This blog compares forged wheels and cast alloy wheels, focusing on materials, manufacturing, benefits, and performance. Forged wheels, made from high-strength aluminum alloys, offer greater durability, strength, and lightweight features, making them perfect for sports and performance cars. On the other hand, cast alloy wheels, though versatile and cost-effective, lack the same strength but are still widely used. This introduction sets the stage for a deeper dive into the differences between these two wheel types.


Materials Used for Forged Wheels and Cast Alloys Wheels
- Forged Wheels: Forged wheels typically use high-strength aluminum alloys like 6061, known for its great balance of strength, lightness, and corrosion resistance. It’s perfect for everyday use, but if you’re racing or pushing performance to the limit, 7075 alloy steps in with even more strength and hardness. Sometimes, a dash of magnesium, silicon, or zinc is added to boost performance further.
- Cast Alloy Wheels: Cast wheels, on the other hand, also use aluminum alloys, though they aren’t as specialized. A356 and 6061 are common choices, but you might find 356 or 319 alloys used depending on the manufacturer.


Understanding Forged Wheels
Definition and Explanation of Forged Wheels:
Forged wheels are single-piece metal wheels, typically made from aluminum, created through a forging process. This involves heating the metal and shaping it under high pressure. The key advantage of forging is how it aligns the metal’s internal grain structure, resulting in a wheel that’s stronger, lighter, and more durable compared to cast wheels.
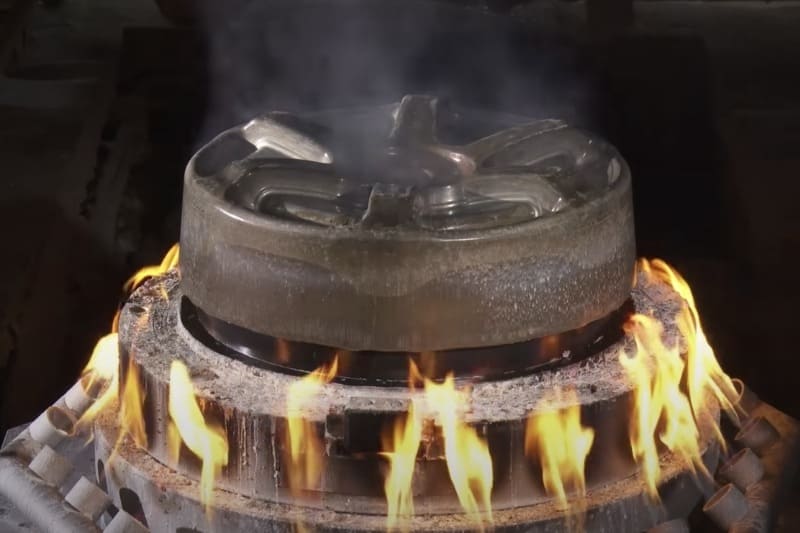


Process of Forging Wheels:
- Heating Aluminum Billets: The process starts by heating aluminum billets to make them malleable without breaking.
- Shaping with High Pressure: The heated billets are pressed into the desired wheel shape using precision tools, ensuring consistent results.
- Cooling and Finishing: After shaping, the wheels are gradually cooled to reduce internal stress, then polished, painted, or coated for the final look.
Advantages of Forged Wheels:
- Strength and Durability: Forging aligns the metal’s structure, making forged wheels tougher and less prone to damage.
- Lightweight: Their denser composition makes them lighter than cast wheels, improving acceleration, braking, and fuel efficiency.
- Enhanced Performance: Forged wheels deliver better handling and responsiveness, making them ideal for high-performance vehicles.
Common Applications and Industries Where Forged Wheels are Used:


Forged wheels are widely used in automotive and motorsports, particularly for high-performance cars, luxury vehicles, and racing. They’re also found in off-road vehicles, aircraft, and military applications, where strength and durability are critical. Forged wheels are favored for their balance of strength, lightness, and performance across industries like automotive, aerospace, and defense.
Exploring Cast Alloy Wheels
Definition and Explanation of Cast Alloy Wheels:
Cast alloy wheels are widely used in the automotive world, from cars and trucks to motorcycles. Made by pouring molten aluminum or other alloys into a mold, these wheels solidify into their final shape as they cool. Known for their affordability and versatility, cast alloy wheels are a popular choice in the automotive aftermarket.


Process of Casting Wheels:
- Pouring Molten Alloy: The process starts by heating an alloy until it melts, then pouring it into a mold shaped like the wheel.
- Cooling and Solidification: The alloy cools and solidifies in the mold, taking on the desired design. Cooling may be sped up using air or water.
- Finishing Touches: After casting, the wheels undergo finishing processes like machining, polishing, or coating to achieve the final look.
Advantages of Cast Alloy Wheels:


- Cost-Effective: Cast alloy wheels are an affordable option compared to forged wheels, making them accessible to a wider audience.
- Design Variety: The casting process allows for a wide range of designs and finishes, offering flexibility to suit different vehicle types.
- Mass Production Friendly: Casting is ideal for large-scale production, making it a go-to method for manufacturers needing high volumes of wheels.
Common Applications and Industries Where Cast Alloy Wheels are Used:
Cast alloy wheels are commonly used in various automotive applications, including:


- Passenger Vehicles: They are a common feature on consumer cars and trucks due to their affordability and stock availability.
- Commercial Vehicles: Cast wheels are also used in light trucks and utility vehicles for their durability at a lower cost.
- Aftermarket Customization: Many car owners swap stock steel wheels for aftermarket alloy wheels to enhance the look and performance of their vehicles.
- OEM Replacements: Auto manufacturers often offer cast alloy wheels as a replacement for factory-installed steel or alloy wheels.
Overall, cast alloy wheels are a cost-effective, flexible option, making them popular across the automotive industry.
Comparing Forged Wheels and Cast Alloy Wheels
Strength and Durability:
The manufacturing process plays a big role in wheel strength. Forged wheels are made through forging, which creates a denser and stronger metal structure. This makes them more resistant to bending and cracking, offering better durability over time. Cast alloy wheels, on the other hand, are made by casting, resulting in a less uniform structure, which makes them more prone to damage. In short, forged wheels are tougher and last longer.


Weight:
Usually, forged wheels are lighter than cast wheels thanks to their dense composition and features of forging, whereas cast alloy wheels are often heavier due to their small density and casting technique.
Performance:
Forged wheels are known for their lightweight build and superior strength, making them ideal for high-performance driving. They improve handling, cornering, and overall responsiveness, giving the driver a more precise and controlled experience. Cast wheels, while offering decent performance, can’t match the precision of forged wheels, especially in racing or high-speed situations where every ounce matters.
Cost:
Forged wheels are more expensive upfront because of the complex manufacturing process, but they offer better long-term value due to their durability and performance. Cast alloy wheels are cheaper to start with but may require more maintenance or replacement over time, which could increase costs in the long run. If you’re after high performance and durability, forged wheels are worth the investment. If you’re on a budget and need something functional, cast wheels might be the better option.


Conclusion
Cast alloy wheels are often more affordable, making them a solid option for those looking for a balance between performance and cost. However, if you prioritize strength and durability, especially for high-performance vehicles, forged wheels are the better choice. Cast wheels offer versatility and good value for money, especially for everyday drivers or first-time buyers. Whether you’re focused on ultimate performance or just need reliable wheels for daily use, understanding the differences between forged and cast wheels is key to making the right choice.