When you hesitate to choose between zinc-plated and stainless steel for your design or product, you may want to know the differences in their corrosion resistance, cost, longevity, appearance, and more. By reading this article, which is written based on HDC Manufacturing’s decades of experience in custom metal processing and surface finishing, you may find the answer.
What is zinc plating?
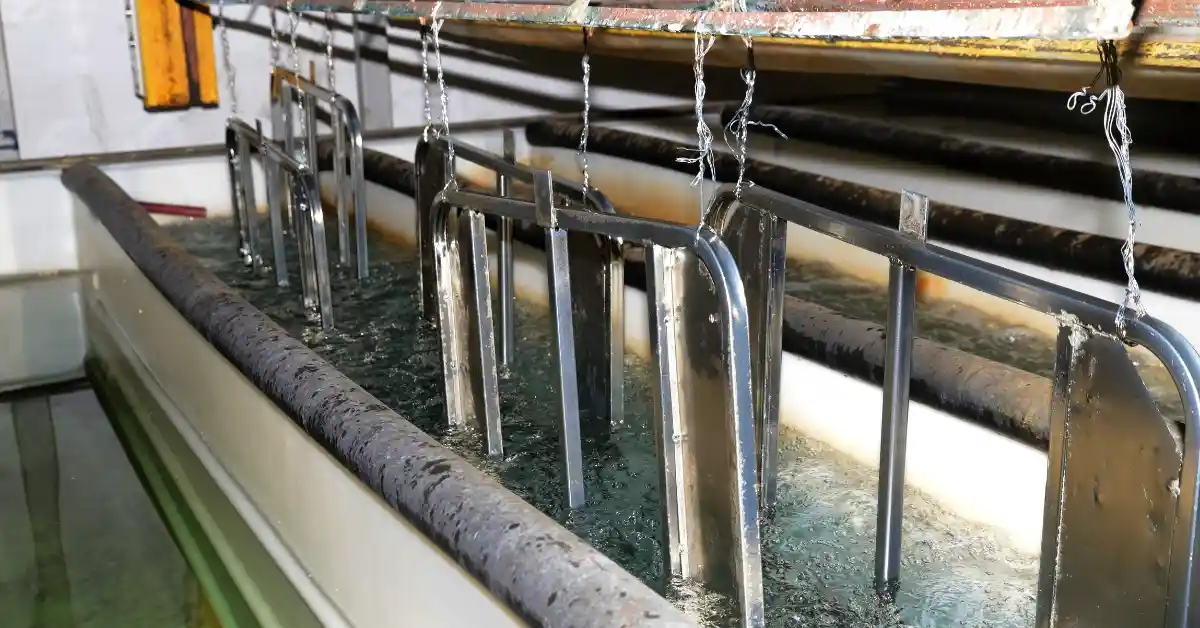

Zinc plating is a type of electroplating process, also called electrogalvanizing. That is, after zinc ions are electrolyzed in the electrolyte, a zinc layer with a thickness of about 5-25 μm is deposited on the metal parts. This zinc coating is the essential reason why the zinc-plated parts can resist corrosion.
This zinc layer acts as a sacrificial coating, protecting the underlying metal from moisture and air. It means that when the zinc-plated metal part is exposed to the humid environment, the zinc layer will be corroded first in place of the underlying steel. The steel substrate will not rust unless the zinc layer wears away.
After zinc plating, metal parts need to be passivated. This post-processing step creates a thin, colored chromate conversion coating on the zinc layer to prevent the zinc coating from white rust. Typically, carbon steel is the most used base material for zinc plating.
What is stainless steel?
Stainless steel is a general-purpose alloy steel. It is based on iron, contains over 10.5% chromium, and different stainless steel grades may include other elements like nickel, molybdenum, or nitrogen.

And chromium is the most core factor that ensures the stainless steel has corrosion resistance. Once chromium comes into contact with oxygen, it forms a film of chromium oxide (Cr₂O₃ ) several nanometers thick, which is also called the passivation film, that can isolate the corrosion of media such as air and water.
