Home > Materials > Carbon Steel > 4140 Steel
4140 Steel: Composition, Characteristics, Processing Methods, and Application Fields
- Walter
Welcome to HDC, the steadfast ally in the bespoke fabrication of metallic components, boasting a reservoir of industry acumen spanning more than a decade. Nestled within our state-of-the-art facilities, adorned with avant-garde apparatus such as 4-axis and 5-axis machining centers, alongside meticulous inspection instruments like coordinate measuring machines, HDC proudly claims its stature as a preeminent purveyor of personalized metal resolutions.
The linchpin of our prowess resides in 4140 Steel Machining. Armed with a proficient cohort and advanced CNC machining prowess, HDC pledges the zenith of quality and precision in each endeavor. Be it intricate constituents or robust fragments, HDC’s unwavering allegiance to excellence ensures an apogee of outcomes when interfacing with 4140 Steel.
Embark upon an odyssey through the plethora of machining alternatives HDC proffers, spanning the gamut from CNC machining to casting, forging, laser incision, and metal stamping. Our pliable capabilities stand poised to attend to a myriad of requirements, delivering bespoke resolutions attuned to the distinctive needs of your undertakings. Select HDC for your metallic craftsmanship requisites, where erudition and ingenuity converge, breathing life into your visionary aspirations.

What is 4140 Steel?
The 4140 steel is a low alloy steel part enriched by chromium, molybdenum and manganese, known for its distinctive quality of high toughness, high torsional strength and good fatigue strength. This composite structure provides with excellent toughness, strength, and wear resistance. The process of heat treatment, annealing and tempering, strengthens the steel for a specific use. 4140 steel’s robustness and durability make it a good choice for producing such components as gears, axles, and bolts where it is widely used across many industries like oil and gas, agriculture, defense and automotive for its ability to stay in good condition even under difficult conditions.
How Is 4140 Steel Named According to What Rule?

4140 steel is designated under the AISI/SAE steel grading system, where the first digit (4) denotes a molybdenum alloy, the second digit (1) indicates additional alloying elements like chromium and molybdenum, and the final two digits (40) specify the steel’s carbon content as approximately 0.40%. This nomenclature provides a quick reference to the steel’s chemical composition and properties, highlighting its use of molybdenum for enhanced strength, toughness, and wear resistance, and making it easy to identify for applications requiring robust materials.
Chemical Composition of 4140 Steel
4140 Steel is classified a low carbon, low alloy steel with good impact resistance, wear resistance, hardenability, structural toughness, strength, and slight corrosion resistance. While it is poor in weldability, it need to heated to more than 800°C if forging it. 4140 is versatile, as a natural tool steel, definitely used for tools and parts of industry machines subject to large loads, such as crankshafts, rear axles, spring clips, collects, gears, steering etc.
| Component | Wt.% |
| Carbon (C) | 0.38 – 0.43 |
| Iron (Fe) | 96.785 – 97.77 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 0.75 – 1.00 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.60 – 0.90 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 0.15 – 0.25 |
| Phosphorus (P) | 0.0 – 0.035 |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.15 – 0.30 |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.0 – 0.04 |
The Influence of Chemical Composition on the Properties of 4140 Steel

One of the essential factors that determine the mechanical properties of the 4140 steel, with about 0.40% carbon, 0.80-1.10% chromium, 0.15-0.25% molybdenum and 0.75-1.0% manganese, is its chemical composition. Carbon gives a combination of strength and ductility, chromium adds additional strength, hardness, tensile strength, and corrosion resistance, molybdenum gives tensile strength at high temperatures as well as resistance to wear and tear, and manganese improves hardenability and imparts resistance cracking. Having such a unique alloy composition, the 4140 steel gains high strength, toughness, wear resistance, and the ability to undergo heat treatment and to be used in the applications which are not damaging and in which performance under stress is crucial, such as gears, axles, and shafts.
Mechanical Properties of 4140 Steel
| Mechanical Properties | Metric | English |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 1020 MPa | 148000 psi |
| Tensile Yield Strength | 655 MPa | 95000 psi |
| Elongation at Break | 17.7 % | 17.7 % |
| Reduction of Area | 46.8 % | 46.8 % |
| Hardness, Brinell | 302 | 302 |
| Hardness, Knoop | 328 | 328 |
| Hardness, Rockwell B | 99 | 99 |
| Hardness, Rockwell C | 32 | 32 |
| Hardness, Vickers | 319 | 319 |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 205 GPa | 29700 ksi |
| Bulk Modulus | 160 GPa | 23200 ksi |
| Shear Modulus | 80.0 GPa | 11600 ksi |
| Poissons Ratio | 0.29 | 0.29 |
| Machinability | 65 % | 65 % |
Physical Properties of 4140 Steel

