Aluminum is one of the most used industrial metals. It offers some of the best strength-to-weight ration. These properties make it as an ideal choice for application where weight is of consideration such as Marine and Aerospace industries. Aluminum has a number of variants and the final product type depending on the technology used for manufacturing. We will discuss two of the manufacturing techniques i.e. Forged vs Billet Aluminum. Each style of manufacturing has its own pros and cons and applications. In this article, we will review the main features and applications of forged and billet aluminum.
Forged Aluminum: An Introduction
As the name suggests, forged aluminum is produced using techniques such as pressing, squeezing or beating aluminum under high pressure. Forging aluminum is an ideal choice when it comes to manufacturing parts with extreme strength and heavy duty resistance against rust and corrosion.
Generally, forging is ideal with 6061 aluminum and 7075 aluminum alloys. These alloys have high yield strength and are ideal for applications where strength is of importance without compromising on weight.
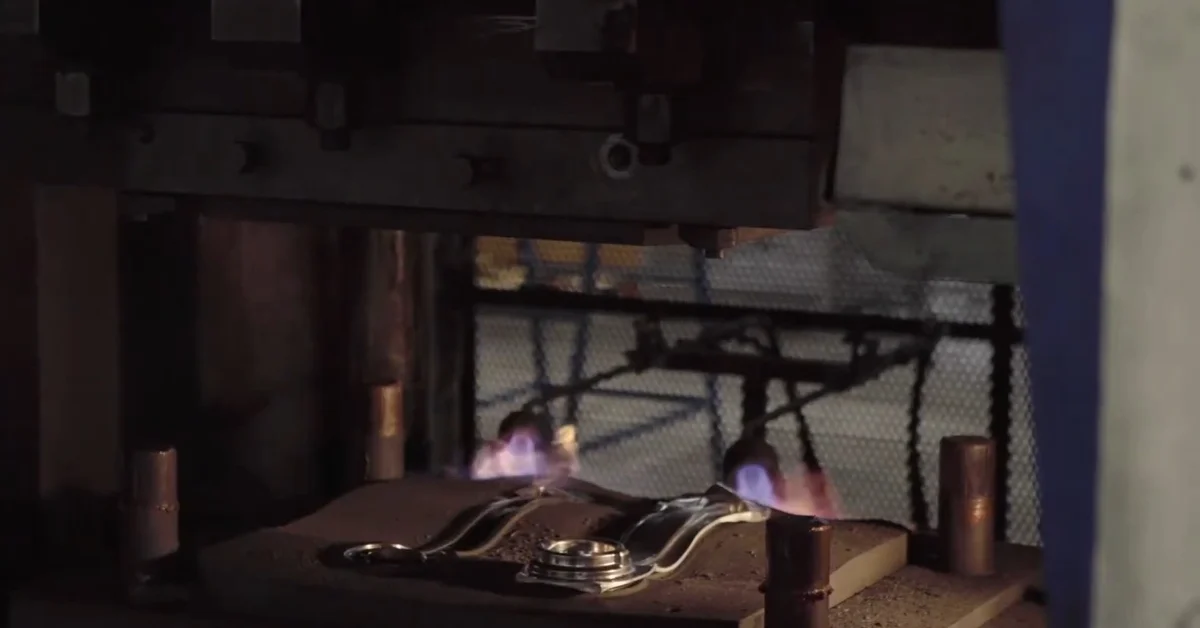

Billet Aluminum
Billet Aluminum is machined aluminum. Usually,, the aluminum that is directly manufactured from the aluminum block is known as billet aluminum. Among the many varieties of aluminum, the 6061 aluminum is ideal for manufacturing using billet aluminum. Billet aluminum is easy to machine, easy to weld and display good welding properties. Commonly, billet aluminum is used in the manufacturing of customized products for cars and motor bikes.
Main difference between Using Forged Aluminum vs Billet Aluminum
Durability and Strength
Forged Aluminum offers great strength. Due to the process of forging, the metallic atoms become closely packed together and aligned in one direction. Ultimately, this results in increasing the strength of the metal. Since the atoms are closely packed, the density of the metal goes up and it becomes highly resistant to corrosion and rust.
On the other hand, the billet aluminum is machined from a solid block. Due to the cutting of at random location, the atoms of the aluminum are not uniform. Furthermore, the random grain structure makes the final block misaligned with rest of the aluminum block. As a result, billet aluminum does not offer a great strength and durability against the gorged aluminum.
Precision and Machinability
When it comes to machinability and precision designing, billet aluminum offers certain benefits over forged aluminum. As a result, the billet aluminum is an ideal process for development of precision parts like billet aluminum wheels. These parts are intricate and require lot of machining which is not possible with forged aluminum.
When used in combination with CNC machining technology, billet aluminum rims are very popular among the vehicles and motorcycles manufacturers.
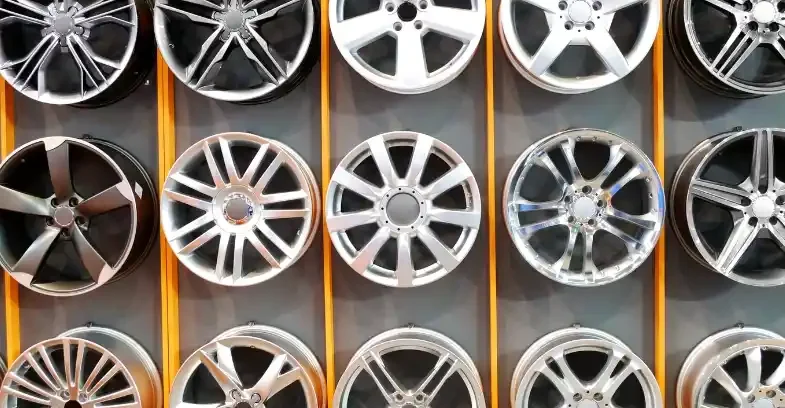

