1. As Machined


A standard finish for metal parts is used when nothing needs to be done in the last section of the process with regard to finishing. It is typically done when the part is already suitable and appropriate for its application’s demands. Additionally, a finished part doesn’t need any final finishes if the material’s whole appearance is recognized as fascinating
2. Anodizing


Aluminum is the material that is commonly used in anodizing. It is changing the component’s surface into an oxide, also known as chemical oxidation that offers extremely durable surfaces. Another thing is that anodizing has different types.
- Type 1: Offers a thin and exceptionally corrosion-resistant surface coating. Usually applied to the aerospace industry.
- Type 2: This type of process is the standard anodizing, that is uniform, consistent, and has corrosion resistance. It also has 2 classes, Class 1 pertains to the un-dyed parts, while Class 2 is the decorative anodizing which enables different color pigmentations.
- Type 3: This type of anodizing is often known as hard coat anodizing. It is usually two to four times thicker than type 2 anodizing, offering great density plus marvelous corrosion and wear resistance. There are 2 classes of type 3 anodizing, Class 1 pertains to a clear solid coat, while Class 2 has a black firm glaze.
3. Bead Blasting


Also known as “sandblasting”, typically applied to projects that require a matte texture finish on their parts. The main objective of bead blasting is to remove any marks or other displeasing defects and imperfections to attain a consistent surface finish. It is often reviewed as one of the visually pleasing finishes for metal sheets.
- Shot Peening: a blasting method that improves fatigue protection, pressure corrosion break resistance, etc.
- Burnishing: used to convey compressive stress for fatigue resistance.
4. Chemical Film Coating


A sealant coat is characterized by a chemical film coating that offers impressive resistance to corrosion. Unquestionable advantages are built on along with the chemical films that keep up the electroconductivity and strengthen the connection of the paint/powder layering towards the material’s base. Additionally, an anodized finish is applicable to chemical film coatings. Chemical film coating has different categorizations.
- Type 1: a rarely used coating that results in a brown or gold shade of coating.
- Type 2: a common clear chemical film coating for military and aerospace applications.
- Class 1A: a thicker coating that upgrades the base material’s corrosion resistance that is concurrently applied as a coat for ornamental purposes or impervious paints.
- Class 3: improve corrosion resistance and is not compromising voltaic conductivity.
5. Powder Coating
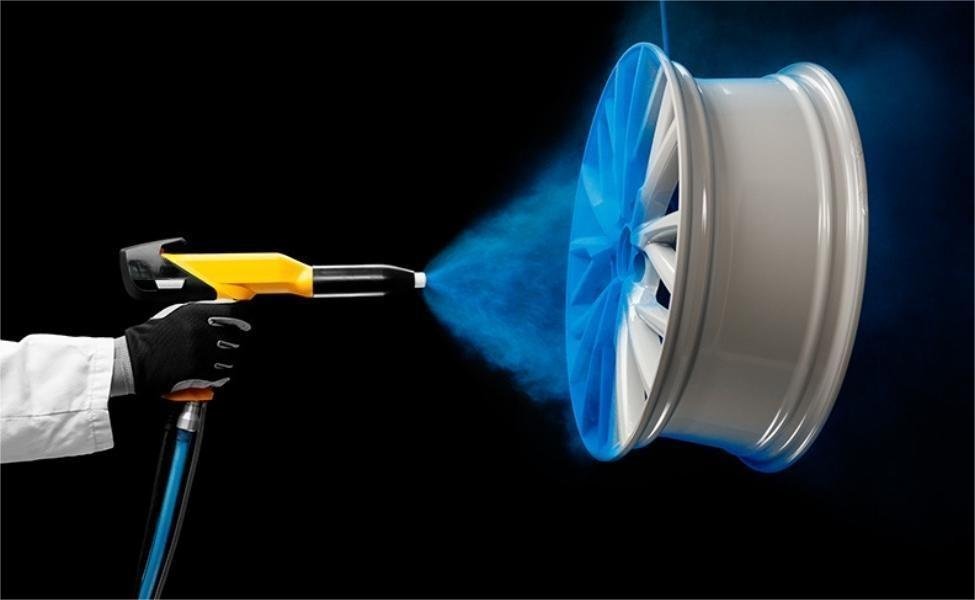


Powder coating offers a wide variety of color pigments that are perfect for aesthetic demands. It has greater longevity than paint and produces matte, shiny, or textured coating. The powder is being placed into the top sheet of the part, it offers a powerful bond that may also accomplish using paint. Powder Coating is one of the surface finishes that offer the broadest color extent
6. Black Coating