In the meantime, this film is extremely stable, even if scratched by external force, it can still regenerate the oxide film to maintain its corrosion resistance capability.
The most common stainless steels are 304SS and 316SS. They both contain nickel, which also enhances their corrosion resistance. And the primary reason 316SS is more corrosion-resistant than 304SS is that it contains 2%-3% molybdenum, which is negligible in 304SS.
Properties of zinc plating vs stainless steel
Corrosion resistance
In many circumstances, stainless steel is more corrosion-resistant than zinc plating, especially in moist, saltwater, or marine environments. When encountering a strong alkaline or acidic situation, zinc-plated steel is more susceptible to rust than stainless steel. Zinc-plated components are ideal for dry,low-humidity, and slightly moist environments.
Durability
For most applications, stainless steel is more durable than zinc plating.
Once the zinc coating is worn or scratched, it can’t be regenerated, and then the zinc-plated steel is exposed to the air and may rust or corrode. Unlike zinc plating, even if the stainless steel surface is scratched or abraded, its self-repairing ability of the chromium oxide film minimizes the risk of damage and maintains corrosion resistance. If your projects or items require long-term stability, stainless steel is a better choice.
Cost-effectiveness
Cost is a key consideration when making a choice between zinc plating and stainless steel. In terms of the initial investment, zinc plating is generally cheaper than stainless steel. While considering the later maintenance cost and long-term use cost, stainless steel is much better according to its advantages of longer durability and good maintenance.
Surface finished
Many custom designs require different surface treatments for a unique look. Zinc plating can produce a colored film on the surface of parts through the post-treatment passivation process, resulting in blue, black, iridescent, and so on. Stainless steel can be finished with polishing, brushing, sandblasting, and other techniques. When polished, it presents a smooth, non-porous, and shiny surface, which zinc-plated steel cannot achieve.
Safety
Safety is also one of the factors to pay attention to in the design and use of products. In a relatively mild environment, zinc-plated steel can maintain stable safety. While in high temperature, highly corrosive, or long-term use situations, stainless steel is much safer for processing and usage scenarios.
Application of zinc plating vs stainless steel
Application of stainless steel
Stainless steel, typically used in places that need high corrosion resistance and hygiene standards, such as medical, food processing, chemical, infrastructure, marine, transportation and other fields. Owing to its aesthetic appeal and durability, stainless steel is normally employed in creating sculptures.
Application of zinc plating
Zinc plating is more suitable when moderate corrosion resistance is sufficient. It is commonly applied in interior decoration, electrical components, agriculture, and other large-scale applications. Additionally, zinc plating is the first choice for cost-effective solutions, such as in brackets, fasteners, and hardware.
Choose between zinc plating and stainless steel
When making a choice between stainless steel and zinc plating, you should consider the following factors:
- Application: Stainless steel is ideal for corrosive, long-term, or hygienic applications. Zinc plating is suited for mild corrosive, short-term, and large-scale applications.
- Corrosion resistance: Zinc plating has moderate corrosion resistance, whereas stainless steel is much more resistant to highly corrosive environments.
- Budget: For large-scale, short-term use projects, zinc plating can strike a balance between cost and corrosion resistance. However, for long-term use, stainless steel is more cost-effective.
- Maintenance needs: Stainless steel needs less maintenance, zinc-plated steel requires ongoing maintenance to prevent rust and corrosion.
In short, stainless steel is a solid option if your design or product needs to face a highly corrosive environment, or is subject to frequent use, or requires a long service life. Zinc plating is more cost-effective and suitable for moderate corrosion and mild environments.
Conclusion
Zinc-plated steel and stainless steel have different advantages and disadvantages. If you need to choose them as your processing materials, you must take into account every factor this article has mentioned. Only after carefully evaluating these conditions can you make a choice that helps your product become more popular with buyers.
HDC Manufacturing provides both zinc plating and stainless steel processing services. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us.