting, it’s important to create the tiny vent holes inside the mold, okay!
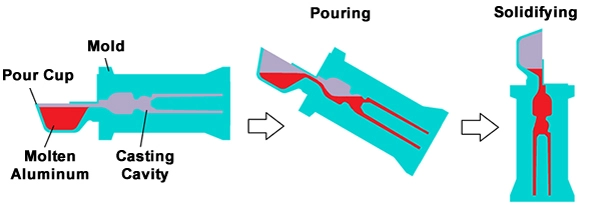
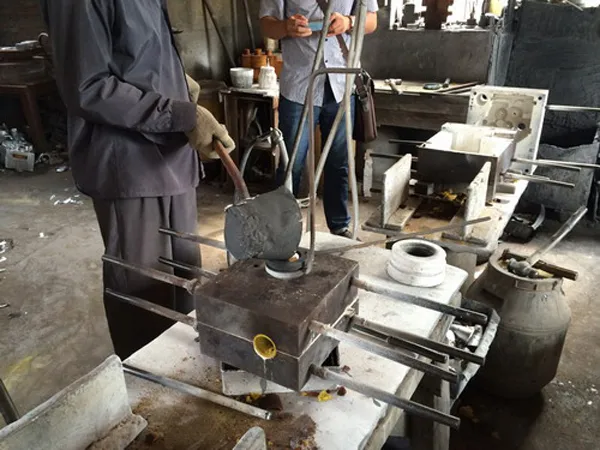
Metal Melting and Pouring
Now, you’ll just heat your chosen metal in the furnace and instantly pour the hot one into the prepared mold via gravity or applying low pressure. Here, keep in mind that before pouring it’s best to remove any oxides to prevent any chemical reactivity.
Solidification and Cooling
Here comes the most interesting part, as mold metal, because of its high thermal conductivity, causes natural controlled cooling. You know, according to the 2nd law of thermodynamics, when two bodies at different temperatures come in contact with each other, heat flows from hotter body to the colder one.
Well! That same principle follows here, as heat from hot molten metal flows towards the relatively cool mold walls.
Mold Opening and Casting Removal
Thus, once all the metal gets solidified, then the next step would be to eject it from the mold. So, you’ll open your mold and remove your casting via metal pins. That’s all! Now just clean your mold and it’s ready for the next use.
Post-processing
Now you have your casting component, right so enhance its look, you’ll just trim off the excess material. And if needed, then you can do further CNC machining, polishing, or inspection processes.
Types of permanent mold casting
Now, let’s dive deeper and have a look at some common types of permanent mold casting that manufacturers mostly deploy!
Slush Casting