This type of surface finish for metals offers to decrease in the material’s reaction to friction and corrosion. Salts are added to the black oxide mixture, serving as oxidizers. The black coating performs superbly on brass, stainless, aluminum, steel, and other metal materials.
7. Electroless Nickel Plating


In this method of surface finish, a chemical bath is performed to plate a particular part. It varies levels of phosphorus furnishing that will better the part’s corrosion resistance. The primary edge of this plating classification is that it uniformly covers unlimited kinds of surfaces, even those certain parts that cannot successfully get to using the other coating techniques. It is undeniably one of the most applicable for metal parts with complicated shapes.
8. Gold and Silver Plating


Gold and silver coatings perform as covering for metal parts through the electroplating procedure. Gold can be an outstanding layer for electrically exposed parts which can deliver resistance to tarnish, corrosion, and oxidation. Silver coating provides finer electrical conductivity and is more economical than gold plating.
9. Electroplating


The electroplating uses a solution that contains liquefied metal ions along with a negatively charged electric current across the metal part for it to be plated. Silver, copper, chromium, gold, zinc, etc., are some of the usual metal materials that are utilized by electroplating. Any metal base part that can accompany electricity may undergo electroplating for its own enhancement.
10. Electroless Plating


It is similar to electroplating but does not utilize electricity, it autocatalytically lets the layer of the part catalyze the coating in an electroless manner. What replaces the electricity is the reduction agent that is contained in the plating solution.
11. Hot Dipping


Hot-dip galvanizing is a kind of surface treatment wherein a material is dipped in melted aluminum, lead, tin, or zinc to create a metallic surface. It is used for a part to have corrosion resistance in extreme circumstances.
12. Thermal Spraying
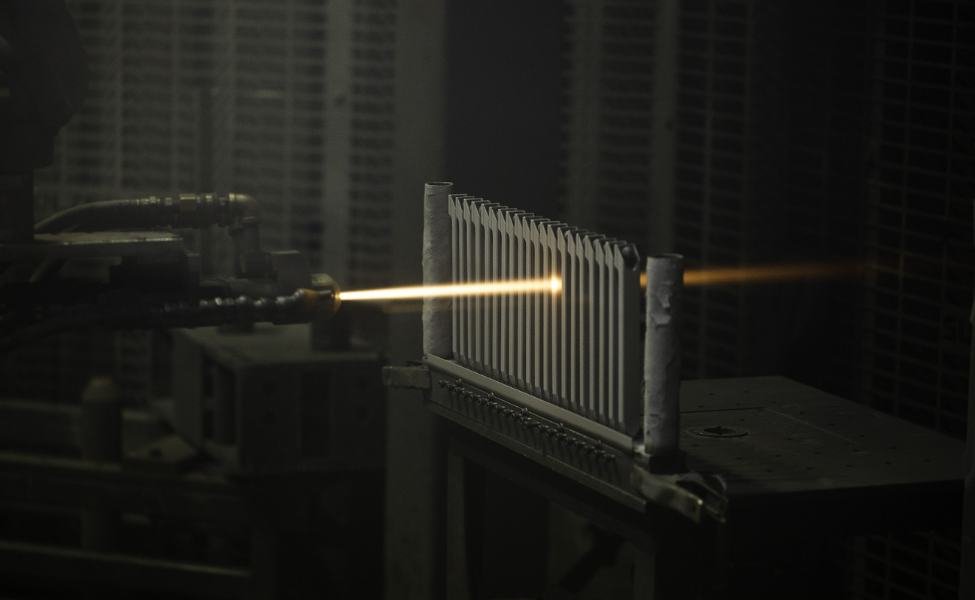


Thermal spraying beautifies and develops the surface of a metal material. It is applied to a wide variety of components and improves the part’s resistance to cavitation, wear, erosion, heat, abrasion, and corrosion. It is also known for providing advantageous surface characteristics like lubricity, chemical resistance, electrical insulation, high and low friction, etc.
13. Brushing


