PEEK, or Polyether ether ketone, is a type of high-performance plastic that’s making waves in industries like aerospace, medical, and automotive.
This blog aims to dig deeper into what makes PEEK so special. We’ll break down its key properties, explore the advantages it offers, and highlight its wide-ranging applications.
Whether you’re an engineer, a manufacturer, or just curious about materials that are pushing the boundaries of innovation, you’ll find valuable insights here.
What is PEEK Plastic?
Polyether Ether Ketone, or PEEK in short, is a semi-crystalline engineering thermoplastic. It belongs to the polyaryletherketone (PAEK) family of polymers with the chemical formula (C19H12O3)n. Its chemical structure, featuring aromatic rings and ether and ketone linkages, gives it high resistance to chemicals, wear, and hydrolysis.
In its raw form, PEEK granules typically appear in a natural color that ranges from beige to light brown.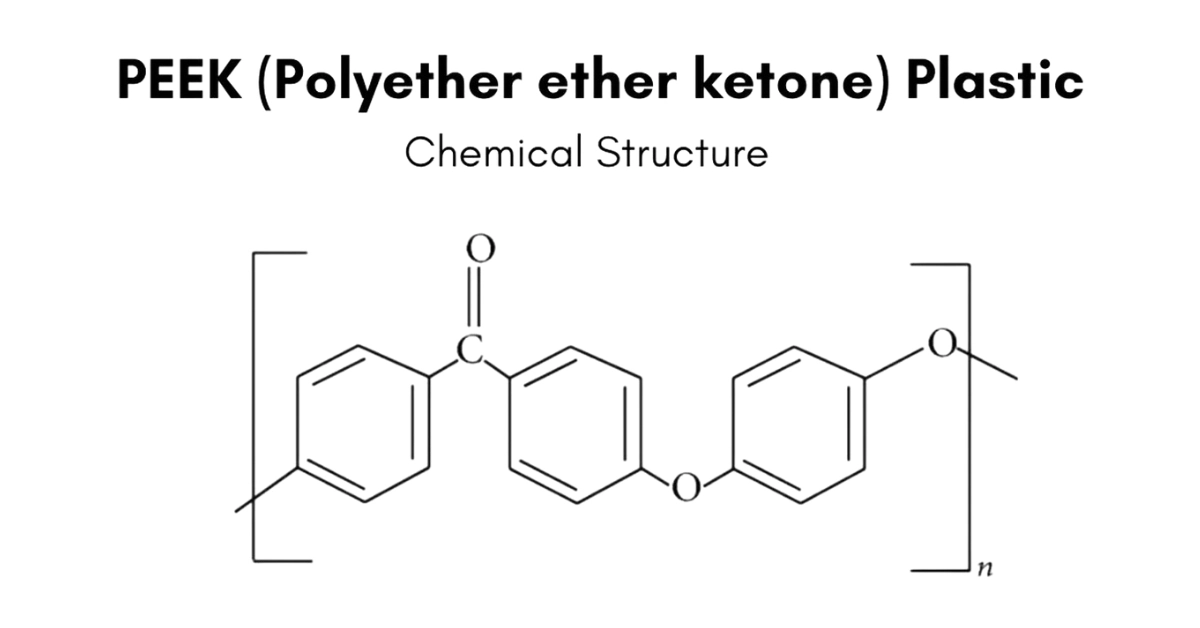
This plastic can withstand temperatures of up to 250°C and resist harsh chemicals, making it ideal for applications in extreme environments.
It also has excellent mechanical strength and wear resistance, which is preferred in industries like aerospace, medical, and automotive.
As a thermoplastic, PEEK can be heated and molded without losing its key properties, making it highly versatile and reliable.
PEEK Plastic Material Properties
Here is the PEEK properties data sheet we have collected, which includes the key performance parameters of PEEK. For more detailed information, please visit Matweb.