Weight and Density of different Aluminum Grades
Some of the most common aluminum grades widely used in industrial applications are 6061 aluminum. Since the 6061 aluminum offers characteristics that are well-rounded, it is easier and convenient to use these in various industrial applications.
The key properties of 6061 aluminum are as follows:
- Density: 2.7 g/cm³, contributing to its lightweight nature.
- Yield Strength: Around 275 MPa (depending on temper), suitable for many structural applications.
- Melting Point: Approximately 582-652 °C.
It is interesting to note that 6061 aluminum holds its properties mostly regardless the process of manufacturing i.e. forging or billet aluminum.
The following table summarizes the main features of each of the Aluminum types:
| Property | Billet Aluminum | Forged Aluminum |
| Strength | Stronger than cast due to uniform structure; but less strong than forged. | Superior strength due to grain alignment and compaction. |
| Machinability | Excellent machinability; ideal for CNC machining and customization. | Tougher to machine due to higher density, but still workable. |
| Finishing | Excellent finish after machining, requiring minimal post-processing. | Requires more finishing than billet but less than cast. |
| Applications | High-precision parts in various industries. | High-stress and demanding applications. |

Applications across Industries
- Aerospace Parts
Manufacturing of aerospace parts is extremely critical as these parts have to undergo stressful testing. Furthermore, the critical nature of aerospace industry demands reliable and trust-worthy parts. In this scenario, major industries rely on aircraft-grade aluminum. However, since strength is of key importance, often forged aluminum is used. An ideal choice of use is aluminum alloy 7075 t6 for the manufacturing of aerospace parts.
Having said this, there are multiple intricate applications in aerospace industry that require precise machining. Therefore, in such applications, billet aluminum is also used.
- Automotive Parts
Automotive is a vast industry that require multiple parts ranging from rims to wheels. Again, as we discussed in the aerospace industry, the automotive industry also has a variety of application for aluminum. For areas where high strength and durability is required, forged aluminum is used. Examples include forged aluminum rims that are ideal for reducing weight and improving fuel efficiency in vehicles.
Whereas, if machining precision and aesthetics are important then billet aluminum is used. Examples are custom wheels and brackets.
- Motorbike Parts
The motorbike industry also has vast levels of aluminum applications that require for a variety of aluminum grades and parts. Some of the most common parts for the motorbike industry is the billet aluminum wheels. These wheels are not only aesthetically appealing, they are also corrosion resistant and light in weight.
- Marine Applications
In addition to the manufacturing industries highlighted above, aluminum alloy 5052 is also widely used in industries due to its high corrosion resistance and strength. Since the aluminum alloy with magnesium and chromium offer great strength and corrosion resistance, it is ideal for the marine industry where there is high exposure to corrosive environment.

Cost Comparison: Forged vs. Billet Aluminum
In terms of upfront costs, forged aluminum costs higher due to intensive machinery and skilled labor required. However, in terms of large production, the marginal costs go down and forged aluminum becomes cost-effective.
On the flip side, billet aluminum offers lower upfront costs. However, since CNC and other precise machining tools are good at producing prototypes but when it comes to large scale manufacturing, billet aluminum does not perform so well.
Conclusion: Billet or Forged Aluminum
Summing up, both the manufacturing processes of billet aluminum and forged aluminum have their sets of pros and cons to share. However, there cannot be any one solution fits all material. Therefore, Billet Aluminum is a good process that offers flexibility in design and high precision.
On the other hand, forged aluminum offers great strength and durability while also being affordable for large scale manufacturing. As a result, you need to make your choice based on your preferences for selection of the right manufacturing process.
Discover more with our blog posts.
Recent Posts
Discover more about our products.
Related Products
Instant Quote!