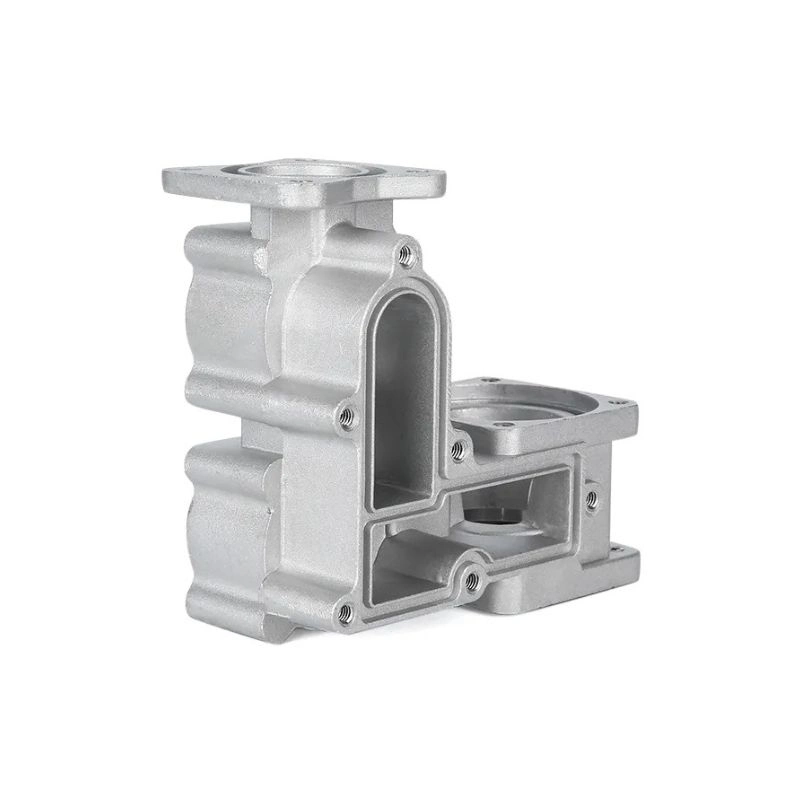
In the realm of modern manufacturing, HDC Manufacturing utilizes multiple state-of-the-art methods to produce high-quality metal parts. A few of these include forging, investment casting, and metal 3D printing. Each manufacturing method offers unique benefits, making them suitable for different applications. Understanding these processes can help in identifying the best technique for specific manufacturing needs.
This article explores the differences, benefits, and costs of each method, highlighting the strengths and limitations of metal 3D printing, forging, and investment casting. Let’s dive in.
Metal 3D Printing: Revolutionizing Complex Part Production
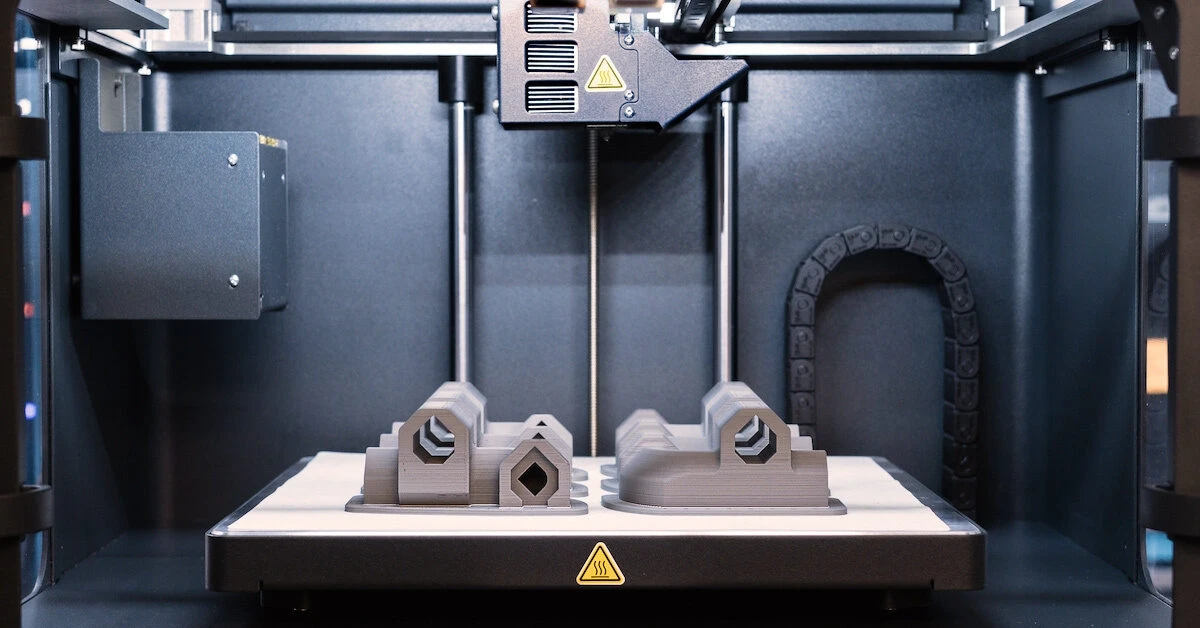
Metal 3D printing, also known as metal additive manufacturing, builds metal parts layer-by-layer from a digital model prepared through CAD software. This process enables the creation of intricate geometries that include complex structures that are not easy to manufacture using traditional manufacturing methods. Metal 3D printing has rapidly become popular due to its efficiency, speed, and precision, especially in industries requiring rapid prototyping.