Slush permanent mold casting is actually used to form the thin-walled or hollow components. Here, the whole process remains the same; as mentioned, the difference comes in the solidification step.
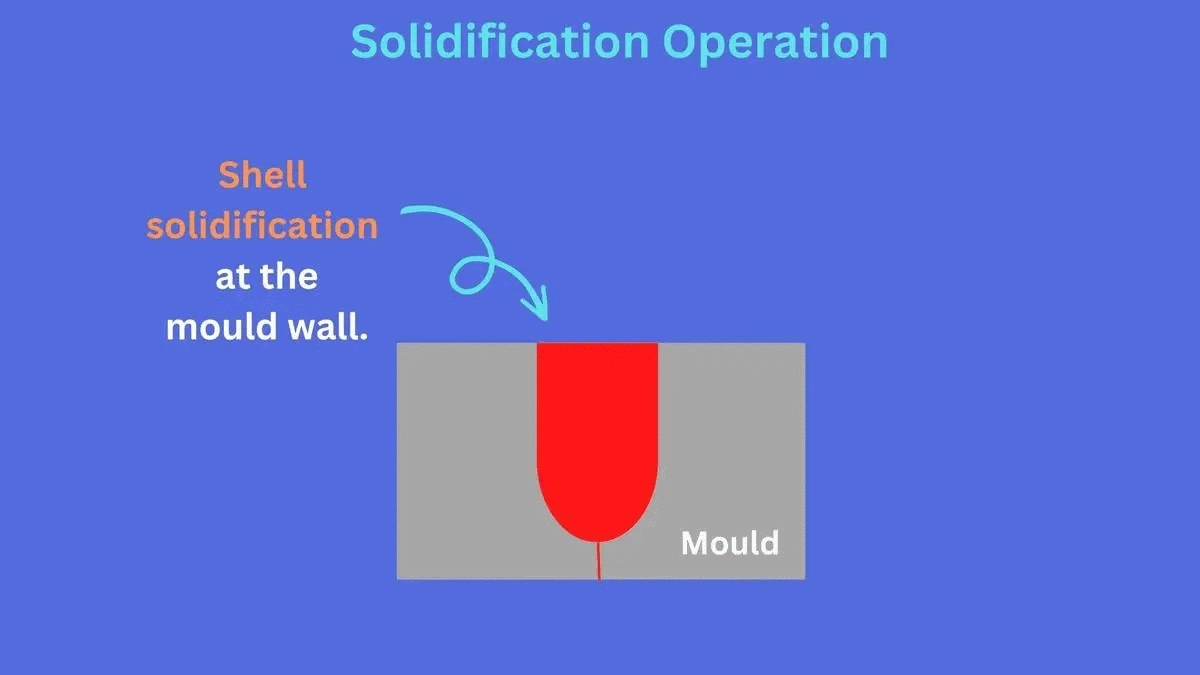
For instance, instead of completely cooling, once the outer layer next to the mold wall solidifies, you’ll stop here and slush out the still-solid liquid metal at the center. Thus in the end you’ll have the thin sold shell, right?
? Ideal Use: Decorative items, toys, & low-stress components.
? Key Benefit: Saves material & produces smooth, detailed surfaces.
Low-Pressure Permanent Mold Casting
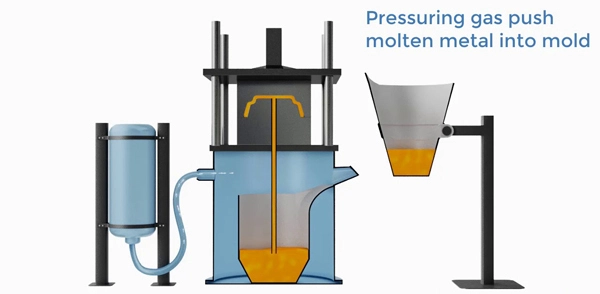
In this type of permanent mold casting, molten metal is forced to put into the reusable mold under low pressure ( typically 0.3–1 bar). This ensures better metal flow and improves the quality and yield. You know the interesting point here is that after solidification step, you’ll release the pressure, thus because of influence of gravity, the unused molten metal would automatically flows back to the furnace.
? Ideal Use: Automotive wheels, engine parts, & aerospace components.
Vacuum Permanent Mold Casting
However, here the permanent mold is basically sealed or connected to a vacuum system. This vacuum actually removes the air and gases from the mold cavity or surrounding atmosphere, thus ensuring the smooth flow of molten metal inside the cavity.
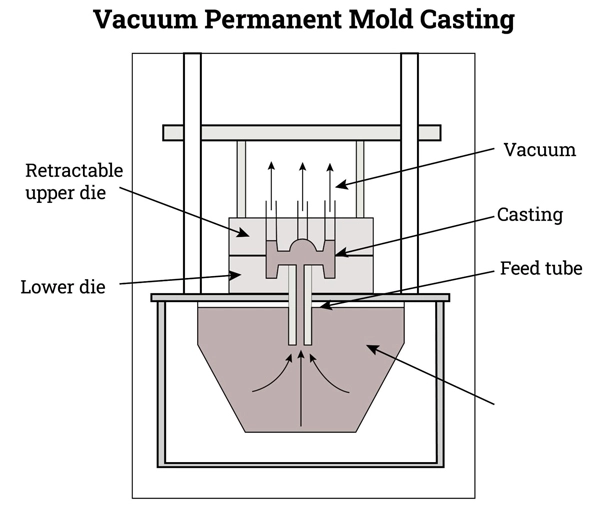
? Ideal Use: High-performance/precision parts like turbine blades & engine housings.