| Physical Properties | Value | |
| Density | 7.85 g/cc | |
| Melting Point | 2,580-2,650 °F | |
| Specific Heat | 1.13 x 10^-1 BTU/lb-°F | |
| Thermal Conductivity | 296 BTU-in/hr-ft^2-°F | |
Equivalent Materials 4140 Steel
| EU | USA | Germany | France | Italy | Spain | Inter |
| EN | – | DIN,WNr | AFNOR | UNI | UNE | ISO |
| 42CrMoS4 (1.7227) | 4140 | 42CrMoS4 | 42CD4u | 42CrMo4 | 40CrMo41 | 42CrMoS4 |
The Price of 4140 Steel

The price of 4140 steel is somewhat volatile to changes that are brought about by factors that include market demand, raw material costs, supply levels, and overall economy. It depends on the steel’s form (e.g., bars, plates, and sheets), size, and other operations such as heat treatment and so on. Because the prices are variable, at any given time, for the most correct and the latest pricing, it is advised to contact steel suppliers or study recent market reports directly. Steel is priced per pound or per metric ton primarily, and cost reductions could be possible on per-unit basis for large volume purchases. Furthermore, passing through the retailers may include shipping, handling, and other fees.
What Limitations Does 4140 Steel Have?
4140 steel despite of its multiple advantages in strength, toughness, and versatility facing the limits such as the reduced weldability requesting special welding procedures to stop cracking, lower corrosion resistance compared to the stainless steels hence protective coatings are required, and the technical problems in machining behaviour due to its hardness which causes a rise in manufacturing costs. Also, its alloying elements add, not only the material but also the processing expenses, thus making it more pricey than the simplest carbon steels. Furthermore, thicker sections are tougher to treat for homogenous properties and, thus, may crack if not tempered properly. Moreover, some specific sizes of 4140 steel are not readily available making customized options time-consuming and costly, leading to delays and extra expenses. Weighing these factors against the benefits is a big decision that is made for each given application.