How Metal 3D Printing Works
Metal 3D printing typically involves Powder Bed Fusion (PBF), a process where a laser or electron beam melts metal powder to form layers. Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Selective Laser Melting (SLM) are two common techniques that fall under PBF, offering excellent dimensional accuracy and a smooth surface finish. These methods are ideal for producing complex parts without the need for molds or tooling.
Advantages of Metal 3D Printing
- Design Flexibility: Complex and lightweight designs are achievable, with minimal material waste.
- Customization: Parts can be tailored to specific needs, ideal for industries like aerospace and medical devices.
- Cost-Effective for Small Batches: It reduces the need for tooling, making it suitable for metal 3D printing services producing prototypes or low-volume runs.
- Lesser Waste: Due to the precise manufacturing, the material waste is reduced substantially.
Challenges and Limitations
- Cost: Metal 3D printing costs can be high due to the expense of the metal 3D printing powder and equipment. A 3D metal printer price is very high depending on the size and type of equipment required.
- Material Limitations: Not all metals are suitable for 3D printing. Common metals for 3D printing include titanium, aluminum, and stainless steel.
- Post-Processing: Some parts require heat treatment or machining to enhance mechanical properties and finish quality.
Generally, the challenges and limitations of Metal 3D printing will reduce with time and the evolution of technology.
Forging: Strength and Durability Through Deformation
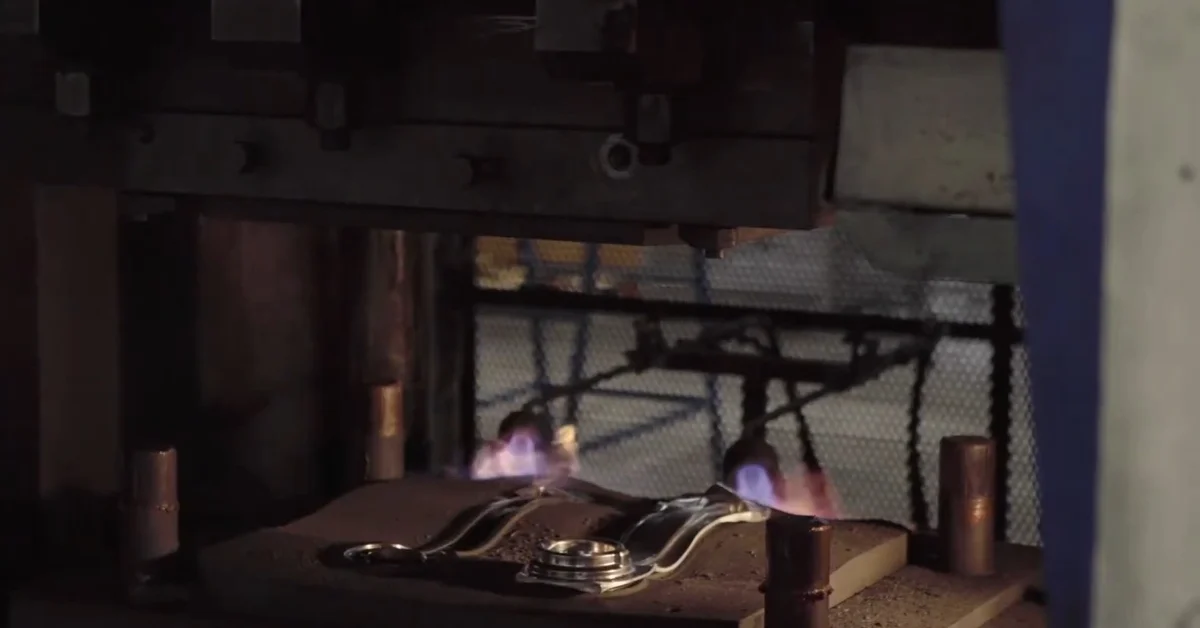

Forging is an ancient metalworking process that uses compressive forces to shape metal, resulting in robust, durable components. HDC Manufacturing’s posses the latest machinery for forging metals that result in excellent mechanical properties, making it an ideal choice for high-stress applications throughout the industry.