It is a powerful method for extracting imperfections and obtaining the desired pattern of the part’s surface. This kind of finishing generates a uniform texture to polish the component’s exterior. Brushing is able to create different line patterns and may use on metal parts after electroplating to offer the part’s aesthetic improvement.
14. Polishing
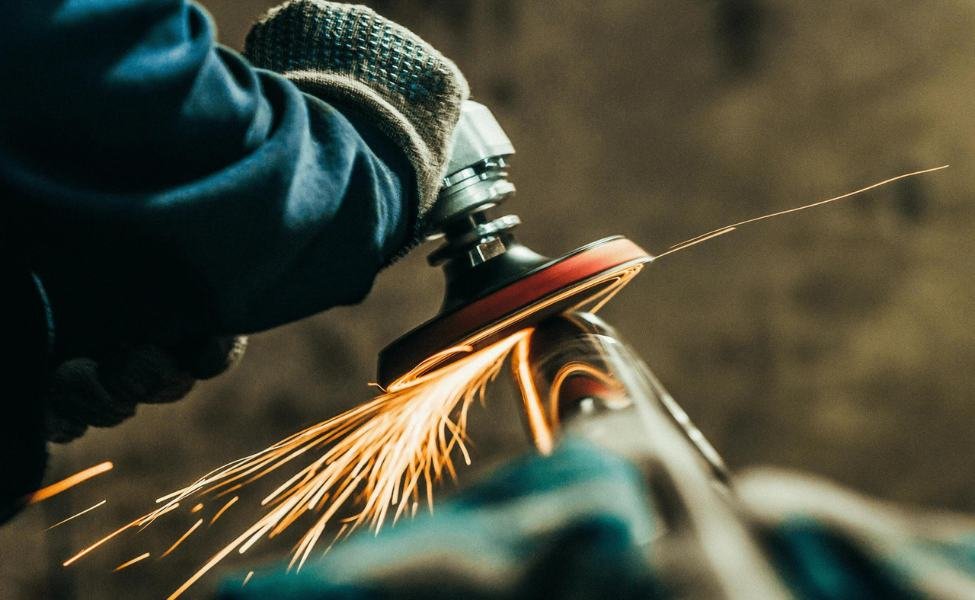


Polishing is a procedure of making the surface mirror-like, bright, and shiny by using an abrasive material or putting a chemical treatment. Its specific aim is to remove roughness and scratches to a machined part as well as better the metal’s glow and luster.
15 Grinding


This surface finish is one of the most popular. It is used to reduce roughness on the surface that is left from the machining process. aluminum, stainless steel, and brass, are some of the varieties of metals that can go through grinding. Grinding for surfaces is the most usual form of grinding machine that uses polishing wheels to smoothen out a surface.
16. Vibratory Finishing


Vibratory finishing is recommended to deburr parts and take off keen edges. It is where a part is positioned in a drum that is full of abrasive materials and employs vibration to create a uniform texture. The machine’s speed and vibration are typically changeable for a certain need of a part depending on its size.
17. Hot Blackening


It is creating a matte black surface finish using a layer of black oxide. Hot blackening is a process where the item is placed into a series of containers consisting of caustics, cleaners, and coolants. It is often used in manufacturing automotive parts.
18. Passivation


Passivation or passivating is where creating a surface film protects the part from chemical sensitivity. It also enhances the corrosion resistance of a metal component. Passivation has different methods, they are:
- Tank Immersion: supports to produce uniformity on a surface finish and corrosion resistance advantage.
- Circulation: circulating a chemical mixture through a method of pipework
- Application of Spray: perfect for the on-site procedure of metal substance.
- Application of Gel: Brushes the gels into the material’s surface, treating the spots from the machining process.
19. Parkerizing


Parkerizing is the perfect method for enhancing the roughness, corrosion, and wear resistance in the part’s surface which protects it from defects and imperfections. It is best for ferrous metals like steel and steel alloys and offers extra protection for these materials.
20. Lapping


The process of lapping involves a machine that applies pressure and moves the grains back and forth to get rid of the irregularities and gives a fine and precise finish to a surface. Lapping also uses an abrasive liquid to get an extremely accurate and glass-looking appearance.
21. Pickling


Pickling is almost always has a part in the process of metal manufacturing. Hot-working on a metal part usually leaves scale and pickling improves the part’s surface by descaling it. Pickling eliminates irregularities and imperfections on every metal component’s surface. This method uses pickle liquor that has a kind of acid that can improve the properties of the metal.
22. Electropolishing


Electropolishing is known as the opposite version of electroplating. It is a process in which a thin layer of a metal part is being removed to create a smooth, sparkling, and extremely clean surface finish. It is also appropriate in polishing parts that are fragile and those components that have intricate geometries.
If you need other surface treatments, Contact Us for more details.