PEEK Physical Properties | |
|---|---|
| Density of PEEK | 1.26 – 1.72 g/cc |
| Water Absorption | 0.0200 – 0.500 % |
| Particle Size | 10.0 – 550 µm |
| Viscosity | 1120 – 1120 cP @Temperature 380 – 380 °C |
| Linear Mold Shrinkage | 0.00100 – 0.0200 cm/cm |
| Melt Flow | 0.260 – 182 g/10 min |
| Spiral Flow | 11.0 – 70.0 cm |
PEEK Mechanical Properties | |
|---|---|
| Hardness, Rockwell M | 85.0 – 109 |
| PEEK Tensile Strength, Ultimate | 90.0 – 250 MPa |
| Tensile Strength, Yield | 11.0 – 125 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | 1.70 – 110 % |
| Elongation at Yield | 3.60 – 45.0 % |
| Shear Strength | 55.0 – 90.0 MPa |
PEEK Thermal Properties | |
|---|---|
| CTE, linear | 4.70 – 216 µm/m-°C |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 1.10 – 2.20 J/g-°C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.173 – 0.950 W/m-K |
| PEEK Melting Point | 178 – 386 °C |
| Maximum Service Temperature, Air | 150 – 310 °C |
| Deflection Temperature at 1.8 MPa (264 psi) | 140 – 336 °C |
| Vicat Softening Point | 280 – 335 °C |
| Softening Point | 168 °C |
| Glass Transition Temp, Tg | 143 – 180 °C |
PEEK Processing Properties | |
|---|---|
| Processing Temperature | 100 – 410 °C |
| Nozzle Temperature | 360 – 440 °C |
| Melt Temperature | 174 – 470 °C |
| Mold Temperature | 149 – 250 °C |
| Injection Velocity | 200 mm/sec |
| Drying Temperature | 120 – 180 °C |
| Moisture Content | 0.0200 – 0.290 % |
| Injection Pressure | 82.7 – 124 MPa |
| Recrystallization Temperature | 285 °C |
How is PEEK Processed?
There are several manufacturing techniques for PEEK plastic, each chosen based on the specific needs of the application:
Injection Molding
This is the most common way to manufacture PEEK parts. Injection molding allows for the efficient production of complex shapes with tight tolerances, making it ideal for large-scale production.
Extrusion
Extrusion is often used for creating PEEK plastic sheets or profiles that can be cut and machined later. This process is essential for applications that require continuous shapes.
CNC Machining
PEEK material machining is ideal for creating high-precision components. CNC machines are used to cut and shape PEEK into detailed parts with exacting specifications. This method is particularly popular in industries like medical and aerospace.
3D Printing
The advent of 3D printing with PEEK has revolutionized rapid prototyping and manufacturing. With its high-temperature resistance, PEEK can now be printed for complex, custom parts in critical applications.
Applications of PEEK Material
Medical Applications
PEEK is biocompatible and resistant to sterilization, making it ideal for medical devices like implants and prosthetics. It’s strong, lightweight, and inert to bodily fluids, reducing the risk of adverse reactions.
Aerospace Applications
In aerospace, PEEK is used for structural components and insulation. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and radiation makes it reliable for extreme environments, while its lightweight nature helps improve fuel efficiency.
Automotive Industry
PEEK is commonly found in high-performance automotive parts, such as bearings and gears, due to its heat resistance and durability. These properties enhance the lifespan of critical components.