How Forging Works
Forging involves heating metal until it becomes malleable, then shaping it using a die. This process can be classified into three main types:
- Open Die Forging: Suitable for large components.
- Closed Die Forging: Used for more intricate shapes.
- Roll Forging: Ideal for cylindrical parts.
Forging typically results in a stronger grain structure and higher tensile strength than casting or 3D printing, thanks to the metal’s compressed structure.
Advantages of Forging
- Strength: The grain structure aligns with the part shape, enhancing durability.
- Cost-Effective for Large Batches: Particularly for high-strength, repetitive parts, forging provides an economical solution.
- Material Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of metals, including steel and aluminum.
Challenges and Limitations
- Complexity Constraints: Forging is less suitable for complex geometries due to the limitations of die shapes.
- High Initial Costs: Die creation for closed die forging can be costly, making it less viable for low-volume production.
- Time-Intensive: The process requires significant lead time for die manufacturing and setup.
- Lesser Material Usage Efficiency: Material waste in the process is higher than that of metal 3D printing.
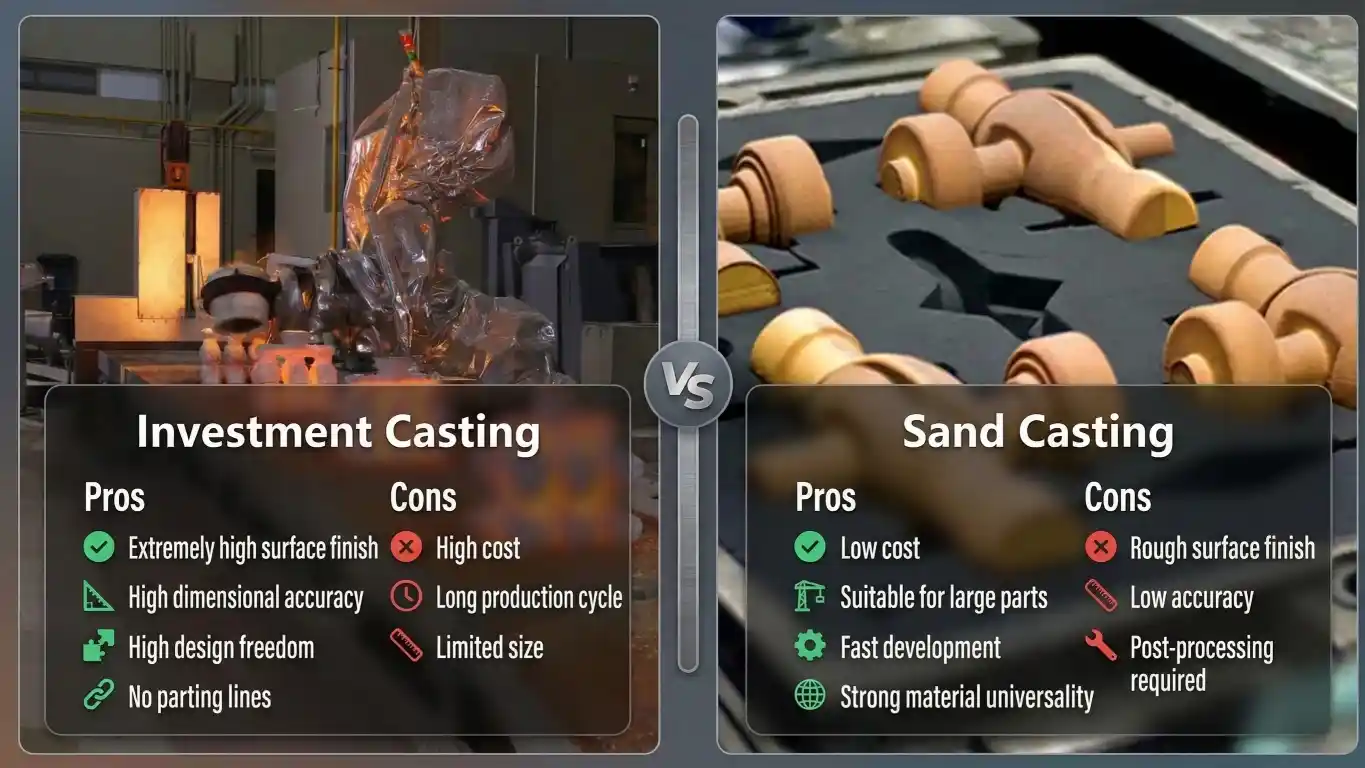
Investment Casting: Precision and Versatility in Metal Parts Production
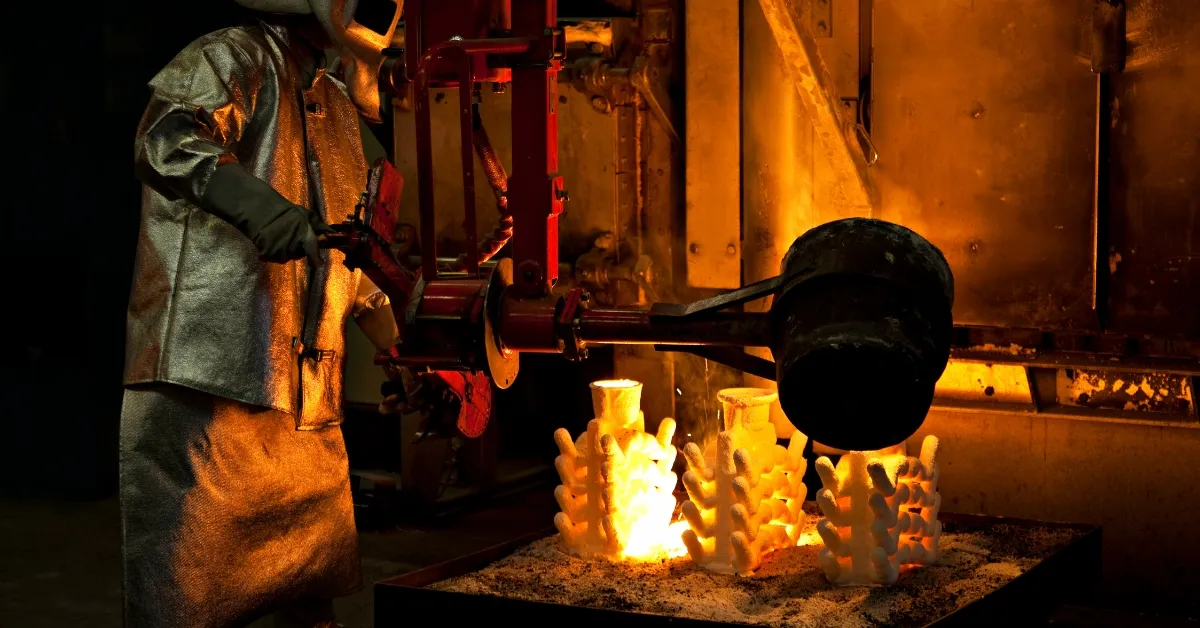

Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, is a traditional method that produces precise and smooth-surfaced metal parts. HDC Manufacturing has the capability to produce high standard and detailed components, with smoothness and dimensional accuracy by using the latest research and technology in the investment casting process.
How Investment Casting Works
In investment casting, a wax pattern is created and coated with a ceramic shell. Once hardened, the wax is melted away, leaving a mold that is then filled with molten metal. This method can produce highly detailed parts with thin walls and smooth surfaces.
Advantages of Investment Casting
- Excellent Surface Finish: Investment casting yields a smooth, near-net shape part, reducing post-processing needs.
- Complex Geometries: It is suitable for creating intricate shapes that are difficult to forge.
- Broad Material Compatibility: Investment casting works well with various alloys, including steel, aluminum, and nickel-based alloys.
Challenges and Limitations
- Costly for Small Batches: Creating molds can be expensive, making it less cost-effective for low-volume production.
- Lead Time: The mold creation process is time-intensive, adding to the overall production time.
- Material Waste: Excess metal used in gating and risers is often recycled but adds to initial material requirements.
Comparing Costs: Which Process is Most Economical?
