1018 Carbon Steel: Composition, Properties, Advantages and Disadvantages, and Application Fields
With a 13-year history in the domain of OEM metal craftsmanship, HDC emerges as a stalwart leader in the realm of precision machining services. The specialized acumen demonstrated in handling 1018 carbon steel underscores our steadfast dedication to delivering unparalleled quality and bespoke solutions.
Operational from our cutting-edge manufacturing facility, HDC distinguishes itself through the seasoned expertise of our engineers and the astute creativity of our highly skilled design team. Their utilization of an extensive array of manufacturing techniques, such as CNC processing, sheet metal manipulation, and casting, manifests a comprehensive strategy that ensures every project benefits from a nuanced comprehension of the distinctive traits inherent in 1018 carbon steel.
The hallmark of HDC lies in an unyielding commitment to efficiency and dependability, a fact substantiated by our impeccable track record of successful projects that serves as a testament to our pursuit of excellence. The incorporation of sophisticated 4-axis and 5-axis CNC machining centers further amplifies our capacity to meet the most intricate requisites of your 1018 carbon steel machining endeavors.

What is 1018 Carbon Steel?
1018 carbon steel is a low-carbon alloy, containing approximately 0.18% (by weight) of carbon. For carbon steel, it is one of the most commonly available grades, and it is recognized as highly weldable, machinable, and versatile. Being rich in carbon content, it presents the good strength and ductility features, which make it extensively used in a number of fields, such as machinery parts, automotive components, structural sections and shafts. The 1018 carbon steel is generally subjected to cold drawing or cold roll in order to further enhance its mechanical properties and surface texture. It is commonly employed in manufacturing and fabrication processes where the desirable characteristics of strength, machinability, and affordability exist in a balance.
Why Is This Type of Carbon Steel Named 1018?
1018 carbon steel is named based on its composition and standardization within the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) system. The “10” in 1018 denotes the basic carbon steel grade, while the “18” indicates its approximate carbon content of 0.18%. This alphanumeric designation provides a standardized way to identify and categorize carbon steels based on their composition and properties, facilitating communication and understanding within the industry.

What Are the Other Names for 1018 Carbon Steel?
- AISI 1018: While nominated according to the AISI designation, or “1018” implying properties and composition.
- UNS G10180: This is the Unified Numbering System (UNS) designation of 1018 carbon steel, which is intended to distinguish commodities in the United States.
- SAE-AISI 1018: This designation combines the SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) and AISI (American Iron and Steel Institute) specifications, which are used in engineering and product environment.
- C1018: This is the standard designation for 1018 carbon steel, often used in industry and trade because it’s the plainest way of describing the material.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 1018 Carbon Steel

Carbon steel 1018 has some pros and cons. Specifically, it is easy to weld and machine which makes it the top pick for different applications serving the various industries. Not only is it affordable but also an option that saves you your costs. Nevertheless, 1018 steel has certain disadvantages for the high malleability, as compared with higher carbon and alloy steels. It possesses the feature of corrosion and may, possibly, become brittle in highly stressed constituents. Such features may need some precautionary measures or protection. Conversely, the material’s drawbacks include its tendency to lose strength with time and its inability to resist large amounts of stress. Nevertheless, its versatility and fabrication simplicity make the material perfect for numerous applications whose moderate strength and ductility are sufficient.
Chemical Composition of 1018 Carbon Steel
1018 carbon steel, as a versatile, adaptable, medium-low carbon steel, demonstrates excellent weldability, formability, machinability, and strength compared with lower carbon steel in a normalized and hot forged state. It is popular among cold-rolled steels and regarded as the premier material choice of carburized gears, such as pins, pinions, spindles, ratchets, and other machinery parts. The common 1018 carbon steel material properties are as follows:

| Component | Wt.% |
| Carbon (C) | 0.14 – 0.20 |
| Iron (Fe) | 98.81 – 99.26 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.60 – 0.90 |
| Phosphorus (P) | 0.0 – 0.04 |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.0 – 0.05 |
The Influence of Various Elements on the Properties of 1018 Carbon Steel
The 1018 carbon steel properties are affected by various elements prevailing in its composition majorly iron and carbon and minimum content of manganese, phosphorous and sulfur. The carbon content gives a range of values (0.18% is typical) for hardness, strength, and machinability; the higher the carbon content, the higher the hardness, but lower ductility and weldability. Manganese is added to improve the hardenability and the strength, and phosphorus is added to better machinability but can reduce ductility too much if in excessive amount. On the upside, sulfur aids in machinability, but turns out to be brittle if it is present too much. In totality, these features or elements determine the mechanical properties of 1018 steel making it one of the most versatile and common materials in industry.