Electronics Industry
PEEK’s excellent insulation makes it a key material in electronics, where it’s used in cables, connectors, and circuit boards to protect against heat and corrosion.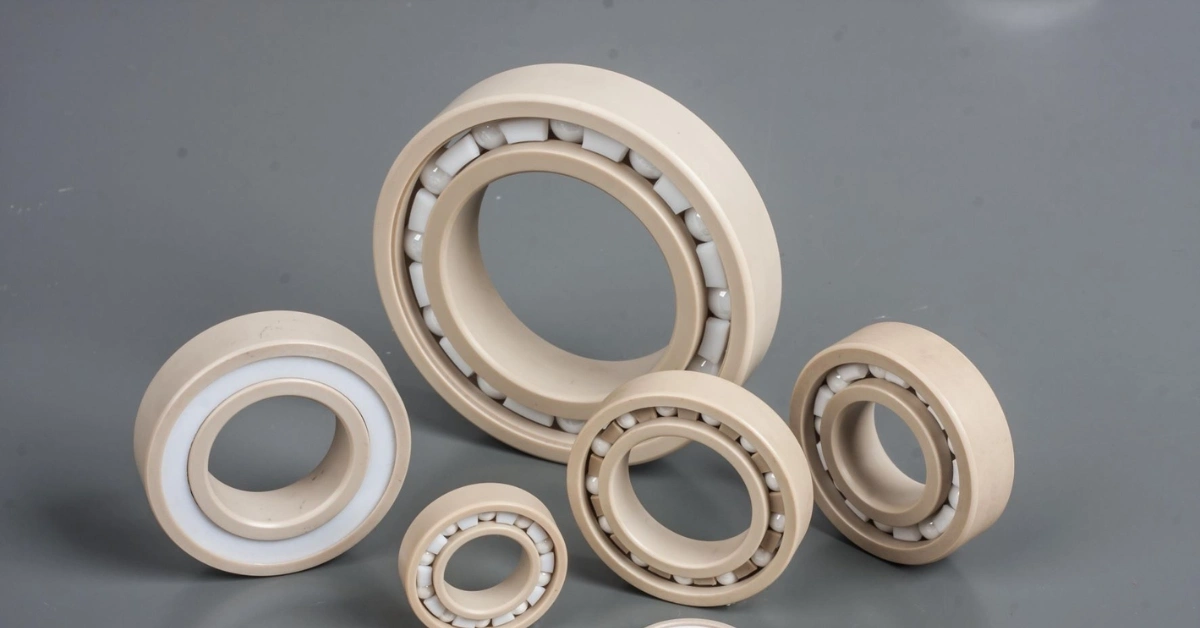
PEEK vs. Other High-Performance Plastics
Compared to other engineering plastics, PEEK offers several advantages:
- Temperature Tolerance: PEEK can handle temperatures up to 260°C, far higher than materials like PTFE or nylon.
- Chemical Resistance: Its resistance to aggressive chemicals surpasses that of many other plastics, making it a top choice for demanding environments.
- Strength: PEEK’s mechanical strength allows it to outperform alternatives like PEI or PPS, particularly in high-stress applications.
When compared to PTFE or PEI, PEEK offers an unbeatable combination of heat resistance, strength, and chemical stability, positioning it as a top-tier material for critical applications.
Limitations of PEEK
Despite its numerous advantages, PEEK does come with some limitations. One of the most significant barriers is its cost. PEEK plastic can cost between $50 to $150 per kilogram, depending on the grade and supplier, making it much more expensive than other engineering plastics like Nylon, which typically costs around $3 to $5 per kilogram, or PTFE, which ranges from $10 to $20 per kilogram. This high cost restricts its use to high-performance or specialized applications where its superior properties justify the investment.
Additionally, PEEK can be challenging to process, particularly for applications requiring very tight tolerances. Its high melting point requires specialized equipment for processing, which can increase production complexity and cost. For instance, injection molding PEEK requires mold temperatures of 160°C to 200°C and barrel temperatures of 370°C to 420°C, much higher than most standard plastics. These factors can complicate manufacturing, especially for smaller-scale projects where precision is critical.
You May Also Want to Know About PEEK
1. Is PEEK toxic?
No, PEEK is non-toxic and biocompatible, making it safe for medical and industrial use.
2. Is PEEK biodegradable?
No, PEEK is not biodegradable. It is highly resistant to degradation and designed for long-term use.
3. Can PEEK be recycled?
Yes, PEEK can be recycled, but the process is complex due to its high melting point and requires specialized equipment.
Conclusion
In summary, PEEK stands out for its superior strength, chemical resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. From medical devices to aerospace components, PEEK plastic continues to prove its value across various industries. HDC offers precision CNC machining services to manufacture PEEK components tailored to your needs.
Discover more with our blog posts.
Recent Posts
Discover more about our products.
Our Products
Instant Quote!