In comparing aluminum vs. titanium, there are factors that you need to consider in terms of usage and application. So, for this article, we’ll go about discussing aluminum and titanium separately, and then provide a careful comparison between them.
You’ll learn everything you need to know about aluminum and titanium, how they work, where they’re used, and all things in between!
Read More: Understanding Mild Steel: Key Features, Uses, and Machining Tips
What is Aluminum?
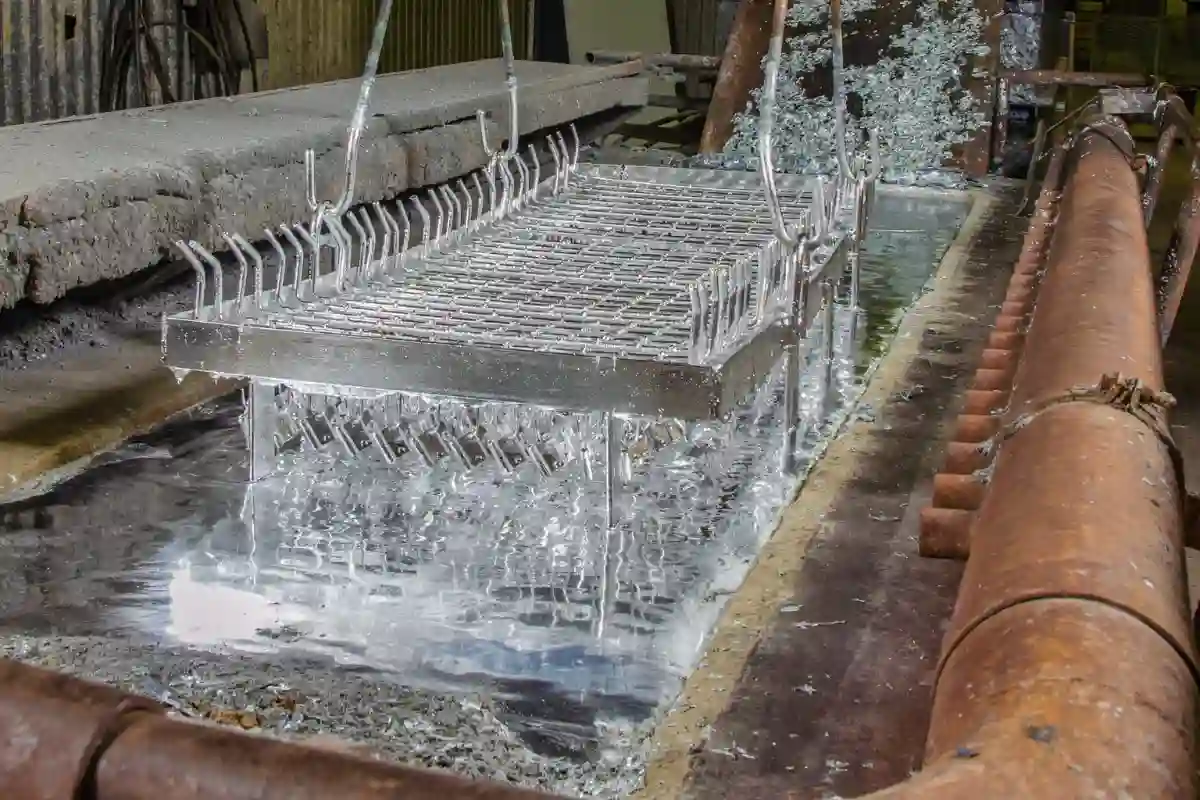
Aluminum stands as a lightweight marvel in the world of metals, transforming industries with its unique blend of strength and versatility.
Discovered in the 19th century, this white and silver-like in color element has become a cornerstone of modern engineering and design. It’s made with bauxite
Its remarkable properties—including corrosion resistance, low density, and excellent conductivity—make it an indispensable material in everything from aerospace to everyday consumer products.
Fun Facts About Aluminum:
- It is the most abundant in the Earth’s crust; it makes up 8% of the composition.
- Aluminum has approximately 15 isotopes, one of which is radioactive (26Al).
- To successfully smelt aluminum, the temperature needs to be at least 660 degrees Celsius or 1,220 degrees Fahrenheit.
- They’re infinitely recyclable, 75% of all aluminum EVER made is still currently in use.
What is Titanium?
Titanium is the ninth most abundant element on Earth and the 22nd element on the ever-famous periodic table. It is a naturally occurring silver-colored metal.
They’re mostly extracted from minerals that are found in the Earth’s crust, such as rutile, sphene, and ilmenite.
What sets titanium apart is its extraordinary strength-to-weight ratio, making it both lightweight and durable. It resists corrosion, heat, and even saltwater, which explains its use in shipbuilding and aerospace engineering.
Fun Facts About Titanium:
- Titanium is as strong as steel but weighs about 45% less.
- It was named after the Titans in Greek mythology, symbolizing strength and power.
- Titanium can withstand temperatures up to 1,668°C without melting.
- About 65% of titanium is used in aircraft and aerospace engineering worldwide.
- Despite its strength, titanium is soft enough to be cut with a sharp steel blade.