Mechanical Properties of 1018 Carbon Steel
| Mechanical Properties | Metric | English |
| 1018 Steel Ultimate Tensile Strength | 440 MPa | 63800 psi |
| 1018 Steel Tensile Yield Strength | 370 MPa | 53700 psi |
| Elongation at Break | 15 % | 15 % |
| Reduction of Area | 40 % | 40 % |
| 1018 Steel Hardness, Brinell | 126 | 126 |
| 1018 Steel Hardness, Knoop | 145 | 145 |
| 1018 Steel Hardness, Rockwell B | 71 | 71 |
| 1018 Steel Hardness, Vickers | 131 | 131 |
| 1018 Steel Modulus of Elasticity | 193 GPa | 28000 ksi |
| Bulk Modulus | 159 GPa | 23100 ksi |
| Shear Modulus | 77.2 GPa | 11200 ksi |
| Poissons Ratio | 0.29 | 0.29 |
Physical Properties of 1018 Carbon Steel

| Physical Properties | Metric | English | Comments |
| Density | 7.87 g/cc | 0.284 lb/in² | |
| 1018 Steel Machinability | 78% | 78% | |
| 1018 Steel Modulus of Elasticity | 205 GPa | 29700 ksi | |
| Electrical Properties | |||
| Electrical Resistivity | 0.0000159 ohm-cm | 0.0000159 ohm-cm | Temperature 0.000 °C/32.0°F, annealed condition |
| 0.0000219 ohm-cm | 0.0000219 ohm-cm | Temperature 100 °C/212°F, annealed condition | |
| 0.0000293 ohm-cm | 0.0000293 ohm-cm | Temperature 200 °C/392°F, annealed condition | |
| Thermal Properties | |||
| Specific Heat Capacity | 0.486 J/g-°C | 0.116 BTU/lb-°F | Temperature >=100°C/212°F, annealed |
| Thermal Conductivity | 51.9 W/m-K | 360 BTU-in/hr-ft²-°F | estimated based on similar materials |
Equivalent Materials of 1018 Carbon Steel
| EU | EN | 1.0479 S275 | ||||
USA | SAE 1018 AISI 1018 UNS G10180 | |||||
Germany | DIN | 1.0419 RSt44-2 RSt 44-2 | ||||
Japan | JIS | SWRCH18A SWRCH18K SWRCH16A SWRCH16K SWRCH19A | ||||
| France | AFNOR | 14-13-12E | ||||
| England | BS | 43A | ||||
| China | GB | ML3 | ||||
| Sweden | SS | 2320 | ||||
| Russia | GOST | St 3-sp St3sp | ||||
1215 Carbon Steel vs 1018 Carbon Steel

In the realm of carbon steels, 1215 Steel and 1018 Steel stand as distinct entities, marked by differences in composition and inherent properties. Noteworthy for its outstanding machinability, attributed to the introduction of lead, 1215 Steel, however, tends to showcase inferior strength compared to its counterpart, 1018 Steel. On the flip side, 1018 Steel presents commendable machinability paired with elevated strength, rendering it apt for diverse applications, spanning general machining to the construction of structural components. The decision between the two pivots on specific needs, favoring 1215 Steel for high-volume precision parts, while 1018 Steel proves versatile for applications that prioritize a harmonious blend of strength and machinability.
1045 Carbon Steel vs 1018 Carbon Steel
1045 Steel, distinguished by an elevated carbon quotient, lays claim to augmented potency and heightened resistance to wear. Conversely, 1018 Steel, marked by a diminished carbon content, proffers enhanced ease of machination but tends to yield to lower strength. The decision between the two pivots on specific requisites, with 1045 Steel garnering favor for applications demanding stalwart vigor and enduring robustness, while 1018 Steel aligns itself with scenarios prioritizing the facilitation of machination.
Processing Methods Suitable for 1018 Carbon Steel