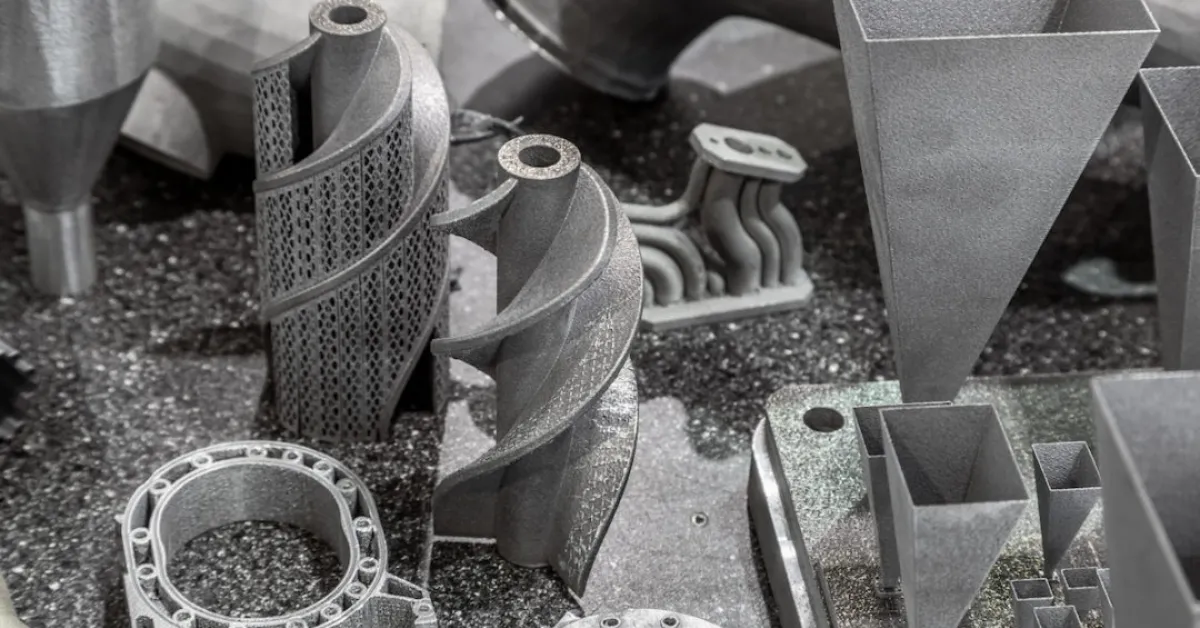

Understanding the cost structure of each process is crucial for selecting the right manufacturing method.
- Metal 3D Printing Costs: The cost of 3D printing metal partscan vary widely. High metal 3D printing costs are often due to the 3D metal printer price and the cost of metal 3D printing powder. According to The Steel Printers, factors like part complexity and volume impact the overall price.
- Forging Costs: Forging is generally economical for high-strength parts in large quantities. However, the cost of creating dies makes it less affordable for small runs.
- Investment Casting Costs: Investment casting is ideal for complex parts but becomes costly for small batches due to mold production. However, it offers a balance between initial setup costs and final part quality, especially for medium to large batch production.
Choosing the Right Process: Key Considerations
When deciding between metal 3D printing, forging, and investment casting, consider the following factors:
- Design Complexity: For highly intricate parts, 3D printing metal provides unmatched flexibility. Investment casting also allows for complexity but has limitations with intricate internal structures.
- Strength Requirements: Forging produces the strongest parts due to the aligned grain structure. It is ideal for applications demanding high tensile strength.
- Batch Size and Production Volume: 3D metal printing is suitable for rapid prototyping and small batches, while forging and casting are more cost-effective for larger production volumes.
- Material Selection: Each method supports different materials. For instance, metal 3D printing materials like titanium and nickel-based alloys are common in additive manufacturing but may be limited for forging.
- Surface Finish Needs: Investment casting offers a smooth surface finish with minimal post-processing, while 3D-printed metal parts require additional finishing steps.
Conclusion
Each metalworking process—metal 3D printing, forging, and investment casting—offers unique benefits, making them suitable for a range of applications. Metal 3D printing is excellent for complex, lightweight designs, especially for low-volume runs or prototyping. Forging provides unparalleled strength, ideal for heavy-duty applications, while investment casting strikes a balance between precision and surface finish. By considering factors such as design complexity, batch size, and material requirements, manufacturers can select the best method to achieve the desired quality and cost efficiency.
As metal 3D printing continues to evolve, it complements traditional manufacturing methods, offering new opportunities for innovation and customization. HDC Manufacturing’s versatile manufacturing capabilities in 3D printing metal and traditional metalworking make it a leader in delivering high-quality, reliable metal parts across industries.