Read: Does Aluminum Rust
Aluminum vs. Titanium: Which is Better?


Aluminum and titanium are two completely different and separate metals. While both have similarities, they have differences in terms of their functionality, use, applications, and much more!
So, let’s take a look at aluminum and titanium side-by-side to see how they’re different.
Elemental Composition
We may sound like we’re just repeating stuff, but to figure it out, you need to know its composition. Aluminum is a lightweight, silvery-white metal and the 13th element on the periodic table. It is highly abundant in the Earth’s crust, making it easily accessible.
Titanium, on the other hand, is element number 22 and has a darker, silver-gray appearance. Though also abundant, titanium is harder to extract and refine, which contributes to its higher cost.
Electrical Conductivity
When it comes to electrical conductivity, aluminum is the clear winner. It is an excellent conductor of electricity, often used in power lines and electronics.
Titanium, however, has much lower electrical conductivity, which limits its applications in electrical systems.
Thermal Conductivity
Now that we know its electrical capabilities, what about its thermal capacities? Aluminum is a popular material for cookware and heat sinks because it once again leads the field in thermal conductivity.
Despite being robust and long-lasting, titanium does not conduct heat as well as aluminum, which may limit its suitability for applications that call for efficient heat transfer.
Weight and Size
Both metals are known for being lightweight, but aluminum is lighter than titanium. This makes aluminum preferable in industries like automotive and aerospace, where weight reduction is critical.
However, titanium offers much greater strength-to-weight ratio, which is why it’s used in high-stress applications such as aircraft frames and implants.
Corrosion Resistance
Titanium excels in corrosion resistance, even in extreme environments like saltwater or acidic conditions.
Aluminum is also corrosion-resistant but is more prone to degradation in harsher environments, especially without protective coatings.
Price and Cost
And last but most definitely not least is pricing. Aluminum is cheaper, more accessible, and more affordable than titanium, both in raw material cost and manufacturing processes. Because of the ease of production, they tend to be cheaper.
On the flipside, titanium’s price is higher. This stems from the complex and energy-intensive process required to extract and refine it, making it less cost-effective for everyday applications. It’s also quite more challenging to achieve and get.
Both materials are lightweight, and both are used for particular applications. However, there are instance and circumstances where one is used and utilized better than the other. s
Read More: How to Clean Aluminum
Titanium vs. Aluminum: Table of Comparison


If you want to have a visual separation of these two metals, let’s take a look at each of them side-by-side through a comparison table.
| Feature | Aluminum | Titanium |
| Elemental Composition | Lightweight, silvery-white, highly abundant; easy to refine | Denser, silver-gray; less abundant and harder to extract |
| Weight | Lighter (2.7 g/cm³); ideal for weight-sensitive projects | Heavier (4.5 g/cm³) but offers superior strength-to-weight ratio |
| Strength | Moderate strength; requires alloying for added durability | Exceptional strength, ideal for high-stress applications |
| Electrical Conductivity | Excellent conductivity; widely used in electrical wiring and power lines | Low conductivity, not suitable for electrical systems |
| Thermal Conductivity | High thermal conductivity; ideal for heat sinks, cookware, and radiators | Lower conductivity; less efficient for thermal transfer |
| Corrosion Resistance | Resistant to rust but needs coatings for harsh environments | Naturally resistant to corrosion, even in saltwater or acidic conditions |
| Cost | Affordable; cost-effective for mass production | Expensive; high refining costs limit its use to premium applications |
| Machinability | Easy to machine, weld, and form into complex shapes | Harder to machine; requires specialized tools and processes |
| Applications | Aircraft, vehicles, packaging, electronics, and construction materials | Aerospace, medical implants, marine equipment, and high-end sports gear |
Here are some key notes about this table comparison of aluminum and titanium:
- Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Titanium outperforms aluminum in applications demanding extreme durability with minimal weight, such as aerospace and medical implants.
- Cost Factor: Aluminum is cheaper, making it ideal for consumer products and large-scale manufacturing. Titanium’s cost restricts it to critical, high-performance uses.
- Corrosion Performance: For marine or chemically aggressive environments, titanium is unbeatable, while aluminum often needs protective coatings.
- Machinability and Processing: Aluminum is far easier to work with, while titanium requires advanced technology for machining and welding.
Order the Best Quality of Aluminum and Titanium From HDC
Aluminum vs. titanium is a common comparison, but here with us here at HDC can give you the best of both worlds. Being China’s best and most trusted manufacturer of metal and metal components, you can bank on us for all that you need.
HDC is a one-stop solution for all metal parts; whether it’s for automotive, bicycle, aerospace, construction, medical, and many more!
Our team is employed with the industry’s best and most trusted engineers, skilled professionals and workers. Thanks to our large investment in the most recent technology and advanced processes, we’re sure of the quality of our work.
Ever since our founding, businesses have entrusted their metal components to us, and you can, too! Don’t hesitate to give us as call or send us an email for any questions you might have. Our customer service team is ready to help you! We can also grant you a free estimate!
Discover more with our blog posts.
Recent Posts
Discover more about our products.
Related Products
Instant Quote!