1018 carbon steel has more than one suitable processing methods because of its great machinability and some strength. These operations include turning, milling, drilling, and tapping, whereby the machines can perform them with little or no tool wear. Besides that, welding techniques like SMAW, GMAW, and GTAW can be used even though at times preheating and post-weld heat treatment might be required to ensure the quality of the welds. The cold working processes (cold drawing and rolling) that enable for more accurate dimensioning and shape related to mechanical properties in its final state. Toughness, however, is not the purpose of heat treatment, yet annealing can be leveraged to improve machinability or to refine its microstructure. Additionally, surface treatments like carbonizing, nitriding or blackening will substantially increase abrasions and corrosion resistance as well as improving aesthetics. Using these multipurpose methods of processing makes 1018 steel a prime choice for various applications across various industries.
Common Applications of 1018 Carbon Steel
- Automotive: Wheel Spacer, Block Guard, Valve Cover, Intake Flange, Wheel Lug Nut, Shift Knob
- Aerospace
- Medical Equipment
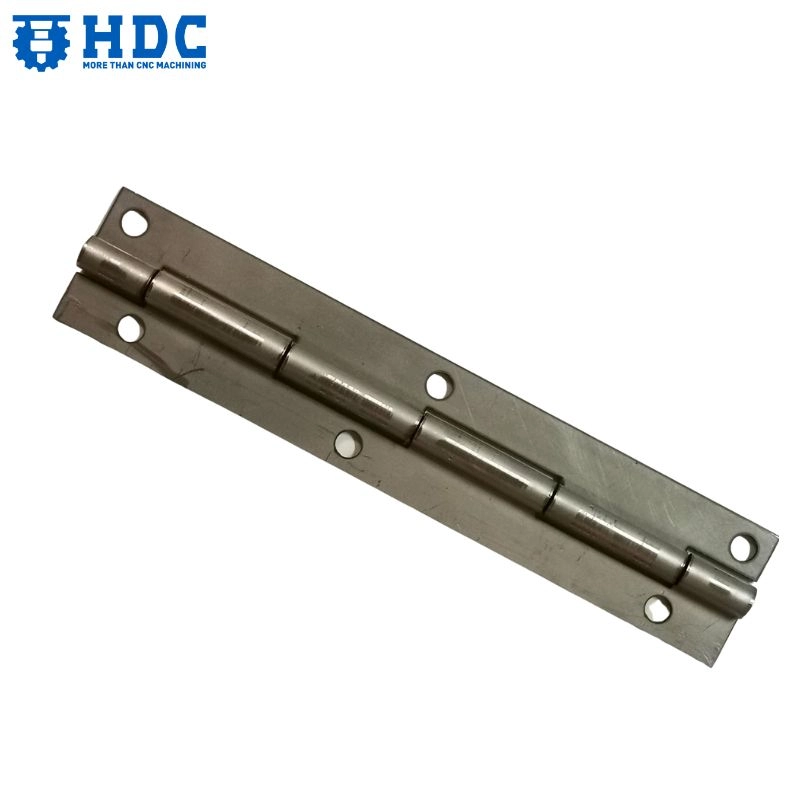
- Furniture and Decor: Piano Hinge, Weld-On Hinge, Barrel Hinge, Screws
- Motorcycle: Sprocket, Wheels, Wheel Hub, Radiator Guard, Footpeg, Triple Clamp, Bar End
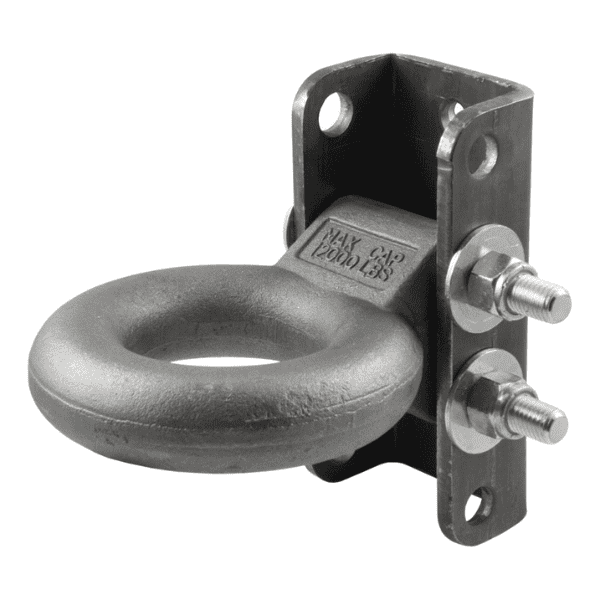
- Trailer: Coupler, Trailer Jack, Receiver Tube, Trailer Paddle Lock, Pintle Hook, Ball Mount
- Bicycle: Bike Stem, Wheel Hub, Crankset
- Kart: Go Kart Sprocket, Go Kart Spacer, Go Kart Wheel Hub, Go Kart Steering Wheel