Duplex Steel Properties, Types, and Applications
- By: HDCMFG
Duplex Stainless Steel combines the best parts of two different kinds of stainless steel. It mixes two structures, called austenite and ferrite, almost equally. Because of its strength and toughness, many industries use it for big projects in tough places. Using this strong steel saves money because builders can use thinner pieces of metal and still get amazing performance.
What is Meant by Duplex Steel?
Duplex steel is a special stainless steel with a two part structure. It is about half austenite and half ferrite. That is why they call it duplex, which means two parts.
The ferrite part makes the steel very strong and helps it resist a type of cracking caused by stress. It is important in big structures. The austenite part makes the steel tough and helps it resist rust in many different places. For example, when it is touching saltwater.
This powerful combination makes Duplex steel much better than regular stainless steels. Duplex steel is twice as strong as common stainless steels like 304. This extra strength means you can use thinner pieces of metal. It will save money and weight both.

Is 304 a Duplex Stainless Steel?
No, 304 is not a duplex stainless steel. Grade 304 is an austenitic stainless steel. It has a single phase structure that is primarily austenite. Unlike duplex steel’s balanced two phase structure, 304 contains only the austenitic phase.
Properties of Duplex Stainless Steel
Chemical Makeup
Duplex steel has special ingredients such as Chromium, from 18% to 29%, is the main ingredient. It forms a protective layer to stop rust.
Molybdenum is up to 5% which makes it better to fight small holes pitting that can form when the metal is under attack.
Nitrogen is added to make the austenite part even stronger and better at fighting rust.
Nickel is used in low amounts. It helps balance the two-part structure and makes Duplex steel more affordable than some other strong stainless steels.
Strength and Toughness
Duplex steel is incredibly strong. Its yield strength the point before it permanently bends is about 400 to 700 MPa. This massive strength is double the strength of standard stainless steel.
Its high strength means engineers can use less material for a project, which saves both cost and weight.
Does Duplex Steel Rust?
While duplex steel is highly resistant to corrosion, it is not completely rust proof. The chromium content forms a protective passive layer. It prevents rust in most environments. However, if the protective layer is damaged, some corrosion can occur. The addition of molybdenum and nitrogen significantly improves its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion.
Machinability of The Steel
Because it’s so strong, cutting and shaping Duplex steel is a bit harder than other stainless steels. It needs more force to cut because the metal is so tough. Workers need to use very sharp tools and they have to cut a little slower to get the job done right. They must use lots of coolant. The purpose is to keep the metal from getting too hot during the cutting process.
Types and Grades of Duplex Stainless Steel
The type of Duplex steel is chosen based on how good it is at fighting corrosion, especially rust holes. Scientists use a number called PREN (Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number) to figure this out. A higher PREN means better protection.

What Are the 4 Types of Duplex Steel?
The basic types of duplex stainless steel are:
Lean Duplex
This type has a lower PREN and uses less expensive ingredients like nickel and molybdenum. It is great because it is still twice as strong as standard stainless steel 304, but it is best used in places that are only mildly corrosive, like everyday storage tanks.
Standard Duplex
This is the most popular type, with Grade 2205 being the favorite. It gives the best mix of cost, strength, and rust fighting ability. It works very well in environments that have some saltwater or chloride chemicals.
Super Duplex
This steel has more chromium and molybdenum to give it a higher PREN, making it very good at fighting rust holes and stress cracking. It is used for the most difficult jobs in very aggressive places.
Hyper Duplex
Hyper duplex gives a very good resistance against corrosion. It is the most expensive type of duplex steel. Because it has the highest amount of special alloying ingredients. Subsequently, it is used in geothermal power plants.
Is Duplex Better Than Stainless Steel?
For oil and gas projects, and chemical processing, duplex is better than 304 and 316 stainless steel. However, for formable and lower cost applications, austenitic stainless steels is more suitable.
What is the Difference Between Duplex and 316 Steel?