Advantages of Permanent Mold Casting
You know, Permanent mold casting offers a wide variety of technical or even economical benefits for various industries. Let’s have a look at them!
+ Superior Dimensional Accuracy: First of all, because of mold strong materials like steel or cast iron, their walls prevent any kind of distortion during solidification. As a result, you’ll get a precisely dimensioned product without requiring too much post-machining.
+ Enhanced Surface Finish: While preparing the mold, you add a coating layer, thus gives it a smooth finish. As a result, the casting inside the mold cavity also has smooth surface finishing of around 200-400 microinches/5-10 micrometers.

+ Faster Production Cycles: Since you can reuse the permanent mold a hundred times. As a result, there is no need for reassembly or mold preparation, thus automatically increasing the production rate.
+ Cost Efficiency in High-Volume Production: Last but not least, this process is highly economical for high-volume production. I agree that the initial mold cost may be high, but it would be compensated by the long-term reuse, minimal waste and faster cycles.
Limitations & Challenges of permanent mold casting
Although the process is highly advantageous but it has some limitations too, which you must be aware of, so you can better decide whether it’s appropriate for you or not.
– Material Limitations: First of all, by using this technique, you’ll cast only the metals having low melting points, otherwise, they may disturb the reusability of the mold.
– Higher Initial Tooling Costs: Although its reusable mold gives you a lot of benefits, as mentioned but its formation also demands both time and even high expenses at the start.
– Limited Complexity in Designs: Furthermore, you already know that its mold is very rigid, right? Thus, because of this it would be very difficult to get the complex designs.
– Not Ideal for Low-Volume Production: Moreover, I must say that, because of high initial investment, as mentioned, it’s not a practical choice for producing small-scale units.
A brief comparison with Other Casting Methods
Let’s compare the permanent mold casting with other methods, so you’ll have a clear picture of all in your mind and choose what suits your needs.
| PMC | Die casting | Sand casting | Investment casting | |
| Mold Type | Reusable metal mold | Reusable metal mold | Single-use sand mold | Single-use ceramic mold |
| Metal Flow Control | Gravity, low pressure, or vacuum | High-pressure injection | Gravity-fed | Gravity-fed |
| Dimensional Accuracy | High | Very high | Low to moderate | High |
| Surface Finish | Smooth | Excellent | Rough | Very smooth |
| Production Rate | Medium to high | Very high | Low | Low to medium |
| Tooling Cost | High | Very high | Low | Moderate |
| Suitable for | Aluminum, magnesium, copper alloys | Non-ferrous metals (e.g., aluminum, zinc) | All metals, including iron | Complex, precise shapes |
| Typical Applications | Automotive parts, fittings, housings | Engine parts, housings, and small precision components | Large castings, prototypes | Aerospace, jewelry, and medical components |
FAQs
1. What materials are used in the permanent mold casting?
In permanent mold casting, the common casting materials are those having low melting points, like aluminum (660°C), magnesium (650°C), and copper alloys (1085°C). On the other hand, reusable molds are usually made up of cast iron or steel for high strength and thermal conductivity.
2. What is the difference between die cutting and permanent mold casting?
In the die-cutting casting process, you’ll pour the molten metal under the influence of high pressure (up to 1500 bar). On the other hand, PMC mostly uses gravity, vacuum, or low pressure to fill the molds.
Conclusive Notes
Now hopefully you are better familiar of what the permanent mold casting process is. Well! In short, you can say that it’s not any new technique but here the manufacturers only use the reusable metal mold that not only increases the production rate but also allows uniform cooling and gives the casting various mechanical properties. Thus making it the best and cost-effective process for the large-scale production.
So, if you want custom CNC machining and metal fabrication service, then look no further than HDC MFG. You just need to give your design, and our experts will transform your ideas into reality. So, what are you waiting for? Request an instant quote today!
Discover more with our blog posts.
Recent Posts
Discover more about our products
HDC Products
Instant Quote!