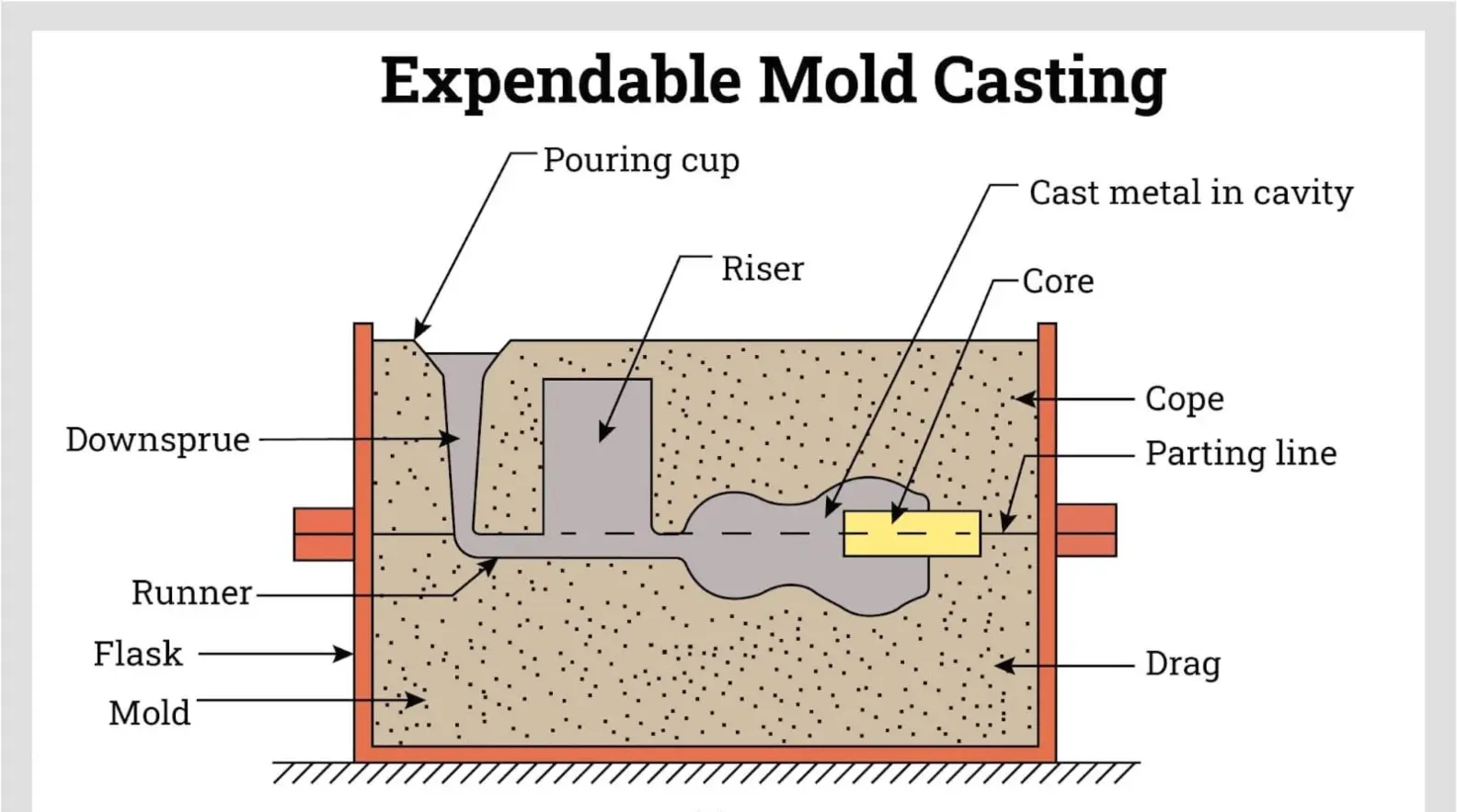
Common Processing Methods Used for 4140 Steel
The properties of 4140 steel will be improved by different methods of processing it to suit various applications. By forging the steel the structure is strengthened and made tougher, while annealing is done to lower hardness and remove internal stresses which makes the steel more easy to work with (more workable). Normalization adds refinement to the grain structure, and thus improving toughness and uniformity come together. Hardening, which is the process of heating and quenching followed by tempering, increases durability and resistance to wear but decreases the toughness to avoid brittleness. Instead, the carburizing process hardens the surface for parts, where the core must be tough and outside parts must be hard. Though fairly tough, 4140 can be machined using proper tools and conditions. The process collectively makes 4140 steel customizable, thus it meets the expected performance of specific applications, such as the required mechanical strength, toughness and wear resistance.
Applications of 4140 Steel

4140 Steel finds diverse applications across various industries:
- Automotive Industry: Used for crafting Wheel Spacers & Adapters, Wheel Lug Nuts, Block Guards, Valve Covers, and Shift Knobs.
- Aerospace Sector: Essential in the production of Exhaust Manifolds, Impellers, Pipe Fittings, and Valve Bodies.
- Medical Equipment Manufacturing: Employed in the creation of critical components such as Medical Screws, Precision Components, and Medical Sensor Power Supply Housings.
- Custom Fabrication: Utilized for Weld-on Hinges and Bullet Hinges in custom product manufacturing.
- Motorcycle Parts: Applied in the manufacture of Sprockets, Triple Clamps, Wheels, Wheel Hubs, Radiator Guards, Twist Throttles, and Footpegs.
- Trailer Components: Integral to the production of Safety Chains, Paddle Locks, Couplers, Hitch Balls, Pintle Hooks, and Trailer Jacks.
- Bicycle Accessories: Found in Bike Stems, Chainrings, Bicycle Hubs, Bike Pedals, and Cranksets.
- Go Kart Components: Essential for crafting Sprockets, Spacers, Wheel Hubs, Bearings, and Steering Wheels.