The primary distinction of duplex and 316 steel is based on three aspects; structure, strength and cost:
Structure
Duplex is of mixed ferrite-austenite structure whereas 316 is completely austenitic.
Strength
The yield strength of duplex is 400-700 Mpa and is about twice as strong as that of 316 which is 200-300 Mpa.
Corrosion Resistance
Duplex is more resistant to stress corrosion cracking and pitting in chloride environments and is therefore superior when used in the salt water.
Nickel Content
In 316, the nickel 10-14% is higher than duplex 4-7% and this makes 316 more costly.
Low Temperature Performance
316 is tougher at lower cryogenic temperatures, and duplex may become brittle below -50 C.
Cost
Duplex is mostly cheaper because of less nickel content and has a superior performance in most applications.
Applications of Duplex Stainless Steel
What is Duplex Used For?
Duplex steel’s combination of strength and toughness makes it ideal for demanding industries:
- Oil and Gas Industry: Used in offshore platforms, subsea pipelines, and pressure vessels where high strength reduces component weight for easier installation at sea.
- Chemical Processing: Found in reactors and storage tanks handling corrosive acids, where long service life reduces maintenance costs.
- Marine Applications: Essential for desalination plants, ships, and coastal structures exposed to corrosive saltwater.
- Power Generation: Used in flue gas desulfurization systems and cooling circuits, with super duplex grades serving geothermal facilities.
- Mining: Applied in leaching tanks and agitators that handle acidic slurries and abrasive materials.
Manufacturing and Processing of Duplex Stainless Steel
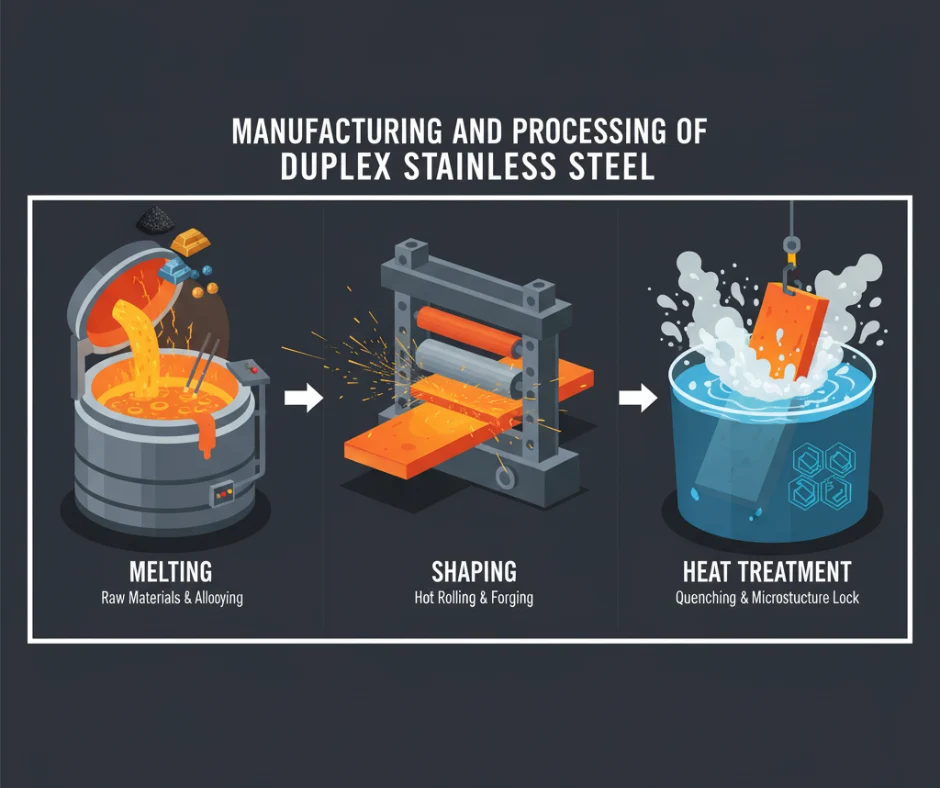
Making Duplex steel requires careful steps to get the perfect two-part structure.
Melting
Workers start by melting raw materials like iron, chromium, and nickel in huge furnaces. They must carefully adjust the amounts of each ingredient to get the steel’s chemical makeup just right.
Shaping
Next, they heat the steel to a high temperature, around 1050°C to 1250°C. Then, they roll or forge the steel into plates, bars, or tubes. The high heat keeps the steel soft enough to shape without cracking.
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment annealing is an important step for Duplex steel. In this process, workers heat the steel very high again and use water to cool it quickly. This instant cooling will lock the two-part structure, the 50/50 mix of austenite and ferrite, into place. This process will give steel its significant strength.
Is Duplex More Expensive Than Stainless Steel?
Duplex steel pricing varies compared to other stainless steel grades. It is generally less expensive than high nickel austenitic grades like 316L due to its lower nickel content. However, duplex costs more than basic 304 stainless steel.
Duplex Steel vs Other Stainless Steel Grades
When you compare Duplex to other stainless steels, Duplex will take a lead. It is twice as strong as the basic stainless steel, Grade 304. Subsequently, it will prevent cracking caused by chloride stress much better. While 304 is cheaper and easier to shape for simple projects, Duplex is a long-term solution.
Compared to Grade 316, which is better at fighting pitting than 304, Duplex is much stronger. Also, Duplex incorporates less expensive nickel than 316. This feature gives duplex steel a better value. Grade 316 is a better choice for very cold places. But Duplex has better strength and overall corrosion resistance in saltwater environments.
Conclusion
Duplex steel has significant strength and corrosion resistance for many important and decisive applications. You select specific grades based on PREN requirements and operating conditions. Manufacturers supply diverse product forms to meet global engineering demands efficiently.
FAQ
Does Duplex Stainless Steel Rust?
Duplex steel resists rusting much better than most steel because of its protective layer of chromium. You must choose the right type, or rust holes can still appear in extremely salty or harsh places.
Is Duplex Stainless Steel Expensive?
It costs more than basic steel but often less than high-nickel stainless steels like 316. Because it’s so strong, you can use less of it, which saves money in the long run.
What is the Carbon Content of Duplex Steel?
It has a very low amount of carbon usually less than 0.03% to make it easier to weld without damaging its rust resistance. This low carbon helps keep the steel tough and corrosion-resistant after welding.
What is the Most Common Duplex Steel Grade?
Grade 2205 is the most common and popular Duplex steel worldwide. It provides a great mix of strength, good rust resistance, and cost for many different industries.
Discover more with our blog posts.
Recent Posts
Discover more about our products
HDC Products
Instant Quote!







